Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
6.14 Classmark Handling
6.15 UE Reachability procedures
6.16 Update CSG Location Procedure
6.17 APN information retrieval procedure
6.18 Procedures to support Dedicated Core Networks
7 Network Management Functionality
...
...
6.14 Classmark Handling p. 204
To support efficient radio interface usage in GPRS, the MS Classmark is handled differently for SGSN-based services than for MSC-based services. In particular, the Classmark information is sent in MM and Iu mode RRC messages to the network and stored in the network as long as the MS is attached, avoiding redundant Classmark retransmissions over the radio interface. This is sometimes called the "idle-mode Classmark" principle.
In order to allow introduction of new radio access technologies in the future, the MS Classmark is split into distinct and independent information sets, the radio access Classmark, and the core network capability. The radio access Classmark is split into two information elements, the MS radio access capability (A/Gb mode) and the UE capability (Iu mode). The core network capability is split into two distinct information elements, the MS network capability IE (which shall be common for A/Gb mode and Iu mode) and for E-UTRAN capable MSs, the UE Network Capability IE.
6.14.1 Radio Access Classmark p. 204
The MS shall send the MS radio access capability in the GPRS Attach Request message to the SGSN regardless, if the MS is about to attach to A/Gb mode or to Iu mode network, as defined in TS 24.008. Both the MS radio access capability and the MS network capability contain some information on the UE's support for other RATs. The SGSN uses the information from the MS network capability, and knowledge about the support of Inter-RAT Handover, to request the MS to send information on the MS's other radio capabilities in the Attach Complete/RA Update Complete.
If the MS supports SRVCC to GERAN (TS 23.216), the MS sends the CS domain's Classmark 2 and Classmark 3 information elements to the SGSN in the Attach Request/Routeing Area Update Request messages in both Iu mode and A/Gb mode.
If the MS supports SRVCC to UTRAN (TS 23.216), the MS sends the CS domain's Classmark 2 information element to the SGSN in the Attach Request/Routeing Area Update Request messages in both Iu mode and A/Gb mode.
6.14.1.1 MS Radio Access Capability (A/Gb mode) p. 204
The MS radio access capability information element contains the A/Gb mode radio capabilities of the MS (e.g. multislot capability, power class), and more generally all the information that should be known by the BSS in order to handle radio resources for that MS with GERAN. The UTRAN Inter RAT handover information that can be sent in the Attach Complete/RA Update Complete contains the information that the BSS needs for inter-RAT handover to other RATs.
The MS radio access capability is a container for a multiplicity of radio access technology-dependent information, i.e. within the MS radio access capability there are independent sub-fields for various technologies such as GSM 900 and GSM 1800. The coding shall allow a BSS to extract only the sub-fields relevant to it without interpreting the other sub fields. This ensures that the MS radio access capability does not need to be interpreted by the NSS, and the full MS radio access capability is always sent by the MS to the SGSN, and thereafter provided to the BSS irrespective of the actual BSS capabilities.
The SGSN shall provide the MS radio access capability as an information element on the Gb interface. It is the responsibility of the SGSN to provide the BSS with the most recent MS radio access capability received from the MS. The MS radio access capability information element can be included in a downlink transfer request, or be sent in a specific message that updates the MS radio access capability information in the BSS. The BSS may at any time request the MS radio access capability for a given MS to be transmitted from the SGSN to the BSS.
Together with the MS radio access capability, the SGSN shall provide the IMSI of the MS when this is known. For a BSS supporting DTM, the IMSI is stored at the BSS and used for radio resource co-ordination; e.g. for a DTM MS.
A specific optimisation allows the BSS to receive a reduced MS radio access capability at initial access directly from the MS. This enables the BSS not to wait for the full MS radio access capability to be provided by the SGSN, and is therefore quicker for the initial MS-originated transmission. The reduced MS radio access capability can be carried in several RR messages depending on the access method, e.g. in the initial random access message, or in the first uplink radio block. Details are provided in TS 24.008 and TS 44.060.
If stored, the SGSN shall provide the Inter RAT handover information and MS Classmark 2 and MS Classmark 3 as information elements on the Gb interface when a Packet Flow Context is established. MS Classmark 2 and 3 are included to support the case that a SRVCC handover is needed following PS domain handover from GERAN to UTRAN/E-UTRAN.
When the MS performs a Routeing Area Update (e.g. at GERAN-UTRAN change with change of RA in idle mode, and, GERAN-UTRAN Handover) the MS radio access capability shall be sent to the SGSN in the Routeing Area Update Request message. The SGSN then provides the BSS with the MS radio access capability.
At inter-RAT Handover, the source, target and all other RATs' MS/UE radio capability (except the UE E-UTRA capability) are exchanged within the container information elements. To support subsequent connections, an A/Gb mode SGSN supporting inter-RAT handover requests the MS to send the Inter RAT handover information in the RA Update Complete message.
To allow for the addition of future radio technologies, frequency bands, and other enhancements, the SGSN shall store the Inter RAT handover information even if it is larger than specified in TS 24.008, up to a maximum size of 255 octets.
