Content for TS 23.401 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.3.6…
4.3.8…
4.3.12…
4.3.16…
4.3.20…
4.3.25…
4.4…
4.6…
4.7…
4.13…
5…
5.1.2…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.3.3…
5.3.3.2
5.3.3.3…
5.3.4…
5.3.4B…
5.3.5…
5.3.8…
5.3.9…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.5.1.2…
5.5.2…
5.5.2.2…
5.5.2.3…
5.5.2.4…
5.6…
5.7.3…
5.7A…
5.10
5.11…
5.19…
D…
D.3…
D.3.4
D.3.5
D.3.6
D.3.7…
D.3.8…
E
F…
J…
K…
L…
M…
O…
5.19 Procedures to support Dedicated Core Networks |R13| p. 382
5.19.1 NAS Message Redirection Procedure p. 382
When DCNs are used, these steps are used to reroute a NAS message (and thereby a UE) from one CN node to another CN node during Attach, TAU or RAU procedure. These steps are also used by the MME/SGSN or HSS initiated Dedicated Core Network Reselection procedure in clause 5.19.3.
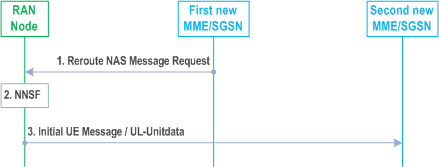
The procedure is started when a first new MME/SGSN decides to move the handling of an Attach Request, TAU Request or RAU Request to another CN node.
Step 1.
The first new MME/SGSN sends a Reroute NAS Message Request (original RAN message, reroute parameters, Additional GUTI/P-TMSI, UE Usage Type, and optionally the IMSI) to the RAN Node. The reroute parameter is a MMEGI (for E-UTRAN) or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID (for UTRAN/GERAN) corresponding to the DCN that corresponds to the UE Usage Type. A UE provided Additional GUTI/P-TMSI (if available) from the NAS Request message is included. The MME/SGSN may determine the MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID corresponding to the DCN using DNS procedures. The original RAN message is the complete PDU received from the RAN which contains the original NAS Request message and all RAN IEs. The UE Usage Type shall be included, if available. For the condition to include the IMSI, see step 6 in clause 5.19.2.
Step 2.
The RAN node's NNSF selects a new MME/SGSN based on the MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID and possibly also based on an Additional GUTI/P-TMSI. If Additional GUTI/P-TMSI identifies an MME/SGSN within the set of valid nodes identified by MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID, it should be the selected node. Otherwise a valid CN node corresponding to the MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID will be selected. If no valid MME/SGSN is available within the set of valid nodes identified by MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID, the RAN node selects an MME/SGSN from the default DCN or selects the MME/SGSN that sent the Reroute Request, based on operator configuration. The MME/SGSN is selected from the network corresponding to the selected CN operator.
Step 3.
Dependent on RAT, the eNodeB/RNC sends the Initial UE message to the selected MME/SGSN or the BSC sends the UL-Unitdata message to the selected SGSN. The initial UE message/UL-Unitdata message includes the NAS Request message, the MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID, UE Usage Type and the IMSI if received from the first SGSN/MME in step 1. The MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID indicates that the message is a rerouted message and the second new MME/SGSN shall not reroute the NAS message. The UE Usage Type shall be included if received in the Reroute NAS Message Request to be used by the second new MME/SGSN to select SGW and PDN-GW (see clauses 4.3.8.1 and 4.3.8.2).
5.19.2 Attach, TAU and RAU procedure for Dedicated Core Network p. 383
When DCNs are used, the Attach, TAU and RAU procedures in this clause apply.
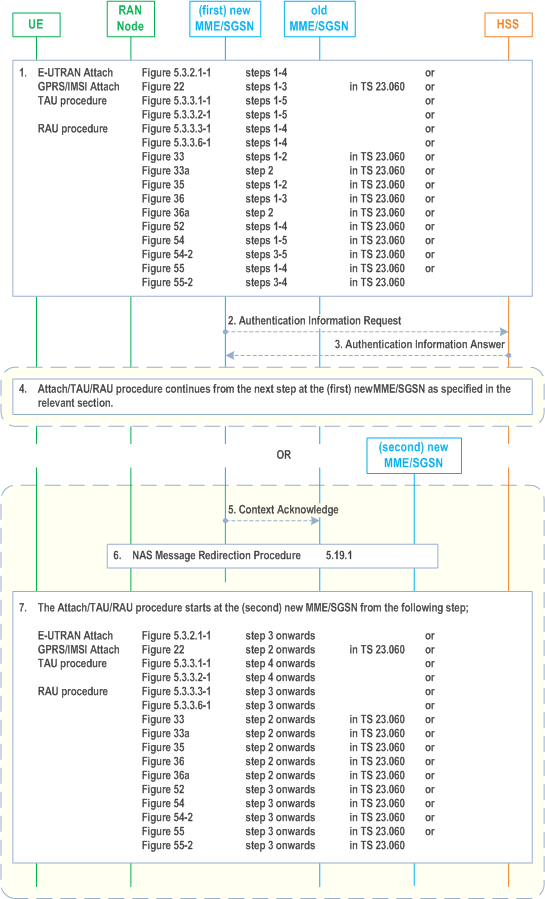
Step 1.
