Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
6.9 Location Management Function
6.9.0 General
6.9.1 Location Management Procedures (A/Gb mode)
6.9.1.1 Cell Update Procedure
6.9.1.2 Routeing Area Update Procedure
...
...
6.9 Location Management Function p. 109
6.9.0 General |R8| p. 109
The Location Management function provides:
- mechanisms for cell and PLMN selection;
- a mechanism for the network to know the Routeing Area for MSs in STANDBY, PMM IDLE, READY, and PMM CONNECTED states;
- a mechanism for the 2G SGSN to know the cell identity for MSs in READY state;
- a mechanism for the Iu mode RAN to know the RAN registration area identity or cell identity for MSs in PMM CONNECTED state;
- a mechanism for the Iu mode RAN to indicate to an MS in RRC Connected mode when a Routeing Area Update procedure shall be performed by providing the RAI; and
- a mechanism for the network in Iu mode to know the address of the serving BSC/RNC handling an MS in PMM CONNECTED state. This mechanism is the serving RNC relocation procedure.
6.9.1 Location Management Procedures (A/Gb mode) p. 109
The PLMN shall provide information for the MS to be able to:
- detect when it has entered a new cell or a new RA; and
- determine when to perform periodic RA updates.
- a cell update is required;
- a routeing area update is required; or
- a combined routeing area and location area update is required.
- It shall initiate the LA update and then initiate the RA update, if the MS is in class A mode of operation.
- It shall perform the LA update first if the MS is not in class A mode of operation.
6.9.1.1 Cell Update Procedure p. 110
A cell update takes place when the MS enters a new cell inside the current RA and the MS is in READY state. If the RA has changed, a routeing area update is executed instead of a cell update.
If the network does not support the Cell Notification which is an optimised Cell Update Procedure (see TS 24.008), the MS performs the cell update procedure by sending an uplink LLC frame of any type except the LLC NULL frame (see TS 44.064) containing the MS's identity to the SGSN. If the network and the MS support the Cell Notification, then the MS shall use the LLC NULL frame containing the MS's identity in order to perform a cell update. The support of Cell Notification is mandatory for the MS the network, but the network and the MS have to support the Cell Update Procedure without using the LLC NULL frame for backward compatibility reasons.
In the direction towards the SGSN, the BSS shall add the Cell Global Identity including RAC and LAC to all BSSGP frames, see TS 48.018. A cell update is any correctly received and valid LLC PDU carried inside a BSSGP PDU containing a new identifier of the cell.
The SGSN records this MS's change of cell and further traffic towards the MS is conveyed over the new cell. If requested by the GGSN according to charging requirements in clause 15.1.1a, the SGSN shall forward the new CGI to the GGSN based on the procedures defined in clause 15.1.3.2. If requested by the S-GW/P-GW according to charging requirements in clause 15.1.0, the SGSN shall forward the new CGI to the S-GW/P-GW based on the procedures defined in clause 15.1.3.2a.
6.9.1.2 Routeing Area Update Procedure p. 110
6.9.1.2.0 General |R8| p. 110
A Routeing Area Update takes place when a GPRS-attached MS detects:
- that it has entered a new RA (except for the case of an MS configured to perform GPRS Attach with IMSI when entering an RA in a new non-equivalent PLMN in RRC-IDLE mode);
- when the periodic RA update timer has expired;
- when the MS has to indicate changed access capabilities or DRX parameters to the network;
- when a change in conditions in the MS requires a change in the extended idle mode DRX parameters previously negotiated with the SGSN;
- for a UE supporting CS fallback, or configured to support IMS voice, or both, a change of the UE's usage setting or voice domain preference for E-UTRAN;
- for an SR-VCC capable MS, the MS has changed its MS Classmark 2, or MS Classmark 3, or Supported Codec information;
- for A/Gb mode, when a suspended MS is not resumed by the BSS (see clause "Suspension of GPRS Services");
- when the MS reselects GERAN/UTRAN with the TIN indicating "GUTI";
- when the MS moves from E-UTRAN-connected to GERAN via Cell Change Order that is not for CS fallback. If the TIN indicates "RAT-related TMSI" the MS shall set the TIN to "GUTI" before initiating the RA update procedure;
- the RRC layer in an E-UTRAN capable UE informs the UE's NAS layer that an RRC connection failure occurred in E-UTRAN and this led the MS to select a GERAN/UTRAN cell;
- when the UE Network Capability and/or MS Network Capability are changed; or
- that it is registered for IMS voice and has moved from a RAT that supports IMS voice over PS sessions (see clause 5.3.8 for more information) to one that does not, or vice versa. It shall be possible using Device Management or initial provisioning to configure the UE to apply/not apply this particular exception.
