Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
16 Interactions with Other Services p. 338
16.0 General |R8| p. 338
This clause describes the interaction between packet-domain services and the following other services for a GPRS-attached MS which is in GERAN/UTRAN PS coverage:
- point-to-point Short Message Service (SMS);
- circuit-switched services;
- supplementary services; and
- CAMEL services.
16.1 Point-to-point Short Message Service p. 338
It shall be possible for a GPRS-attached MS to send and receive short messages over the PS domain when it is in GERAN/UTRAN PS coverage. An MS that is GPRS-attached and not IMSI-attached shall transfer SMs over the PS domain. MSs that are both GPRS-attached and IMSI-attached shall transfer SMs over the PS domain or over the CS domain (if the CS domain is used, then paging for Mobile-terminated SMS may go through the SGSN).
The following two clauses define the operation of mobile-terminated and mobile-originated SMS routeing and transfer over the PS domain. More detailed definitions are contained in TS 23.040. They apply to SGSNs supporting the Gd or the Gdd interface.
16.1.1 Mobile-terminated SMS Transfer p. 338
Figure 96 and the description below show an example of a successful delivery of an SM to an MS in GERAN/UTRAN PS coverage over the PS domain.
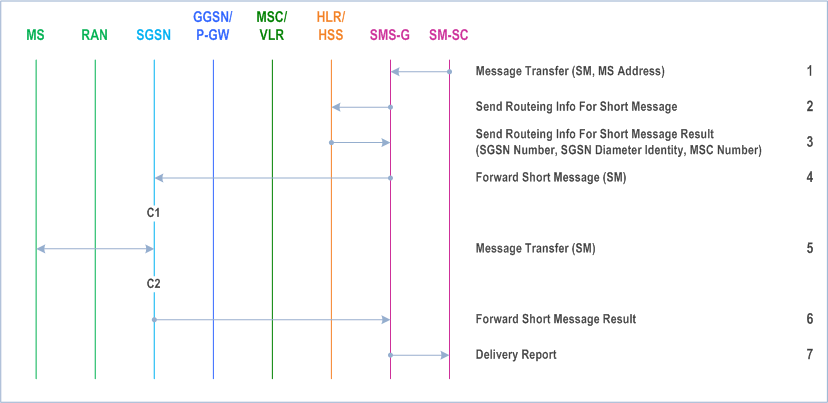
Step 1.
CAMEL is not supported by SGSNs using EPS interfaces; otherwise CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed according to TS 23.078:
The short message service centre determines it shall send an SM to an MS. SM SC forwards the SM to an SMS gateway MSC (SMS GMSC).
Step 2.
SMS GMSC examines the destination MS Address, and sends a Send Routeing Info For Short Message message to the relevant HLR/HSS.
Step 3.
HLR/HSS checks the subscriber data (e.g. ODB data and Call Barring Info) for the MS and determines that the MS is allowed to receive the SMS. The HLR/HSS returns a Send Routeing Info For Short Message Result message to the SMS GMSC. The result may contain the MS's current SGSN Number, the MSC Number, or both. The result also contains the SGSN Diameter identity if the SGSN number is present and if Gdd is supported. If the result does not contain an SGSN Number (i.e., the HLR/HSS knows that the MS is not reachable via an SGSN), and if the result does contain an MSC Number, non-GPRS SMS delivery procedures are followed. If the result contains an SGSN Number, the SMS transfer proceeds according to the following events.
Step 4.
SMS GMSC forwards the SM to the SGSN.
Step 5.
SGSN transfers the SM to the MS on the RP and CP layers, as defined in TS 24.011.
Step 6.
SGSN returns a Forward Short Message Result message to the SMS GMSC indicating successful delivery of the SM.
Step 7.
SMS GMSC returns a Delivery Report to the SM SC indicating successful delivery of the SM.
C1)
CAMEL_T_SMS_INIT.
The procedure returns as result "Continue".
C2)
CAMEL_T_SMS_DELIVERED.
This procedure does not return a result.
