Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
A (Normative) APN and P-GW/GGSN Selection p. 349
A.0 General |R8| p. 349
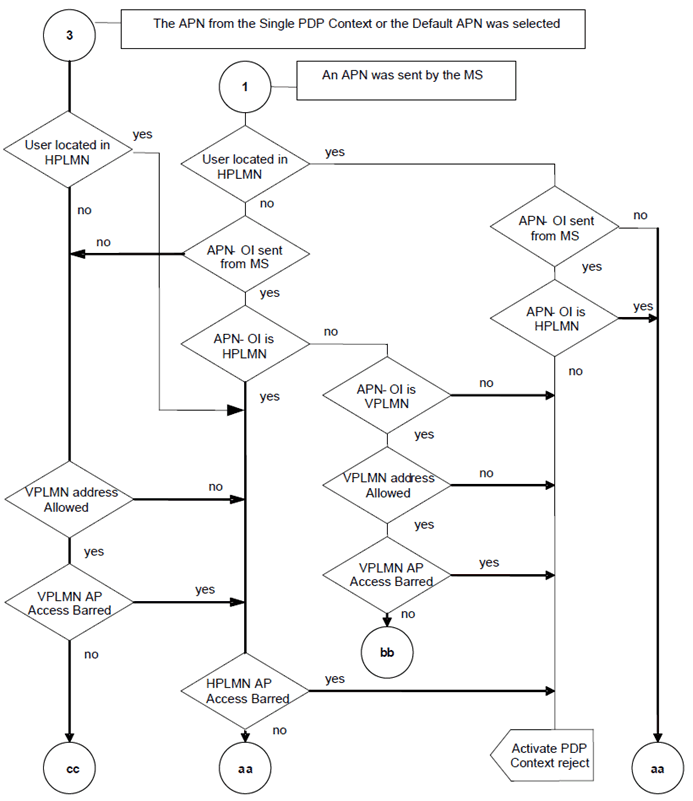
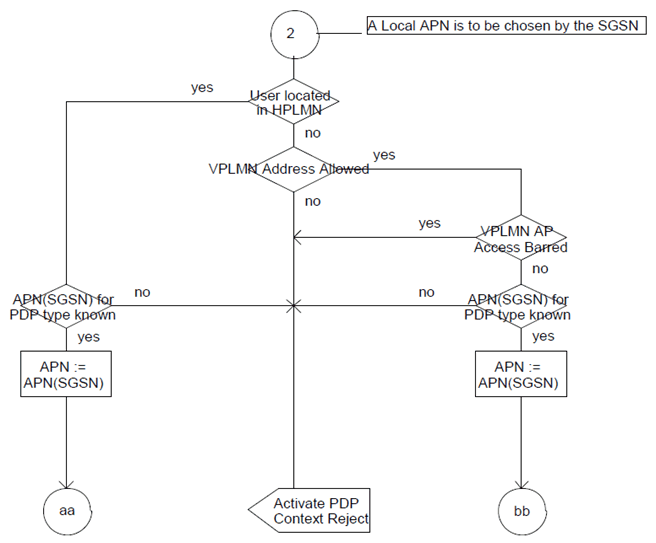
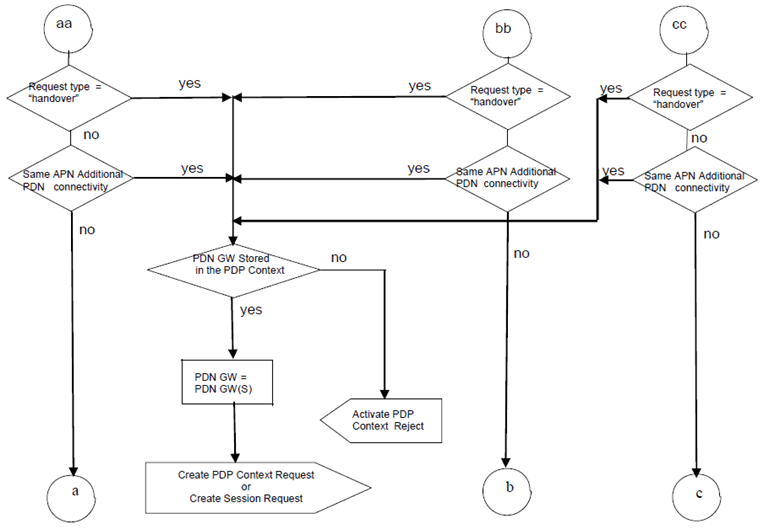
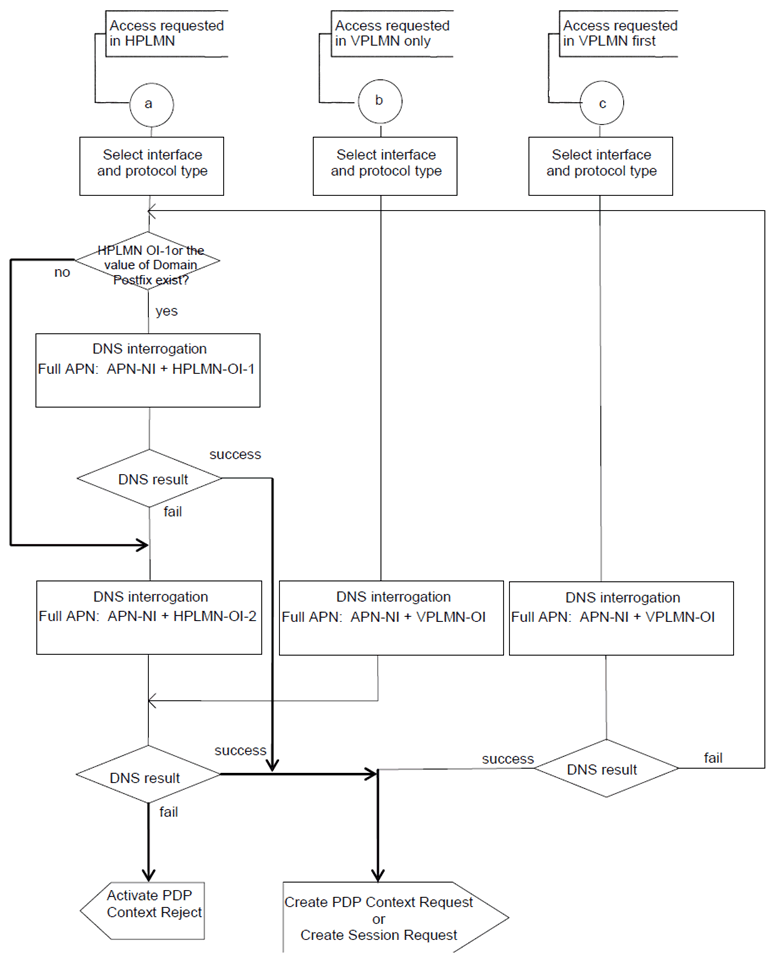
This Annex contains the rules applied by the SGSN upon PDP context activation to determine the APN and the corresponding P-GW/GGSN.
The selection process used by the SGSN to select P-GW and GGSN is described in clause 5.3.7.1. The procedures specified in TS 29.303 apply to DNS-based P-GW selection.
APN selection refers to the process of selection and construction of the full APN (APN-NI + APN-OI). This full APN is then employed for interrogation of the DNS server to obtain the GGSN or P-GW address.
A.1 Definitions p. 349
The SGSN knows from the subscription data the following parameters (S for Subscribed): PDP type (S), PDP address (S), APN (S), and VPLMN address allowed. In addition, the S4-SGSN and MME receive a PDN subscription context that is marked as default (and associated default APN) for E-UTRAN UEs.
The SGSN may know from configuration the Local APN supporting a given PDP type. This APN is called APN (SGSN) and does not include an APN Operator Identifier. APN (SGSN) shall not be an APN with LIPA permisssions set to "LIPA-only" or "LIPA-conditional".
The SGSN knows the parameters requested by the MS (R for Requested): PDP type (R), PDP address (R), and APN (R). APN (R) is the APN Network Identifier requested by the MS.
In case of "an APN chosen by the SGSN" the activated PDP context is always linked with a dynamic PDP address.
An MS may have multiple subscription records for the same PDP type and the same PDP address, but with different APNs.
An MS may have one or two subscription records with the same PDP type and the same APN: one with a static PDP address, one with a dynamic PDP address.
An MS may have multiple subscription records with the same APN, but with different PDP types.