6.9.1.2.1 Intra SGSN Routeing Area Update p. 111
The Intra SGSN Routeing Area Update procedure is illustrated in Figure 32. This procedure applies for S4-SGSNs and for Gn/Gp SGSNs.
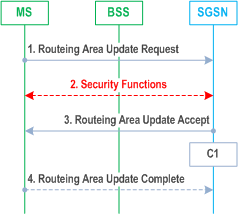
1)
For some network sharing scenario (e.g. GWCN) if the PLMN-ID of the RAI supplied by the RNC is different from that of the RAI in the UE's context, then the SGSN shall informs the HLR.
If the routeing area update procedure fails a maximum allowable number of times, or if the SGSN returns a Routeing Area Update Reject (Cause) message, the MS shall enter IDLE state.
The CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedure in TS 23.078 C1:
The MS sends a Routeing Area Update Request (P-TMSI, old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature, Update Type, MS Radio Access Capability, DRX parameters, extended idle mode DRX parameters, MS Network Capability, Support for restriction of use of Enhanced Coverage, additional P-TMSI/RAI, Voice domain preference and UE's usage setting) to the SGSN. Update Type shall indicate RA update or periodic RA update. The BSS shall add the Cell Global Identity including the RAC and LAC of the cell where the message was received before passing the message to the SGSN, see TS 48.018. MS Radio Access Capability contains the MS GPRS multislot capabilities, supported frequency bands, etc as defined in TS 24.008. DRX Parameters are included if the MS has altered its DRX Parameters. Extended idle mode DRX parameters information element is included if the MS wants to enable extended idle mode DRX.
If the E-UTRAN capable UE's TIN indicates "GUTI" and the UE holds a valid GUTI then the UE indicates the GUTI as the old P-TMSI and old RAI. If the UE's TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT related TMSI" and the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then these two elements are indicated as old P-TMSI and old RAI. Mapping a GUTI to a P-TMSI and an RAI is specified in TS 23.401. In this scenario of intra SGSN RAU, the TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT-related TMSI".
If the E-UTRAN capable UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then the UE indicates these parameters as additional P-TMSI/RAI, regardless whether the old P-TMSI and old RAI indicate the same parameters or parameters mapped from a GUTI.
The Gn/Gp SGSN shall ignore this additional P-TMSI/RAI.
The UE sets the voice domain preference and UE's usage setting according to its configuration, as described in clause 5.3.15.
2)
Security functions may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "Security Function".
3)
The SGSN validates the MS's presence in the new RA. If, due to regional subscription restrictions, the MS is not allowed to be attached in the RA, or if subscription checking fails, the SGSN rejects the routeing area update with an appropriate cause. If all checks are successful, the SGSN updates the MM context for the MS. A new P-TMSI may be allocated. A Routeing Area Update Accept (P-TMSI, P-TMSI Signature, IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication, SMS-Supported, Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter) is returned to the MS. The IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication is set as described in clause 5.3.8.
If ISR is activated for the MS when the S4-SGSN receives the Routeing Area Update Request in the intra SGSN scenario, the S4-SGSN should maintain ISR by indicating ISR Activated in the Routeing Area Update Accept message.
If the SGSN decides to enable extended idle mode DRX for an MS that included the extended idle mode DRX parameters, it includes the extended idle mode DRX parameters information element.
"SMS-Supported" is indicated to the MS when the HSS has indicated "SMS in SGSN Support". It indicates to the MS that it can obtain SMS services via PS domain NAS from the SGSN. An MS that needs only PS services and SMS services over NAS should not perform any procedures via CS domain when it can obtain SMS services via PS domain NAS from SGSN.