To allow for the addition of future radio technologies, frequency bands, and other enhancements, the SGSN shall store the MS radio access capability even if it is larger than specified in TS 24.008, up to a maximum size of 255 octets.
6.14.1.2 UE Capability (Iu mode) p. 205
The UE capability information element contains all the radio capabilities of the MS (power control, code resource, UE mode, ciphering, PDCP capabilities, etc.) that the RNC has to know in order to handle radio resources for this MS.
The MS sends the UE capability information element to the serving RNC upon RRC connection establishment, and the RNC stores it. This is done before the Attach Request or Routeing Area Update Request message is sent.
At SRNC relocation the source RNC sends the UE capability transparently through the core network to the target RNC. If the RNC has not received the UE capability information it can request the MS to send the information.
At inter-system change the UE capability is transferred from the MS to the serving RNC on RRC connection establishment before the Routeing Area Update Request message is sent.
Details are provided in TS 25.331 and TS 25.413.
The SGSN may also request for Voice Support Match Indicator. If requested, the RAN shall then derive and provide an indication to the SGSN whether the UE capabilities are compatible with the network configuration as defined in clause 6.9.5.
6.14.2 Core Network Capability p. 206
The MS network capability IE contains mostly non radio-related capabilities (e.g. the GSM GPRS ciphering, UMTS authentication, and TI extension capabilities) related to GERAN and UTRAN access. In the coding of the information element certain capabilities may be grouped together in a single indicator.
The UE network capability IE mostly contains information related to the MS's E-UTRAN core network capabilities.
The SGSN stores the MS network capability and UE network capability, which is used both by the local SGSN and for transfer to the new SGSN/MME for any type of inter SGSN/inter-RAT mobility. To avoid interoperability problems when roaming between A/Gb mode and Iu mode, the MS network capability shall be included in the routeing area update request sent by the MS. At inter-SGSN RA update, the network shall use this MS Network Capability and ignore the same IE received in MM Context from the old SGSN/old MME.
If the MS's MS network capability and/or UE network capability information changes (including cases of being in E-UTRAN coverage and having ISR activated), the UE shall perform a Routeing Area Update ('type' different to 'periodic') when it next returns to GERAN/UTRAN coverage.
To allow for the addition of future features, the SGSN shall store the UE Network Capability and the MS Network Capability even if either or both is larger than specified in TS 24.008/TS 24.301, up to a maximum size of 32 octets for each IE.
An E-UTRAN capable MS notifies the SGSN of its E-UTRAN capability using the MS Network Capability.
6.14.3 Gb Coverage Class Information |R13| p. 206
The aim of this procedure is to assist the GERAN in optimising the radio paging and the radio resource assignment procedure.
The BSS sends the Gb Coverage Class Information to the SGSN within a BSSGP PDU when reported by the MS. When the MS needs to be paged, the SGSN shall provide the most recently received Gb Coverage Class Information to the BSS as part of the BSSGP Paging Request message. Additionally, the associated cell identity that was indicated in the BSSGP PDU carrying that Gb Coverage Class Information, i.e. the cell identity for which the Coverage Class is reported by the MS, shall also be included. The BSS may use this information to enhance the paging towards the MS.
Furthermore, while in READY state the MS can be in packet idle mode requiring a radio resource assignment when new downlink BSSGP PDU arrives at the BSS. To ensure a successful radio resource assignment using the required coverage enhancement on the radio interface, the most recently received Gb Coverage Class and the associated cell identity for which that Gb Coverage Class was provided to the SGSN shall be included in all downlink BSSGP PDUs.
6.15 UE Reachability procedures |R9| p. 206
There are two procedures necessary for any service related entity that would need to be notified on the reachability of the UE at NAS level:
- UE Reachability Notification Request procedure, and
- UE Activity Notification procedure.

1)
The UE Activity Notification procedure is illustrated in Figure 6.15-2.
If a service-related entity requests the HSS to provide an indication regarding UE reachability, the HSS stores the request in the URRP-SGSN parameter. If the value of URRP-SGSN parameter has changed from "not set" to "set", the HSS sends a UE-REACHABILITY-NOTIFICATION-REQUEST (URRP-SGSN) to the SGSN. If the SGSN has an MM context for that user, the SGSN stores URRP-SGSN to indicate the need to report to the HSS information regarding changes in UE reachability, e.g. when the next NAS activity with that UE is detected.
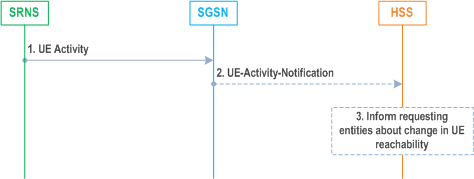
1)
The SGSN receives an indication regarding UE reachability, e.g. an Routeing Area Update Request message from the UE.
2)
If the SGSN contains an MM context of the UE and if URRP-SGSN for that UE is configured to report once that the UE is reachable, the SGSN shall send a UE-Activity-Notification (IMSI, UE-Reachable) message to the HSS and clears the corresponding URRP-SGSN for that UE.