16.1.1.1 Unsuccessful Mobile-terminated SMS Transfer p. 339
The SGSN or the HLR/HSS may not be able to deliver the SM to the MS. This may for example happen when the MS is not attached to GPRS, when the radio channel conditions are bad, or when the Mobile-terminated SMS is barred.
When the SGSN cannot deliver the SM to the MS, the SGSN sets the Mobile station Not Reachable for GPRS flag (MNRG), and returns a failure report to the SMS GMSC. Based on the routeing information received from the HLR/HSS, the SMS GMSC shall do one of the following:
- If an MSC/VLR is available for the MS, the SM is forwarded to the MS via the MSC/VLR. A successful delivery report shall be returned to the SM SC.
- If an MSC/VLR is not available for the MS, the Message Waiting Indication information in the HLR/HSS shall be updated and an unsuccessful delivery report shall be returned to the SM SC.
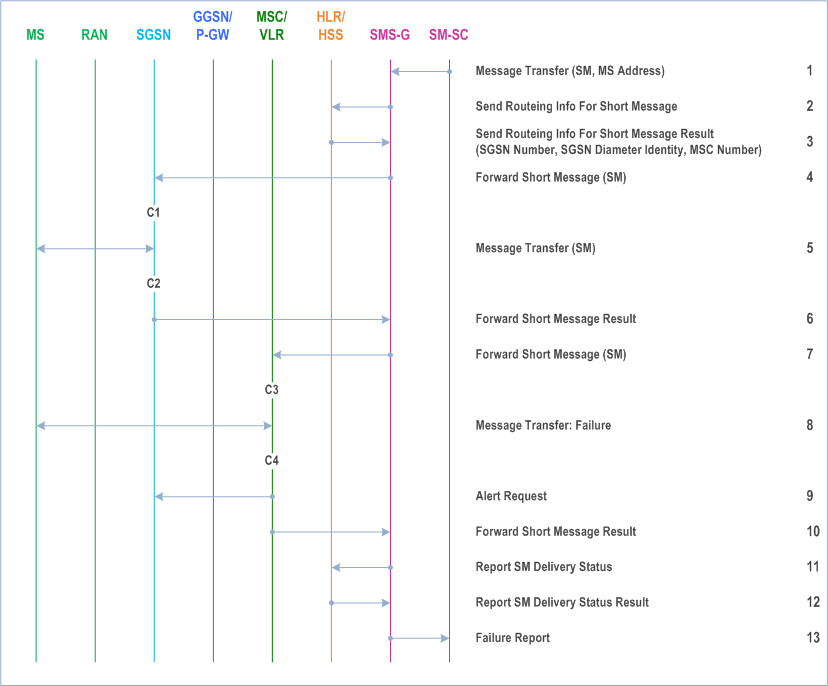
Step 1.
CAMEL is not supported by SGSNs using EPS interfaces; otherwise CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed according to TS 23.078:
The short message service centre determines it shall send an SM to an MS. SM SC forwards the SM to a SMS GMSC.
Step 2.
SMS GMSC examines the destination MS Address, and sends a Send Routeing Info For Short Message message to the relevant HLR/HSS.
Step 3.
HLR/HSS checks the subscriber data (e.g. ODB data and Call Barring Info) for the MS to determine whether the MS is allowed to receive the SMS. If the Mobile-terminated SMS is barred, the HLR/HSS returns a Send Routing Info for Short Message Error message with an appropriate cause. If the Mobile-terminated SMS is not barred, the HLR returns a Send Routeing Info For Short Message Result message to the SMS GMSC. The Result contains an SGSN Number and an MSC Number. The result also contains the SGSN Diameter identity if Gdd is supported.
Step 4.
SMS GMSC forwards the SM to the SGSN.
Step 5.
SGSN attempts to transfer the SM to the MS, but fails.
Step 6.
SGSN sets MNRG and returns a Forward Short Message Result message to SMS GMSC indicating unsuccessful delivery of the SM.
Step 7.
SMS GMSC selects an alternative route for the SMS, and forwards the SM to the MSC/VLR.
Step 8.
MSC/VLR attempts to transfer the SM to the MS, but fails.
Step 9.
The MSC/VLR requests the setting of the NGAF at the SGSN.