If the MS included support for restriction of use of Enhanced Coverage, the SGSN sends Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter to the MS in the Routeing Area Update Accept message. MS shall store Enhanced Coverage Allowed parameter and shall use the value of Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter to determine if enhanced coverage feature should be used or not.
4)
If P-TMSI was reallocated, the MS acknowledges the new P-TMSI by returning a Routeing Area Update Complete message to the SGSN.
C1)
CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session, CAMEL_PS_Notification and CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Context.
They are called in the following order:
- The procedure CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session is called once per session. It returns as a result "Continue".
- Then the procedure CAMEL_PS_Notification is called once per session. It returns as a result "Continue".
- Then the procedure CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Context is called once per PDP context. It returns as a result "Continue".
6.9.1.2.2 Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update p. 113
The Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update procedure is illustrated in Figure 33 for mobility between two Gn/Gp SGSNs and for mobility from S4-SGSN to Gn/Gp SGSN. The Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update procedure between two S4-SGSNs shows differences for the steps in the boxes (A) and (B). The Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update procedure from Gn/Gp SGSN to S4-SGSN shows differences for the steps in the box (B). These different step descriptions of the boxes are described in clause "Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update and Combined Inter SGSN RA / LA Update using S4".
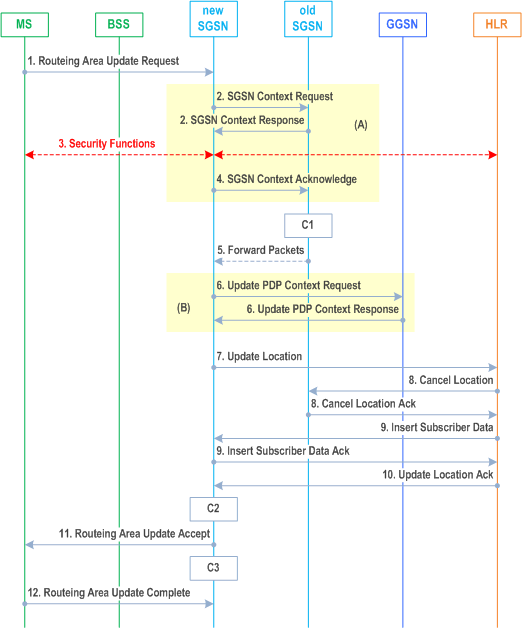
Step 1.
Step 2.
Step 3.
Step 4.
Step 5.
Step 6.
Step 7.
Step 8.
Step 9.
Step 10.
Step 11.
Step 12.
For a rejected routeing area update operation, due to regional subscription, roaming restrictions, access restrictions (see TS 23.221 and TS 23.008) or because the SGSN cannot determine the HLR address to establish the locating updating dialogue, the new SGSN should not construct an MM context. In the case of receiving the subscriber data from HLR, the new SGSN may construct an MM context and store the subscriber data for the MS to optimize signalling between the SGSN and the HLR. A reject shall be returned to the MS with an appropriate cause. Upon return to idle, the MS shall act according to TS 23.122.
If the new SGSN is unable to update the PDP context/EPS Bearer Context in one or more GGSNs/P-GWs, the new SGSN shall deactivate the corresponding PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure". This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routeing area update.
The PDP Contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts shall be sent from old to new SGSN in a prioritized order, i.e. the most important PDP Context/EPS Bearer Context first in the SGSN Context Response message. (The prioritization method is implementation dependent, but should be based on the current activity).
The new SGSN shall determine the Maximum APN restriction based on the received APN Restriction of each PDP context/EPS Bearer Context from the GGSN/P-GW or old S4-SGSN and then store the new Maximum APN restriction value.
If the new SGSN is unable to support the same number of active PDP contexts as received from old SGSN, the new SGSN should use the prioritisation sent by old SGSN as input when deciding which PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts to maintain active and which ones to delete. In any case, the new SGSN shall first update all contexts in one or more GGSNs/P-GWs and then deactivate the context(s) that it cannot maintain as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure". This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routeing area update.
If the timer described in step 2 expires and no Cancel Location (IMSI) was received from the HLR, the old SGSN stops forwarding N PDUs to the new SGSN.
