Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
6.13.1.2 A/Gb mode to Iu mode Intra-SGSN Change p. 185
6.13.1.2.1 A/Gb mode to Iu mode Intra-SGSN Change using Gn/Gp |R8| p. 185
The intersystem change from A/Gb mode to Iu mode takes place when a GPRS-attached MS changes from A/Gb mode to GERAN or UTRAN Iu mode. Depending on the GPRS mobility management state before the intersystem change and whether the RA is changed or not, one of the following procedures is initiated by the MS:
- When an MS in STANDBY state changes to Iu mode inside the current RA, the MS shall follow the selective RA update procedures, see clause "Selective RA Update".
- When an MS in STANDBY state changes to Iu mode and the RA changes, the MS shall initiate the Iu mode RA update procedure, see clause "Routeing Area Update Procedure".
- When an MS in READY state changes to Iu mode independent of whether the RA has changed or not, the MS shall initiate the Iu mode RA update procedure and afterwards initiate the RABs by the Service Request procedure, see clause "MS Initiated Service Request Procedure". The RA update procedure is either combined RA / LA update or only RA update.
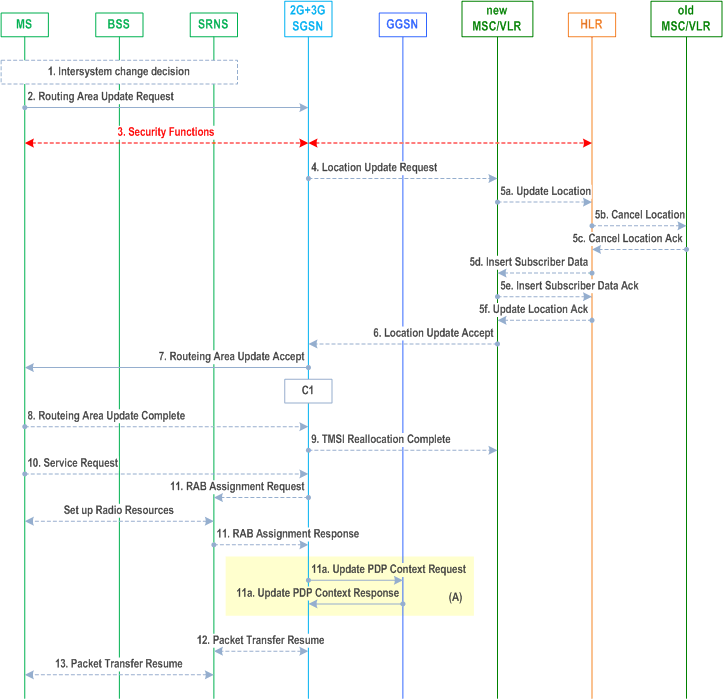
Step 1.
For some network sharing scenario (e.g. GWCN) if the PLMN-ID of the RAI supplied by the RNC is different from that of the RAI in the UE's context, then the SGSN shall informs the HLR.
The CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedure in TS 23.078:
The MS or the RAN decides to perform an intersystem change which makes the MS switch to a new cell where Iu mode has to be used, and stops transmission to the network.
Step 2.
The MS initiates an RRC connection establishment and sends a Routeing Area Update Request (P-TMSI, Old RA, Old P-TMSI Signature, Update Type, CM, Voice domain preference and UE's usage setting) message to the combined 2G+3G SGSN. Update Type shall indicate RA update or combined RA / LA update or, if the MS wants to perform an IMSI attach, combined RA / LA update with IMSI attach requested and also if the MS has a follow on request, i.e. if there is pending uplink traffic (signalling or data). The SGSN may use, as an implementation option, the follow-on request indication to release or keep the Iu connection after the completion of the RA update procedure. The SRNS shall add an identifier of the area where the message was received before passing the message to the 2G+3G SGSN. The 2G+3G SGSN stops transmission of N PDUs to the MS. The UE sets the voice domain preference and UE's usage setting according to its configuration, as described in clause 5.3.15.
Step 3.
Security functions may be executed.
Step 4.
If the association has to be established i.e. if Update Type indicates combined RA / LA update with IMSI attach requested, or if the LA changed with the routeing area update, the 2G+3G SGSN sends a Location Update Request (new LAI, IMSI, SGSN Number, Location Update Type) to the VLR. Location Update Type shall indicate IMSI attach if Update Type in step 1 indicated combined RA / LA update with IMSI attach requested. Otherwise, Location Update Type shall indicate normal location update. When the SGSN does not provide functionality for the Intra Domain Connection of RAN Nodes to Multiple CN Nodes, the VLR number is derived from the RAI. When the SGSN provides functionality for Intra Domain Connection of RAN Nodes to Multiple CN Nodes, the SGSN uses the RAI and a hash value from the IMSI to determine the VLR number. The VLR creates or updates the association with the 2G+3G SGSN by storing SGSN Number. In networks that support network sharing, the Location Update Request includes the identity of the selected core network operator if the SGSN has received this information from the RNS, as described in TS 23.251.