Attach, TAU, or RAU procedure is initiated as specified in the relevant clauses of this specification and TS 23.060. The relevant steps of the procedure as specified in the Figure above are executed. The following modifications apply:
Step 2.
- In the RRC Connection Complete message transferring the NAS Request message, the UE provides the DCN-ID, if available. If the UE has a PLMN specific DCN-ID the UE shall provide this value and if no PLMN specific DCN-ID exist the pre-provisioned default standardized DCN-ID shall be provided, if pre-provisioned in the UE. The RAN node selects a DCN and a serving MME/SGSN within the network of the selected core network operator based on the DCN-ID and configuration in the RAN node. The NAS Request message is sent to the selected node. The DCN-ID is provided by the RAN to the MME/SGSN together with the NAS Request message.
- E-UTRAN Initial Attach Procedure (clause 5.3.2.1 (Figure 5.3.2.1-1)) and Combined GPRS/IMSI Attach procedure (clause 6.5.3 of TS 23.060 (Figure 22)): In the Identification Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
- Tracking area update procedure (clause 5.3.3.1 (Figure 5.3.3.1-1) and 5.3.3.2 (Figure 5.3.3.2-1)): In the Context Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
- Routing area update procedure (clause 5.3.3.3 (Figure 5.3.3.3-1) and 5.3.3.6 (Figure 5.3.3.6-1), clauses 6.9.1.2.2 (Figure 33), 6.9.1.2.2a (Figure 33a), 6.9.1.3.2 (Figure 35), 6.9.2.1 (Figure 36), 6.9.2.1a (Figure 36a), 6.13.1.1.1 (Figure 52), 6.13.2.1.1 (Figure 54), 6.13.2.1.2 (Figure 54-2), 6.13.2.2.1 (Figure 55), 6.13.2.2.2 (Figure 55-2) of TS 23.060): In the Context Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
If the (first) new MME/SGSN, i.e. the MME/SGSN that has not received any MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID from RAN, does not have sufficient information to determine whether it should serve the UE, it sends an Authentication Information Request message to the HSS requesting UE Usage Type by adding the parameter "Send UE Usage Type" flag in the message. The MME/SGSN may also request one or more authentication vectors in addition to the UE Usage Type. The (first) new MME/SGSN has sufficient information in the following cases and may then skip this step and step 3:
Step 3.
- The (first) new MME/SGSN has received the UE Usage Type from the old MME/SGSN in the Identification Response (for Attach) or Context Response (for TAU/RAU) message or Forward Relocation Request (for Handover).
- Based on configuration in the (first) new MME/SGSN and UE context information, the MME/SGSN is able to determine whether it should serve the UE.
The HSS, if supporting DCNs, provides the UE Usage Type in the Authentication Information Answer message, if any is stored for the UE. The UE Usage Type is returned by the HSS in addition to requested authentication vectors.
Step 4.
If the (first) new MME/SGSN determines that it shall not reroute the NAS message to another CN node, the MME/SGSN either continues from the designated step as stated in the Figure above or depending on operator configuration rejects the NAS request message and the NAS procedure ends in this step. The NAS message is rejected with parameters, e.g. backoff timer, such that the UE does not immediately re-initiate the NAS procedure.
The MME/SGSN sends the DCN-ID, if available, for the DCN to the UE in the NAS Accept message. The UE updates its stored DCN-ID parameter for the serving PLMN if DCN-ID for serving PLMN is changed.
Step 5.
If the (first) new MME/SGSN determines that it should reroute the NAS request message to another CN node, the procedure is a TAU or RAU procedure and UE context was received from the old MME/SGSN, the (first) new MME sends a Context Acknowledge message with cause code indicating that the procedure is not successful. The old MME/SGSN shall continue as if Context Request was never received.
Step 6.