If the routeing area update procedure fails a maximum allowable number of times, or if the SGSN returns a Routeing Area Update Reject (Cause) message, the MS shall enter IDLE state.
If "SMS-Supported" is indicated to the MS, the MS should not initiate Location Update or IMSI attach with the MSC for only obtaining SMS services as SMS services via PS domain NAS are provided by the SGSN.
The CAMEL procedure calls shall be performed, see referenced procedures in TS 23.078:
The MS sends a Routeing Area Update Request (old RAI, old P-TMSI Signature, Update Type, MS Radio Access Capability, DRX parameters, extended idle mode DRX parameters, MS Network Capability, Support for restriction of use of Enhanced Coverage, additional P-TMSI/RAI, Voice domain preference and UE's usage setting) to the new SGSN. Update Type shall indicate RA update or periodic RA update. The BSS shall add the Cell Global Identity including the RAC and LAC of the cell where the message was received before passing the message to the SGSN. MS Radio Access Capability contains the MS GPRS multislot capabilities, supported frequency bands, etc. as defined in TS 24.008. DRX Parameters are included if the MS has altered its DRX Parameters. Extended idle mode DRX parameters information element is included if the MS wants to enable extended idle mode DRX.
If the E-UTRAN capable UE's TIN indicates "GUTI" and the UE holds a valid GUTI then the UE indicates the GUTI as the old P-TMSI and old RAI. If the UE's TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT related TMSI" and the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then these two elements are indicated as old P-TMSI and old RAI. Mapping a GUTI to a P-TMSI and an RAI is specified in TS 23.401. In this scenario of inter SGSN RAU, the TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT related TMSI".
If the E-UTRAN capable UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then the UE indicates these parameters as additional P-TMSI/RAI, regardless whether the old P-TMSI and old RAI indicate the same parameters or parameters mapped from a GUTI.
The Gn/Gp SGSN shall ignore this additional P-TMSI/RAI.
The UE sets the voice domain preference and UE's usage setting according to its configuration, as described in clause 5.3.15.
Step 2.
The new SGSN sends SGSN Context Request (old RAI, TLLI, old P-TMSI Signature, New SGSN Address) to the old SGSN to get the MM and PDP contexts for the MS. If the new SGSN provides functionality for Intra Domain Connection of RAN Nodes to Multiple CN Nodes, the new SGSN may derive the old SGSN from the old RAI and the old P-TMSI (or TLLI) and send the SGSN Context Request message to this old SGSN. Otherwise, the new SGSN derives the old SGSN from the old RAI. In any case the new SGSN will derive an SGSN that it believes is the old SGSN. This derived SGSN is itself the old SGSN, or it is associated with the same pool area as the actual old SGSN and it will determine the correct old SGSN from the P-TMSI (or TLLI) and relay the message to that actual old SGSN. The old SGSN validates the old P-TMSI Signature and responds with an appropriate error cause if it does not match the value stored in the old SGSN. This should initiate the security functions in the new SGSN. If the security functions authenticate the MS correctly, the new SGSN shall send an SGSN Context Request (old RAI, TLLI, MS Validated, New SGSN Address) message to the old SGSN. MS Validated indicates that the new SGSN has authenticated the MS. If the old P-TMSI Signature was valid or if the new SGSN indicates that it has authenticated the MS, the old SGSN stops assigning SNDCP N PDU numbers to downlink N PDUs received, and responds with SGSN Context Response (MM Context, PDP Contexts, Negotiated Evolved ARP). If the MS is not known in the old SGSN, the old SGSN responds with an appropriate error cause. The old SGSN stores New SGSN Address, to allow the old SGSN to forward data packets to the new SGSN. Each PDP Context includes the SNDCP Send N PDU Number for the next downlink N PDU to be sent in acknowledged mode to the MS, the SNDCP Receive N PDU Number for the next uplink N PDU to be received in acknowledged mode from the MS, the GTP sequence number for the next downlink N PDU to be sent to the MS and the GTP sequence number for the next uplink N PDU to be tunnelled to the GGSN. The old SGSN starts a timer and stops the transmission of N-PDUs to the MS. The new SGSN shall ignore the MS Network Capability contained in MM Context of SGSN Context Response only when it has previously received an MS Network Capability in the Routeing Area Request.
