Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
5.6.2 User Plane (Iu mode) p. 62
5.6.2.1 MS - GGSN user plane with GERAN in Iu mode p. 62
5.6.2.2 MS - P-GW/GGSN user plane with UTRAN p. 63
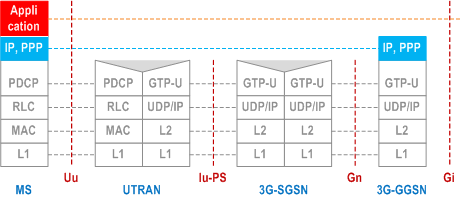
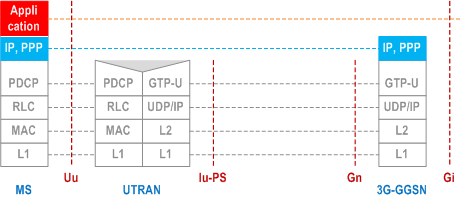
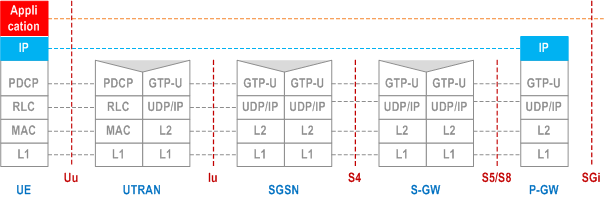
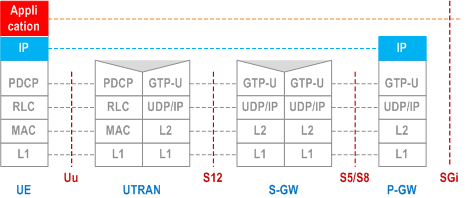
Legend:
- Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP): This transmission functionality maps higher-level characteristics onto the characteristics of the underlying radio-interface protocols. PDCP provides protocol transparency for higher-layer protocols. PDCP supports e.g. IPv4, PPP and IPv6. Introduction of new higher-layer protocols shall be possible without any changes to the radio-interface protocols. PDCP provides protocol control information compression. PDCP is specified in TS 25.323.
- GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for the user plane (GTP-U): This protocol tunnels user data between UTRAN and the 3G SGSN, and between the GSN CN nodes in the backbone network. GTP shall encapsulate all PDP PDUs. GTP is specified in TS 29.060.
- SGSN controls the user plane tunnel establishment and may establish a Direct Tunnel between UTRAN and GGSN as shown in Figure 6b or a Direct Tunnel between UTRAN and S-GW as shown in Figure 6d.
- UDP/IP: These are the backbone network protocols used for routeing user data and control signalling.
- Radio Link Control (RLC): The RLC protocol provides logical link control over the radio interface. There may be several simultaneous RLC links per MS. Each link is identified by a Bearer Id. RLC is defined in TS 25.322.
- Medium Access Control (MAC): The MAC protocol controls the access signalling (request and grant) procedures for the radio channel. MAC is specified in TS 25.321.
5.6.2.3 Core Network Node - Core Network Node |R5| p. 64
This user plane is the same as for A/Gb mode, see clause "Core Network Node - Core Network Node" above.