If the (first) new MME/SGSN determines that it should reroute the NAS request message to another CN node, it uses the "NAS Message Redirection Procedure" in clause 5.19.1. The NAS message is re-routed to a (second) new MME/SGSN. If the IMSI was retrieved unencrypted from the UE by the (first) new MME/SGSN in step 1, the (first) new MME/SGSN shall include the IMSI in the Reroute Message Request.
Step 7.
The (second) new MME/SGSN, i.e. the MME/SGSN that receives the rerouted NAS message from RAN with MMEGI or Null-NRI/SGSN Group ID, performs NAS procedure as stated for E-UTRAN in this specification and for GERAN/UTRAN in TS 23.060 from the steps shown in the Figure above. The following modifications apply:
- E-UTRAN Initial Attach Procedure (clause 5.3.2.1 (Figure 5.3.2.1-1)) and Combined GPRS/IMSI Attach procedure (clause 6.5.3 of TS 23.060 (Figure 22)): In the Identification Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
- Tracking area update procedure (clause 5.3.3.1 (Figure 5.3.3.1-1) and 5.3.3.2 (Figure 5.3.3.2-1)): In the Context Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
- If the IMSI was received from the first (new) MME/SGSN as part of the NAS Message Redirection Procedure, the second (new) MME/SGSN does not have to retrieve the IMSI from the UE.
- Routing area update procedure (clause 5.3.3.3 (Figure 5.3.3.3-1) and 5.3.3.6 (Figure 5.3.3.6-1), clauses 6.9.1.2.2 (Figure 33), 6.9.1.2.2a (Figure 33a), 6.9.1.3.2 (Figure 35), 6.9.2.1 (Figure 36), 6.9.2.1a (Figure 36a), 6.13.1.1.1 (Figure 52), 6.13.2.1.1 (Figure 54), 6.13.2.1.2 (Figure 54-2), 6.13.2.2.1 (Figure 55), 6.13.2.2.2 (Figure 55-2) of TS 23.060): In the Context Response message, the old MME/SGSN provides UE Usage Type parameter, if available.
- The MME/SGSN sends the DCN-ID, if available, for the new DCN to the UE in the NAS Accept message. The UE updates its stored DCN-ID parameter for the serving PLMN if DCN-ID for serving PLMN is changed.
5.19.2a Impacts to Handover Procedures p. 386
When DCNs are used, the impacts to the handover procedures are captured as below.
-
Forward Relocation Request message: When MME changes during handover, in the step where Forward Relocation Request message is sent from the Source MME/SGSN to Target MME/SGSN, the source MME/SGSN also includes the UE Usage Type, if available, in the message. This applies to the following clauses and step:
- 5.5.1.2.2 S1-based handover, normal: Step 3
- 5.5.2.1.2 Preparation phase (E-UTRAN to UTRAN Iu mode Inter RAT handover): Step 3
- 5.5.2.2.2 Preparation phase (UTRAN Iu mode to E-UTRAN Inter RAT handover): Step 3
- 5.5.2.3.2 Preparation phase (E-UTRAN to GERAN A/Gb mode Inter RAT handover): Step 3
- 5.5.2.4.2 Preparation phase (GERAN A/Gb mode to E-UTRAN Inter RAT handover): Step 3
-
Selection of new SGW: In the step, subsequent to the Forward Relocation Request message, in which the target MME/SGSN determines if the Serving-GW is to be relocated, if the target MME/SGSN supports DCN, the target MME/SGWN also determines if the existing Serving-GW supports the DCN for the UE based on UE Usage Type of the UE, locally configured operator's policies as well as UE related context information available at the target network, e.g. information about roaming. This applies to the following clauses and step:
- 5.5.1.2.2 S1-based handover, normal: Step 4
- 5.5.2.1.2 Preparation phase (E-UTRAN to UTRAN Iu mode Inter RAT handover): Step 4
- 5.5.2.2.2 Preparation phase (UTRAN Iu mode to E-UTRAN Inter RAT handover): Step 4
- 5.5.2.3.2 Preparation phase (E-UTRAN to GERAN A/Gb mode Inter RAT handover): Step 4
- 5.5.2.4.2 Preparation phase (GERAN A/Gb mode to E-UTRAN Inter RAT handover): Step 4
- Handover from service area where DCN is not used to an area where DCN is supported: When handover occurs from a service area where DCN is not used to a service area where DCN is supported and the MME or SGSN changes, the target MME or SGSN obtains the UE Usage Type information from the HSS during the subsequent TAU or RAU procedure. If the target MME/SGSN determines that the Serving-GW does not support the UE Usage Type, the target MME/SGSN triggers the Serving-GW relocation as part of the handover procedures described in clause 5.5. If the target MME or SGSN does not serve the UE Usage type, the handover procedure should complete successfully and then the target MME or SGSN may use the procedure in clause 5.19.3 Step 5 onwards, to change the serving DCN of the UE.