When the MS is in its HPLMN, if the MS requests an APN that does not correspond to any GGSN or P-GW of its HPLMN, the request shall be rejected by the SGSN. When the MS is in a VPLMN, if the MS requests an APN that does not correspond to any GGSN or P-GW of its HPLMN nor of this VPLMN or any of its associated PLMNs when the VPLMN is a shared network, the request shall be rejected by the SGSN.
If APN (S) = wild card (see TS 23.003), it means either:
- that a Local APN (a locally defined PDN) has to be chosen by the SGSN (APN (SGSN)) if no APN (R) has been provided; or
- that a PDP context with dynamic PDP address may be activated towards any APN requested by the MS.
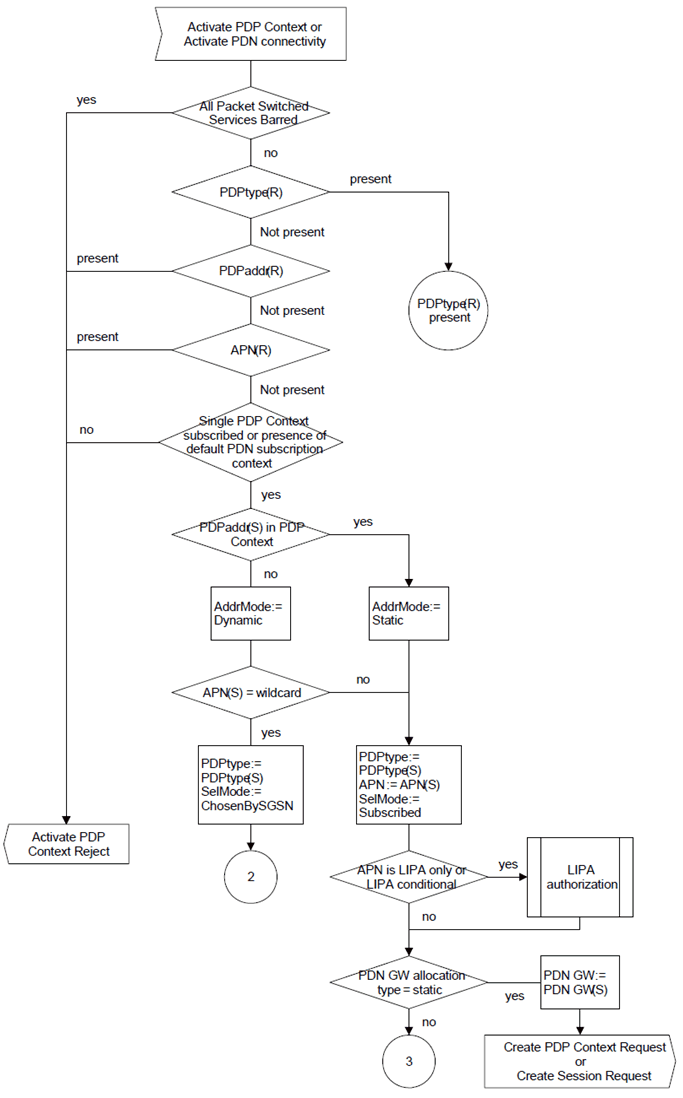
