Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
9.2.2.3 Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure using Gn
9.2.2.3A Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure using S4
9.2.2.4 S4-SGSN triggered Serving GW relocation
...
...
9.2.2.3 Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure using Gn |R7| p. 248
The Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure allows the GGSN to initiate the Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure (see clause 9.2.2.1.1). The Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure when using Gn is illustrated in Figure 69b.
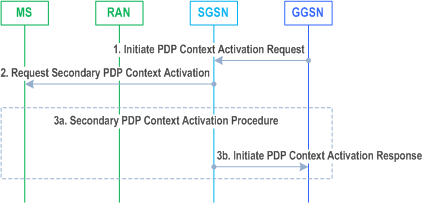
1)
The GGSN sends an Initiate PDP Context Activation (Linked NSAPI, QoS Requested, TFT, Protocol Configuration Options, Correlation-ID, Negotiated Evolved ARP)) message to the SGSN. The QoS Requested, TFT, and Protocol Configuration Options are sent transparently through the SGSN. The TFT shall contain uplink packet filter(s) and should contain downlink packet filter(s). The Correlation-ID is used by the GGSN to correlate the subsequent Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure (as described below) with this message. The Negotiated Evolved ARP may be included if the GGSN supports this IE and if the support of Evolved ARP has been indicated by the SGSN.
If the MS is in IDLE state and extended idle mode DRX is enabled for the MS, the SGSN will trigger Network Initiated Service Request Procedure from step 2 (which is specified in clause 6.12.2), and start a timer which is configured to a value smaller than the GTP re-transmission timer. If the SGSN receives no response from the MS before the timer expires, the SGSN rejects the Initiate PDP Context Activation message with a rejection cause indicating that the MS is temporarily not reachable due to power saving and, if a Delay Tolerant Connection indication was set for the PDN connection, the SGSN sets the internal flag Pending Network Initiated PDN Connection Signalling. If the Initiate PDP Context Activation message is rejected with a cause indicating that the MS is temporarily not reachable due to power saving, then the GGSN re-attempts the same procedure after it receives the indication that the UE is available for end to end signalling in a subsequent PDP Context Modification procedure.
2)
The SGSN sends a Request Secondary PDP Context Activation (Linked TI, TI, QoS Requested, TFT, Protocol Configuration Options) message to the MS. The Linked TI indicates the TI value assigned to the Active PDP Context corresponding to the Linked NSAPI previously received as described in step 1 above. The SGSN shall store a linkage between the TI value assigned to the new PDP Context, and the Correlation-ID received from the GGSN in the Initiate PDP Context Activation message.
3)
The MS sends an Activate Secondary PDP Context Request:
- That initiates the Secondary PDP Context activation procedure as described in 9.2.2.1.1. The Linked TI, TI, QoS Requested, and Protocol Configuration Options sent in the Activate secondary PDP Context Request shall be the same as previously received in step 2 above. The TFT shall contain the packet filters received in the Request Secondary PDP Context Activation message. The MS shall apply the uplink packet filters in the TFT on any uplink traffic, only packets conforming to any of the uplink packet filters in the TFT may be sent on the PDP context. If the MS did not receive a TFT in the Request Secondary PDP Context Activation message (which can only happen in case of a pre-Release 11 GGSN), the MS shall either send the Activate secondary PDP Context Request without a TFT or reject the request. The MS shall maintain the previously negotiated Bearer Control Mode for the PDP Address/APN pair (see clause 9.2) and ignore any BCM parameter, if included in the Request Secondary PDP Context Activation message.
- The SGSN returns an Initiate PDP Activation Response (Cause) message to the GGSN. This acknowledges the PDP context activation request towards the GGSN.
9.2.2.3A Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure using S4 |R8| p. 249
The Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure allows the P-GW to initiate the Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure towards the MS. The Network Requested Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure when using S4 is illustrated in Figure 69c.
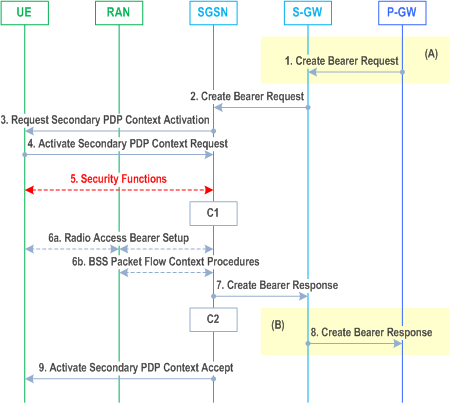
1)
The PDN-GW uses the QoS policy to assign the EPS Bearer QoS, i.e., it assigns the values to the bearer level QoS parameters QCI, ARP, GBR and MBR; see TS 23.401. The PDN-GW may have interacted with PCRF beforehand (refer to TS 23.203). The PDN-GW sends a Create Bearer Request message (Bearer QoS, TFT, S5/S8 TEID, LBI, Protocol Configuration Options) to the Serving GW, the Linked EPS Bearer Identity (LBI) is the EPS Bearer Identity of a bearer for this MS and PDN connection.
The TFT shall contain uplink packet filter(s) and should contain downlink packet filter(s).
2)
The Serving GW sends the Create Bearer Request (EPS Bearer QoS, TFT, UL TEID, LBI, CGI/SAI/RAI change report required, Protocol Configuration Options) message to the SGSN.