3)
When the HSS receives the UE-Activity-Notification (IMSI, UE-Reachable) message or the Update Location message for an UE that has URRP-SGSN set, it triggers appropriate notifications to the entities that have subscribed to the HSS for this notification.
6.16 Update CSG Location Procedure |R11| p. 207
The Update CSG Location procedure takes place when the SGSN/VLR needs to retrieve the CSG subscription information of the MS from the CSS.
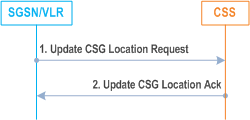
1)
The SGSN/VLR sends an Update CSG Location Request (SGSN/VLR Number, IMSI, MSISDN) to the CSS. The MSISDN is included if available.
2)
The CSS acknowledges the Update CSG Location message by sending an Update CSG Location Ack (IMSI, CSG Subscription data) message to the SGSN/VLR.
6.17 APN information retrieval procedure |R13| p. 208
This procedure is used by the RCAF to retrieve the APNs of the active PDN connections of the UEs served by a specific (congested) UTRAN cell. The RCAF leverages this information to determine the PCRFs serving these UEs and subsequently report RAN user-plane congestion information (RUCI) to the PCRFs.
The RCAF determines the SGSNs that are serving the congested UTRAN cell based on the Routing Area Identities served by the congested UTRAN cell. For further details on the related DNS procedure see TS 29.303. The following steps are applied for all SGSNs serving the congested UTRAN cell.

1)
The RCAF sends an APN information request to the SGSN. The request shall include the IMSIs for which the RCAF wants to retrieve APN information.
2)
The SGSN sends the APN information response to the RCAF. The response shall contain the the list of APNs of the active PDN connections of each IMSI.
6.18 Procedures to support Dedicated Core Networks |R13| p. 209
6.18.1 NAS Message Redirection Procedure p. 209
This procedure is described in the clause 5.19.1 of TS 23.401.
6.18.2 Attach and RAU procedure for Dedicated Core Network p. 209
When DCNs are used, modification to the Attach and RAU procedures described in the clause 5.19.2 of TS 23.401 apply to the procedures described in the following clauses of this specification:
- 6.5.3 Combined GPRS / IMSI Attach procedure
- 6.9.1.2.2 Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update
- 6.9.1.2.2a Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update and Combined Inter SGSN RA / LA Update using S4
- 6.9.1.3.2 Combined Inter SGSN RA / LA Update
- 6.9.2.1 Routeing Area Update Procedure
- 6.13.1.1.1 Iu mode to A/Gb mode Intra SGSN Change using Gn/Gp
- 6.13.1.1.2 Iu mode to A/Gb mode Intra SGSN Change using S4
- 6.13.2.1.1 Iu mode to A/Gb mode Inter-SGSN Change using Gn/Gp
- 6.13.2.1.2 Iu mode to A/Gb mode Inter-SGSN Change using S4
- 6.13.2.2.1 A/Gb mode to Iu mode Inter-SGSN Change using Gn/Gp
- 6.13.2.2.2 A/Gb mode to Iu mode Inter-SGSN Change using S4
6.18.2a Impacts to Relocation Procedures p. 209
When DCNs are used, the impacts to the relocation procedures are captured as below.
- Forward Relocation Request message: When SGSN changes during relocation, in the step where Forward Relocation Request message is sent from the Source SGSN to Target SGSN, the source SGSN also includes the UE Usage Type, if available, in the message. This change applies to the following clauses and step:
-
Selection of new SGW: In the step, subsequent to the Forward Relocation Request message, in which the target S4-SGSN determines if the Serving GW is to be relocated, if the target S4-SGSN supports DCN, the target S4-SGWN also determines if the existing Serving GW supports the DCN for the UE based on UE Usage Type of the UE, locally configured operator's policies as well as UE related context information available at the target network, e.g. information about roaming. This applies to the following clauses and step:
- 6.9.2.2.1a Serving RNS Relocation Procedure, Combined Hard Handover and SRNS Relocation Procedure, and Combined Cell / URA Update and SRNS Relocation Procedure Using S4: Step 1
- Relocation from service area where DCN is not used to an area where DCN is supported: When relocation occurs from a service area where DCN is not used to a service area where DCN is supported, the target SGSN obtains the UE usage type information from the HSS during the subsequent RAU procedure. If the target SGSN determines that the Serving GW does not support the UE Usage Type, the target SGSN triggers the Serving GW relocation as part of the handover procedures described in clause 6.9.2. If the target SGSN does not serve the UE Usage type, the relocation procedure should complete successfully and then the target SGSN may use the procedure in clause 5.19.3 of TS 23.401 Step 5 onwards, to change the serving DCN of the UE.
6.18.3 SGSN or HSS initiated Dedicated Core Network Reselection p. 210
The HSS initiated core network reselection for DCNs is described in the clause 5.19.3 of TS 23.401.
7 Network Management Functionality p. 210
The Network Management function provides mechanisms to support O&M functions related to GPRS.