Step 5.
If the subscriber data in the VLR is marked as not confirmed by the HLR, the new VLR informs the HLR. The HLR cancels the data in the old VLR and inserts subscriber data in the new VLR:
Step 6.
- The new VLR sends an Update Location (new VLR) to the HLR.
- The HLR cancels the data in the old VLR by sending Cancel Location (IMSI) to the old VLR.
- The old VLR acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI).
- The HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, subscriber data) to the new VLR.
- The new VLR acknowledges with Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI).
- The HLR responds with Update Location Ack (IMSI) to the new VLR.
The new VLR allocates a new VLR TMSI and responds with Location Update Accept (VLR TMSI) to the 2G+3G SGSN. VLR TMSI is optional if the VLR has not changed.
Step 7.
The 2G+3G SGSN validates the MS's presence in the new RA. If due to roaming restrictions or access restrictions the MS is not allowed to be attached in the RA, or if subscription checking fails, the 2G+3G SGSN rejects the routeing area update with an appropriate cause. If the network supports the MOCN configuration for network sharing, the SGSN may, if the MS is not a 'Network Sharing Supporting MS', in this case decide to initiate redirection by sending a Reroute Command to the RNS, as described in TS 23.251 instead of rejecting the routeing area update. If all checks are successful, the 2G+3G SGSN updates MM and PDP contexts for the MS. A new P-TMSI may be allocated. A Routeing Area Update Accept (P-TMSI, P-TMSI Signature, IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication, Emergency Service Support) message is returned to the MS. The 2G+3G-SGSN derives for this intersystem change the corresponding PDCP sequence numbers from the N PDU sequence numbers stored in the SGSN PDP contexts by adding eight most significant bits "1". These PDCP sequence numbers are stored in the SGSN PDP contexts. The IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication is set as described in clause 5.3.8.
The Emergency Service Support indicator shall be included when going to UTRAN to inform the MS that Emergency PDP contexts are supported, i.e. the MS is allowed to request activation of emergency PDP context when needed.
Step 8.
The MS acknowledges the new P-TMSI by returning a Routeing Area Update Complete message to the SGSN.
Step 9.
The 2G+3G SGSN sends a TMSI Reallocation Complete message to the VLR if the MS confirms the VLR TMSI.
Step 10.
If the MS has pending uplink data or signalling, it shall send a Service Request (P-TMSI, RAI, CKSN, Service Type) message to the SGSN. Service Type specifies the requested service. Service Type shall indicate one of the following: Data or Signalling.
Step 11.
The 2G+3G SGSN requests the SRNS to establish a radio access bearer by sending a RAB Assignment Request (RAB ID(s), QoS Profile(s), GTP SNDs, GTP SNUs, PDCP SNUs, UE-AMBR, MSISDN, APN, Charging characteristics) message to the SRNS. If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN provides to the RNC the GGSN's Address for User Plane and TEID for uplink data. The PDCP sequence numbers are derived from the N PDU sequence numbers and stored in the PDP contexts in step 7). The SRNS sends a Radio Bearer Setup Request (PDCP SNUs) message to the MS. The MS responds with a Radio Bearer Setup Complete (PDCP SNDs) message. The SRNS responds with a RAB Assignment Response message. MSISDN, APN and Charging characteristics are optional parameters and only transferred if SGSN supports SIPTO at Iu-ps.
Step 11a.
If the SGSN established Direct Tunnel it shall send Update PDP Context Request to the GGSN(s) concerned and include the RNC's Address for User Plane, downlink TEID for data and DTI to instruct the GGSN(s) to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8. The GGSN(s) update the Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and return an Update PDP Context Response. Otherwise, if there were changes of for example the RAT type that e.g. can be used for charging, the SGSN sends Update PDP Context Request (SGSN Address and TEID, QoS Negotiated, RAT type) message to the GGSN.
Step 12.
Traffic flow is resumed between the 2G+3G SGSN and the SRNS. N-PDUs that were already sent to the MS in acknowledged mode SNDCP and that are not yet acknowledged by the MS are tunnelled by the 2G+3G SGSN to the SRNS together with their related N-PDU number (SNDCP sequence number). No PDCP sequence numbers shall be indicated for these N-PDUs. The SRNS shall discard all N PDUs with N PDU sequence numbers older than the eight least significant bits of PDCP-SND received from the MS. Other N PDUs shall be transmitted to the MS. The MS shall discard all N PDUs with sequence numbers older than the eight least significant bits of the PDCP SNU received from the SRNS. All other N PDUs shall be transmitted to the SRNS. The SRNS negotiates with the MS for each radio bearer the use of lossless PDCP or not regardless whether the old 2G-SGSN used acknowledged or unacknowledged SNDCP for the related NSAPI or not.