If the MS is in IDLE state and extended idle mode DRX is enabled for the MS, the SGSN will trigger Network Initiated Service Request Procedure from step 2 (which is specified in clause 6.12.2), and start a timer which is configured to a value smaller than the GTP re-transmission timer. If the SGSN receives no response from the MS before the timer expires, the SGSN sends a Create Bearer Response with a rejection cause indicating that the MS is temporarily not reachable due to power saving and, if a Delay Tolerant Connection indication was set for the PDN connection, the SGSN sets the internal flag Pending Network Initiated PDN Connection Signalling. The rejection is forwarded by the Serving GW to the PDN-GW. In this case, the steps 3-9 are skipped.
3)
Same as step 2 in clause 9.2.2.3, where Linked NSAPI equals LBI. The LBI is received from the S-GW in the Create Bearer Request message.
The SGSN may include an indication whether the traffic of this PDP context is allowed to be offloaded to WLAN as described in clause 5.3.21.
4)
The MS initiates the Secondary PDP Context activation procedure as described in clause 9.2.2.1.1.
The MS shall maintain the previously negotiated Bearer Control Mode for the PDP Address/APN pair (see clause 9.2) and ignore any BCM parameter, if included in the Request Secondary PDP Context Activation message.
The SGSN validates the Activate Secondary PDP Context Request using the TI indicated by Linked TI. The same S-GW and P-GW addresses are used by the SGSN as for the already-activated PDP context(s) for that TI and PDP address.
5)
In A/Gb mode, security functions may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "Security Function".
6a)
In Iu mode, RAB setup is done by the RAB Assignment procedure.
6b)
In A/Gb mode, BSS packet flow context procedures may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "BSS Context".
7)
The SGSN acknowledges the bearer activation to the Serving GW by sending a Create Bearer Response (EPS Bearer Identity, UL TEID, DL TEID, User Location Information) message. The SGSN sets the EPS Bearer Identity to an equivalent value as the NSAPI for the Bearer associated with the MS. The DL TEID value can be either the SGSN user plane TEID (2G or non-DT 3G) or the RNC user plane TEID.
8)
The Serving GW acknowledges the bearer activation to the PDN-GW by sending a Create Bearer Response (EPS Bearer Identity, S5/S8-TEID, User Location Information) message. The PDN-GW may interact with PCRF (refer to TS 23.203, e.g. to to deliver User Location Information and/or UE Time Zone Information if it was requested by the PRCF.
If the dedicated bearer activation is rejected with a cause indicating that the MS is temporarily not reachable due to power saving, then the PDN-GW re-attempts the same procedure after it receives the indication that the is MS available for end to end signalling in the subsequent Modify Bearer Request message.
9)
Same as step 7 in clause 9.2.2.1.1.
9.2.2.4 S4-SGSN triggered Serving GW relocation |R12| p. 251
This procedure is used if the S4-SGSN determines the Serving Gateway is to be relocated due to events other than those described in the mobility events scenarios (see clause 6.9.2.2). Such scenario exists during the establishment of PDN connection for SIPTO at Local Network with standalone L-GW or SIPTO above RAN. The MS sends an Activate PDP Context Request message to the S4-SGSN which determines that the Serving GW should be relocated.
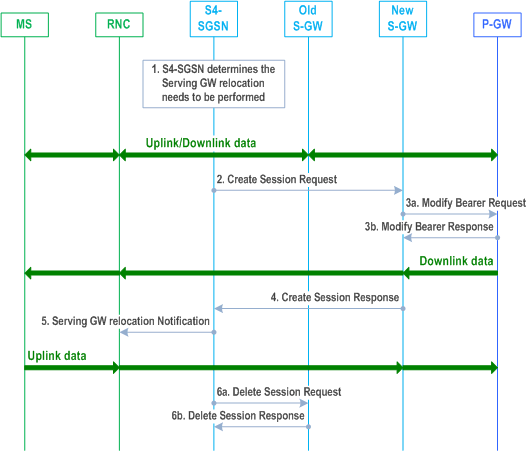
1)
If the Serving GW relocation procedure towards a new Serving GW fails, based on operator policy, the S4-SGSN should go back to the old Serving GW and disconnect the PDN connection (e.g. SIPTO at local network) that are not allowed to remain connected.
The Serving GW relocation procedure may be triggered by the S4-SGSN due to events that may benefit from a Serving GW relocation other than the ones described in the mobility procedures.
2)
The SGSN selects the new Serving GW as described in clause 4.3.8.2 of TS 23.401 on "Serving GW selection function" and 4.3.15, and sends a Create Session Request message (SGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, EPS Bearer ID(s), SGSN Address for Control Plane, RNC Address(es) and TEID(s) for User Traffic (Direct Tunnel is used), PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, DTI). If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN shall include the DTI to instruct the S-GW to apply Direct Tunnel specific error handling procedure as described in clause 13.8.
3a)
The new Serving GW sends Modify Bearer Request (EPS Bearer ID(s), serving network identity, CGI/SAI, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication) messages to the P-GWs involved.
3b)
The P-GWs acknowledge with sending Modify Bearer Response (TEID, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action) messages to new S-GW. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this EPS Bearer context.
4)
The new Serving GW acknowledges the user plane switch to the SGSN via the message Create Session Response (Cause, Serving GW Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, Serving GW Address for Control Plane, Protocol Configuration Options, PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action). The SGSN starts timer, to be used in step 6a.
5)
The SGSN sends Serving GW Relocation Notification message to the RNC. The SGSN provides to the RNC the new Serving GW's Address for user Plane and TEID(s) for Uplink data. The RNC starts using the new Serving GW address and TEID(s) for forwarding subsequent uplink packets.
6a)
When the timer has expired after step 5, the SGSN releases the bearer(s) in old S-GW by sending a Delete Session Request message.
6b)
The old S-GW acknowledge bearer deletion.