5.19.3 MME/SGSN or HSS initiated Dedicated Core Network Reselection p. 387
If DCNs are deployed, this procedure is used by the HSS to update (i.e. add, modify or delete) the UE Usage Type subscription parameter in the serving node. This procedure may result in change of serving node of the UE. This procedure may also be used for MME/SGSN initiated serving node change for UEs, e.g. when configuration about the UE Usage Types served by MME/SGSN is changed. This procedure may also be used after a handover procedure by the target MME/SGSN to redirect a UE to a serving node of another DCN.
If UE assisted DCN selection feature is supported by the Core Network, the UE is provided with the new DCN-ID.
The subscription change may be applied to a large number of UEs and similar considerations as in the case of MME/SGSN rebalancing specified in clause 4.3.7.3 should be applied to avoid sudden redirection of UEs that could overload the core network nodes (and possibly the RAN if paging is needed).
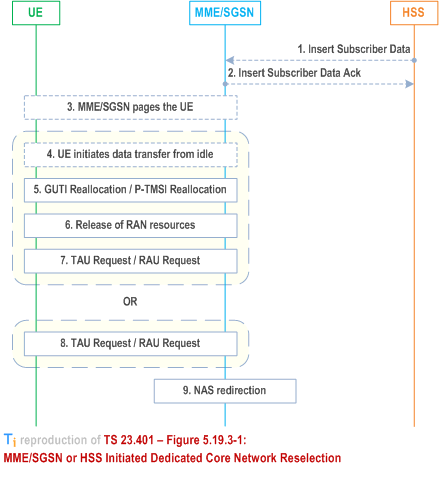
Steps 1 and 2 apply for HSS initiated Dedicated Core Network Reselection procedure only.
Step 1.
If MME/SGSN decides to transfer the UE to another CN either Steps 4 through 7 or Step 8 occur. Steps 4 through 7 occur if the UE is already in connected mode or UE enters connected mode by initiating data transfer. Step 8 occurs if the UE is in idle mode and performs a TAU/RAU procedure. If the MME/SGSN determines that only DCN-ID shall be updated in the UE (i.e. serving CN node is kept) only step 4 and 5 occurs.
The HSS sends an Insert Subscriber Data Request (IMSI, Subscription Data) message to the MME/SGSN. The Subscription Data includes UE Usage Type information or UE Usage Type withdrawal information.
Step 2.
The MME/SGSN updates the stored Subscription Data and acknowledges the Insert Subscriber Data Request message by returning an Insert Subscriber Data Answer (IMSI) message to the HSS. The procedure ends if the MME/SGSN can continue to serve the UE.
Step 3.
If the MME/SGSN decides to transfer the UE immediately to another CN or if the MME/SGSN determines that DCN-ID immediately needs to be updated and the UE is in idle-mode, the MME/SGSN pages the UE. Alternatively the MME waits until the UE becomes active.
Step 4.
Either triggered by the paging or by uplink data the UE initiates NAS connection establishment. Alternatively the UE initiates NAS connection establishment by sending a TAU/RAU Request.
Step 5.
When a NAS connection already exists or when a NAS connection is established for initiating data transfer, the MME/SGSN triggers the GUTI Reallocation/P-TMSI Reallocation procedure. If DCN-ID is available and the MME/SGSN determines that the UE shall be updated with a new DCN-ID, the new DCN-ID shall be included in the GUTI Reallocation Command/P-TMSI Reallocation Command.
If the MME/SGSN determines that a CN node re-selection needs to be performed, a non-broadcast TAI/RAI shall be included.
Step 6.
The MME/SGSN releases RAN resources and UE is moved to idle mode.
Step 7.
The non-broadcast TAI/RAI triggers the UE to immediately start the TAU/RAU procedure. If available, the new DCN-ID shall be sent from the UE to the RAN.
The MME/SGSN receives the TAU/RAU Request message.
Step 8.
The UE performs a TAU/RAU request. The MME/SGSN receives the TAU/RAU Request message.
Step 9.
If the UE Usage Type for the UE has been added or modified and if it is not served by the MME/SGSN, or if the UE Usage Type has been withdrawn from the HSS subscription data and subscriptions without UE Usage Type are not served by the MME/SGSN, the MME/SGSN triggers the NAS Message redirection procedure of clause 5.19.1 to redirect the UE. This is followed by step 7 of clause 5.19.2 where the TAU/RAU procedure completes at the MME of the selected DCN.