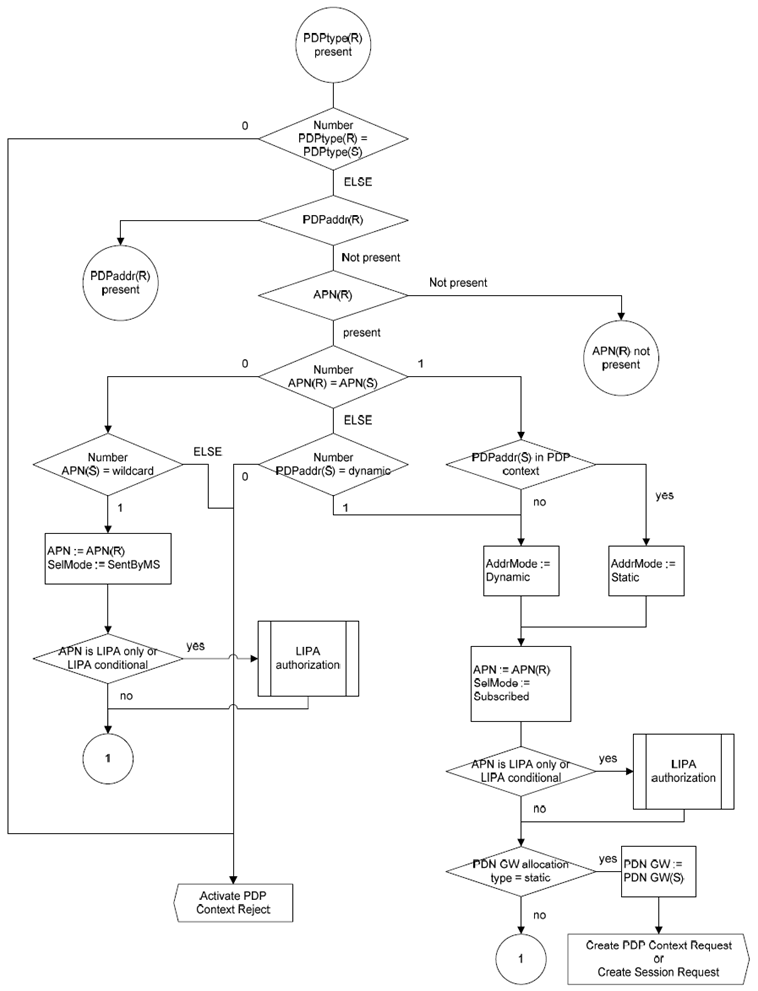
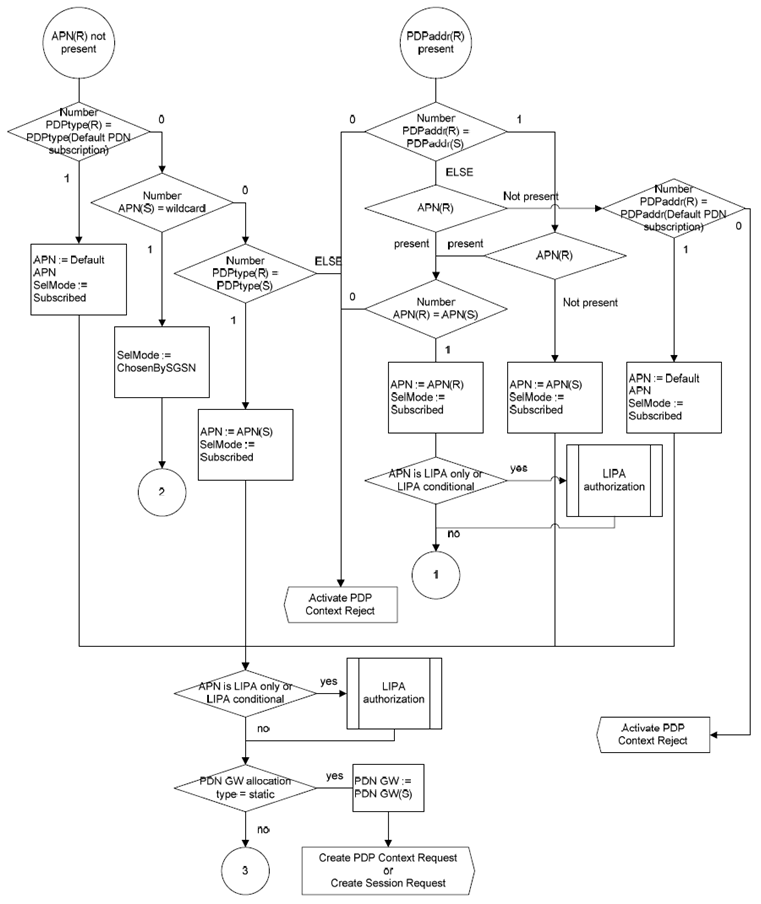
A.2 Selection Rules p. 350
The SGSN shall select the APN to be used to derive the GGSN or P-GW address, and set the selection mode parameter according to the rules in the SDL diagrams in this clause. The following definitions apply to the SDL diagrams:
AddrMode:
Addressing Mode, temporary parameter set in the selection process to either of:
AddrMode := static
AddrMode := dynamic
APN OI:
APN Operator Identifier.
HPLMN AP:
HPLMN Access Point.
HPLMN OI-1:
HPLMN APN Operator Identifier type 1 (derived from the APN OI Replacement field in the subscriber's profile).
HPLMN OI-2:
HPLMN APN Operator Identifier type 2 (derived from IMSI).