Step 13.
The traffic flow is resumed between the SRNS and the MS.
C1)
CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session, CAMEL_PS_Notification and CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Context.
- The procedure CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session is called once relative to the session. In Figure 53, the procedure returns as result "Continue".
- Then the procedures CAMEL_PS_Notification is called once relative to the session. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- Then the procedure CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Context is called once per PDP context. In Figure 53, the procedure returns as result "Continue".
6.13.1.2.2 A/Gb mode to Iu mode Intra-SGSN Change using S4 |R8| p. 188
In this case, clause 6.13.1.2.1 applies except for step 11, as well as clause-specific general statements stated below.
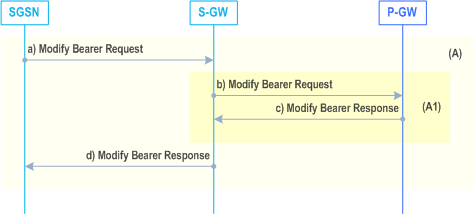
a)
If the SGSN established Direct Tunnel it shall send Modify Bearer Request (RNC Address and TEID, serving network identity, CN Operator Selection Entity, RAT type) message to the Serving GW and include the RNC's Address for User Plane, downlink TEID for data and DTI to instruct the Serving GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling as described in clause 13.8. Otherwise, if there were changes of for example the RAT type that e.g. can be used for charging, the SGSN shall send Modify Bearer Request (SGSN Address and TEID, serving network identity, CN Operator Selection Entity, RAT type) message to the Serving GW and include the SGSN's Address for User Plane, downlink TEID for data.
b)
The Serving GW informs the P-GW(s) about the change of for example the RAT type that e.g. can be used for charging, by sending the message Modify Bearer Request (Serving GW Address and TEID, RAT type) to the concerned P-GW(s). If dynamic PCC is deployed, and RAT type information needs to be conveyed from the P-GW to the PCRF, then the P-GW sends RAT type information to the PCRF as defined in TS 23.203.
c)
Each P-GW updates its context field and returns a Modify Bearer Response (MSISDN, P-GW address and TEID) message to the Serving GW. MSISDN is included if available in the stored UE context.
d)
The Serving GW updates the Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and return a Modify Bearer Response (Serving GW address and TEID, P-GW address and TEIDs (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP-based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic) message.
6.13.1.3 Selective RA Update p. 189
The MS shall use the following procedures when in STANDBY or PMM IDLE state.
Note that upon expiry of the periodic RA update timer, the MS shall carry out the periodic routeing area update procedure.
6.13.1.3.1 Uplink Signalling or Data Transmission p. 189
In STANDBY or PMM IDLE state the MS shall not perform an RA update procedure until uplink data or signalling information is to be sent from the MS.
If the MS is in the same mode (A/Gb mode or Iu mode) as when it last sent data or signalling, the procedures defined for that mode shall be followed. This shall be the sending of an LLC PDU in A/Gb mode, or for example sending of a Service Request message in Iu mode.
If the MS is in a different mode (A/Gb mode or Iu mode) as when it last sent data or signalling, the RA update procedure shall be performed before the sending of data or signalling. The RA update procedure needs not be performed if the signalling message is a power-off detach.
6.13.1.3.2 Downlink Signalling or Data Transmission p. 189
If the SGSN receives data for an MS in STANDBY or PMM IDLE state or, if the SGSN uses S4 and receives a Downlink Data Notification from the S-GW, the SGSN shall page in the RA where the MS is located. This may include both A/Gb mode and Iu mode cells.
If the MS receives this page in the same mode (A/Gb mode or Iu mode)as when it last sent data or signalling, the procedures defined for that mode shall be followed. This shall be the sending of an LLC PDU in a cell where the MS has to use A/Gb mode or, for example, sending of a Service Request message in a cell where the MS has to use Iu mode. When receiving such trigger from the RAN, if the S4-SGSN has no S4/S12 downlink user plane TEIDs for the UE, it sends Modify Bearer Request (S4/S12 downlink user plane TEIDs and IP address) to the S-GW, which establishes the downlink user plane towards the S4-SGSN or S12 RNC.
If the MS receives this page in a different mode (A/Gb mode or Iu mode) as when it last sent data or signalling, the RA update procedure shall be performed. The SGSN shall accept this RAU as a valid response.