Content for TS 23.280 Word version: 19.5.1
1…
5…
6
7…
8…
9…
10…
10.1.5…
10.2…
10.2.6…
10.3…
10.6…
10.7…
10.7.3.8…
10.8…
10.9…
10.9.3.9…
10.10…
10.10.3
10.11…
10.12…
10.13…
10.14…
10.15…
10.16…
10.17…
10.18…
10.18.3…
11…
11.5…
A…
B…
C…
E…
10.18.3 Recording procedures p. 373
10.18.3.1 General p. 373
The MC recording procedures for MCPTT and MCVideo group and private communications utilize Session Recording Protocol [40]. The Session Recording Client (SRC) is located in the MC service server. Recording server represents the Session Recording Server (SRS) in the Session Recording Protocol architecture.
Recording of communication sessions involves delivering real-time media and metadata of an MC service user or MC service group from an MC service server to the recording server.
10.18.3.2 Procedure for recording communication sessions of an MC service user p. 373
Figure 10.18.3.2-1 below illustrates the recording procedure for communication sessions of an MC service user (MCPTT ID, MCVideo ID).
Pre-conditions:
- The user (MCPTT ID or MCVideo ID) has been configured as a target for recording in the MC service user profile (see clause A.3 of TS 23.281 and clause A.3 of TS 23.379) and the user profile has been uploaded to the MC service server.
- The target MC service user has performed MC user authentication and service authorization (see clause 5.1.1 and clause 5.1.2 of TS 33.180) and has fetched its user profile(s) from the configuration management server.
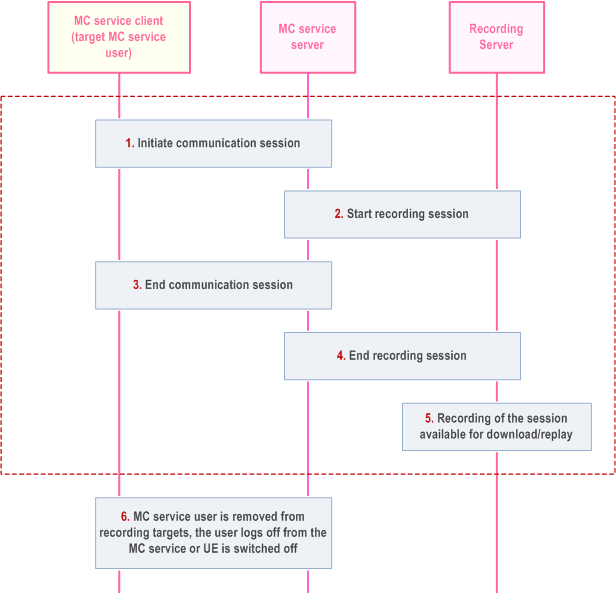
Step 1.
An MC communication session (MCPTT/MCVideo private call) involving the target user is initiated.
Step 2.
A Session Recording Client (SRC) in the MC service server starts a recording session (see RFC 7866) with the recording server.
Step 3.
The MC communication session ends.
Step 4.
The recording session ends.
Step 5.
The recording server stores the recording session, and it is available for download and/or replay.
Step 6.
When the user (MCPTT ID / MCVideo ID) is removed from the recording targets or the user logs off from the MC service or the UE is switched off, an ongoing recording session (if exists) is terminated.
10.18.3.3 Procedure for recording communication sessions of an MC service group p. 374
Figure 10.18.3.3-1 below illustrates recording procedure for communication session of an MCPTT group or MCVideo group service.
Pre-conditions:
- The target group (MCPTT group ID or MCVideo group ID) has been configured as a target for recording in the common group configuration data (A.4) and the group configuration data has been uploaded to the MC service server.
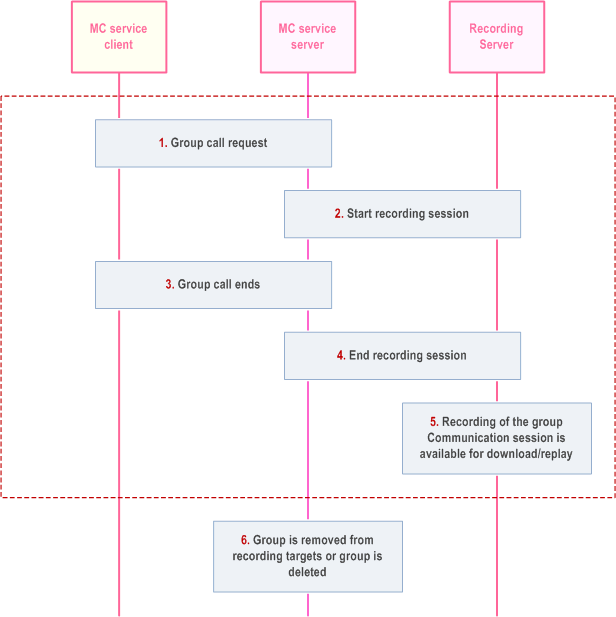
Step 1.
An MC group communication session (MCPTT/MCVideo group call) involving the target group is initiated.
Step 2.
A Session Recording Client (SRC) in the MC service server starts a recording session (RFC 7866) with the recording server.
Step 3.
Group communication session ends.
Step 4.
The recording session ends.
Step 5.
The recording server stores the recording session, and it is available for download and/or replay.
Step 6.
When the group is removed from the recording targets (see clause 10.18.2.1) or the group is deleted (see 10.2.8), an ongoing recording session (if exists) is terminated.
10.18.4 Replay procedure p. 375
10.18.4.1 General p. 375
The MC replay procedure between MC replay UE and recording server utilized reference point REC-1 (see clause 7.5.2.29).
10.18.4.2 Procedure for fetching a recording from a recording server p. 375
Figure 10.18.4.2-1 below illustrates the procedure for fetching a recording from a recording server.
Pre-conditions:
- Replay UE has performed initial bootstrap and the initial UE configuration.
- MC replay user has performed user authentication and service authorization with IdMS.
- MC replay user has fetched its user profile from the CMS.
- Recording server has up-to-date copy of the user profile of the MC replay user.
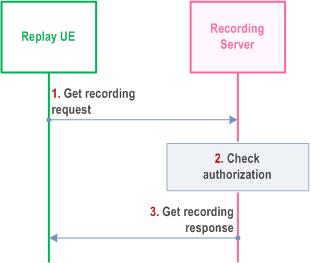
Step 1.
MC replay user, utilizing replay client in the replay UE, sends a Get recording request to the recording server.
Step 2.
Recording server checks that the replay user (MCRec ID) is authorized to replay recordings of the requested user or group.
Step 3.
If authorized, recording server sends Get recording response to the replay UE.