Number <condition>:
determines the PDP context subscription records that satisfy the given condition.
ODB parameter:
Operator Determined Barring parameter configured in subscriber data to one of:
All Packet Oriented Services barred
Roamer Access to HPLMN-AP barred
Roamer Access to VPLMN-AP barred
PDPaddr:
PDP address.
SelMode:
APN selection mode, temporary parameter set in the selection process to either of:
SelMode := ChosenBySGSN:
VPLMN AP:
Network-provided APN, subscription not verified.
SelMode := SentByMS:
MS-provided APN, subscription not verified.
SelMode := Subscribed:
MS or Network-provided APN, subscription verified.
VPLMN Access Point.
VPLMN OI:
VPLMN APN Operator Identifier or the APN Operator Identifier of an associated PLMN when the VPLMN is a shared network.
PDN-GW allocation type:
PDN-GW allocation type is not for the GGSN selection but only for the PDN-GW selection. It is either static or dynamic.
Static:
+:
for the determined APN, the selected PDN-GW has been statically allocated.
Dynamic:
for the determined APN, the selected PDN-GW can be dynamically allocated.
concatenation operation.
The subscription data may contain the information whether SIPTO is allowed or prohibited for each subscribed APN or the SGSN may know from configuration whether SIPTO is allowed or prohibited for a given APN. An indication that SIPTO is allowed or prohibited for the wild card APN allows or prohibits SIPTO for any APN that is not present in the subscription data. When a PDP context for SIPTO is established, the SGSN uses either the RAI (Routing Area Identity) and/or the serving RNC identifier depending on the operator's configuration during the DNS interrogation as specified in TS 29.303. In roaming scenario the GW selection for a PDP context with SIPTO is only possible when a GGSN or a P-GW in the visited PLMN is selected. Therefore in a roaming scenario with home routed traffic, GW selection for SIPTO is not performed. When the UE is in a network with A/Gb mode and SIPTO is allowed for the given APN, the RAI may also be used for PGW/GGSN selection. In this way when the UE enters UTRAN or E-UTRAN the PDP context deactivation with reactivation request to find an optimal PGW/GGSN for SIPTO may not be needed.
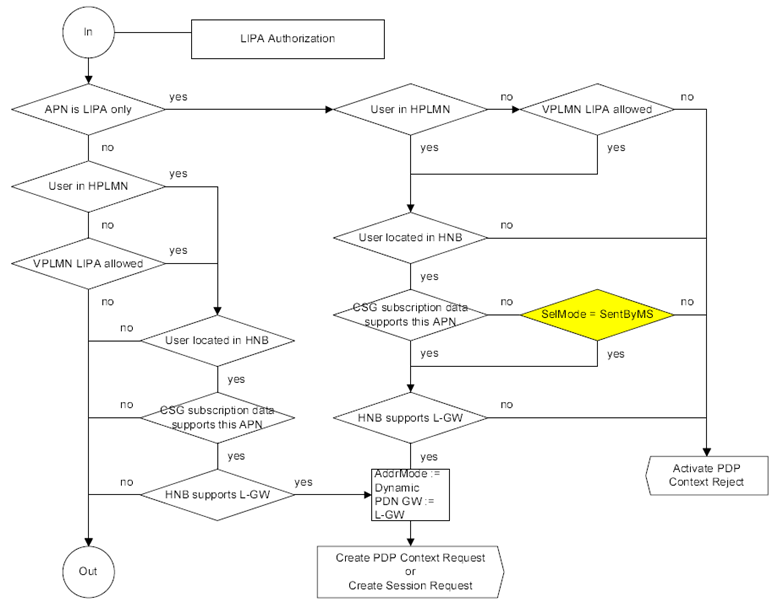
The subscription data may also contain the information on whether:
- an APN is LIPA-conditional, LIPA-prohibited, or LIPA-only;
- a CSG in the UE's CSG subscription data supports APN(s) that are LIPA-only or LIPA-conditional; and
- LIPA is allowed in a list of VPLMNs when roaming.
| Index | Gateway node | Interface type | Protocol on S5/S8 | Service parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GGSN | Gn/Gp | n.a. | no |
| 2 | P-GW | Gn/Gp | n.a. | yes |
| 3 | P-GW | S4 | GTPv2 | yes |
| 4 | P-GW | S4 | PMIP | yes |