Step 10.
VLR sets MNRF and returns a Forward Short Message Result message to the SMS GMSC indicating unsuccessful delivery of the SM.
Step 11.
SMS GMSC sends a Report SM Delivery message to the HLR/HSS.
Step 12.
HLR/HSS updates its Message Waiting Indication fields and returns a Report SM Delivery Result message to the SMS GMSC.
Step 13.
SMS GMSC returns a Failure Report to the SM SC indicating unsuccessful delivery of the SM.
C1)
Figure 69 shows that the SGSN sends a Ready for SM (MS Reachable) message to the HLR/HSS when the MS becomes reachable and MNRG is set in the SGSN. The SGSN indicates also to the MSC/VLR when the MS becomes reachable and NGAF is set in the SGSN. If the MNRF is set at the MSC/VLR, the MSC/VLR sends a Ready for SM (MS Reachable) message to the HLR/HSS. Reception of a Ready for SM message or Update Location message when MNRG is set in the HLR/HSS shall trigger the SMS alert procedure as defined in TS 23.040.
MNRG remains set in the SGSN independently of whether the MSC/VLR was successful in delivering the SM or not.
This means that the SGSN in certain cases sends a Ready for SM message to the HLR/HSS when an MS becomes reachable via the SGSN, even if no SM is waiting. This causes a small amount of duplicate signalling between the SGSN and the HLR/HSS only.
CAMEL_T_SMS_INIT.
The procedure returns as result "Continue".
C2)
CAMEL_T_SMS_FAILURE.
This procedure does not return a result.
C3)
CAMEL_T_SMS_INIT.
The procedure returns as result "Continue".
C4)
CAMEL_T_SMS_FAILURE.
This procedure does not return a result.
16.1.2 Mobile-originated SMS Transfer p. 341
Figure 98 and the description below explain the steps involved in sending an SM from an MS in GERAN/UTRAN PS coverage over the PS domain.
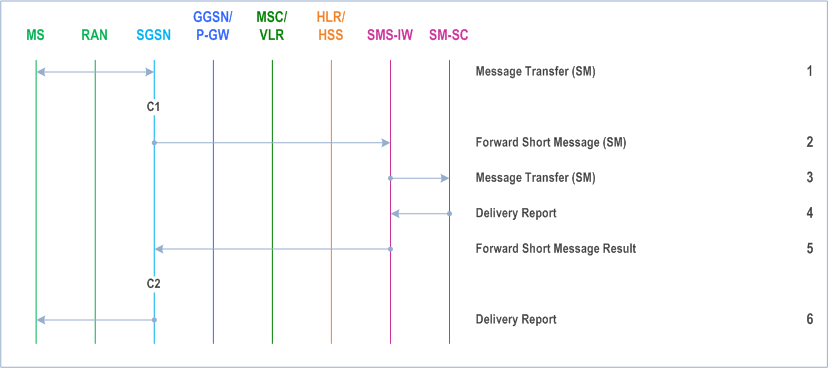
Step 1.
CAMEL is not supported by SGSNs using EPS interfaces; otherwise; otherwise CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed according to TS 23.078.
The MS has an SM to send, and transfers the SM to the SGSN via RP and CP.
Step 2.
SGSN checks the MS subscription data (e.g. ODB data and Call Barring Info), and determines that the MS is allowed to originate the SMS. SGSN forwards the SM to a SMS interworking MSC (SMS IWMSC). If the MS is not allowed to originate the SMS, the SGSN returns an RP Error message with an appropriate cause.
Step 3.
SMS IWMSC passes the SM to the addressed SM SC.
Step 4.
SM SC returns a Delivery Report to the SMS IWMSC indicating successful delivery of the SM.
Step 5.
SMS IWMSC returns a Forward Short Message Result message to the SGSN indicating successful delivery of the SM.
Step 6.
SGSN returns a Delivery Report to the MS indicating successful delivery of the SM.
C1)
CAMEL_O_SMS_INIT.
The procedure returns as result "Continue".
C2)
CAMEL_O_SMS_SUBMITTED
This procedure does not return a result.