SNDCP and GTP sequence numbers are not relevant for a new S4-SGSN if provided by an old Gn/Gp SGSN and need not to be provided by an old S4-SGSN as the EPS network shall not configure usage of "delivery order required" and no acknowledged mode NSAPIs (SNDCP) as described in clause "Network Configuration for Interaction with E-UTRAN and S4-SGSNs".
If the MS uses power saving functions and the DL Data Buffer Expiration Time for the MS has not expired, the old SGSN indicates Buffered DL Data Waiting. When this is indicated, data forwarding from the old SGSN to the new SGSN shall be done and the user plane set up in conjunction to the RAU procedure (see clause 5.3.13.7).
If the new SGSN supports CIoT GSM Optimization, the CIoT GSM Optimization support indication is included in the SGSN Context Request indicating support for various CIoT Optimisations (e.g. support for Non-IP data, SCEF, etc.).
Based on the CIoT GSM Optimization support indication, old SGSN only transfers the PDP Context(s) that the new SGSN supports. If the new SGSN does not support CIoT GSM Optimization, Non-IP PDP Context(s) are not transferred to the new SGSN. If the PDP Context(s) has not been transferred, the old SGSN deactivate that PDP Context(s) and any buffered data in the old SGSN is discarded after receipt of SGSN Context Acknowledge.
Step 3.
Security functions may be executed. These procedures are defined in clause "Security Function". Ciphering mode shall be set if ciphering is supported. If the SGSN Context Response message did not include IMEISV and ADD is supported by the SGSN, the SGSN retrieves the IMEISV from the MS.
If the security functions fail (e.g. because the SGSN cannot determine the HLR address to establish the Send Authentication Info dialogue), the Inter SGSN RAU Update procedure fails. A reject shall be returned to the MS with an appropriate cause.
Step 4.
The new SGSN sends an SGSN Context Acknowledge message to the old SGSN. This informs an old Gn/Gp SGSN that the new SGSN is ready to receive data packets belonging to the activated PDP contexts. Only old Gn/Gp SGSNs may forward data to a new Gn/Gp or S4-SGSN.
The old SGSN marks in its context that the MSC/VLR association and the information in the GGSNs and the HLR are invalid. This triggers the MSC/VLR, the GGSNs, and the HLR to be updated if the MS initiates a routeing area update procedure back to the old SGSN before completing the ongoing routeing area update procedure. If the security functions do not authenticate the MS correctly, then the routeing area update shall be rejected, and the new SGSN shall send a reject indication to the old SGSN. The old SGSN shall continue as if the SGSN Context Request was never received.
Step 5.
Only old Gn/Gp SGSNs may forward data to a new SGSN. An old Gn/Gp SGSN duplicates the buffered N PDUs and starts tunnelling them to the new SGSN. Additional N PDUs received from the GGSN before the timer described in step 2 expires are also duplicated and tunnelled to the new SGSN. N PDUs that were already sent to the MS in acknowledged mode and that are not yet acknowledged by the MS are tunnelled together with the SNDCP N PDU number. No N PDUs shall be forwarded to the new SGSN after expiry of the timer described in step 2.
SNDCP N-PDU numbers are not relevant for S4-SGSNs as the network shall not configure usage of acknowledged mode NSAPIs (SNDCP) as described in clause "Network Configuration for Interaction with E-UTRAN and S4-SGSNs". A new S4-SGSN indicates reserved TEID and IP address parameters from an SGW to an old Gn/Gp SGSN so that the old Gn/Gp SGSN can forward data packets when needed. The SGW discards any packets received from old Gn/Gp SGSN.
Step 6.
The new SGSN sends Update PDP Context Request (new SGSN Address, TEID, QoS Negotiated, Negotiated Evolved ARP, serving network identity, CN Operator Selection Entity, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, NRSN) to the GGSNs concerned. The SGSN shall send the serving network identity and the CN Operator Selection Entity to the GGSN. The CN Operator Selection Entity indicates whether the Serving Network has been selected by the UE or by the network. NRSN indicates SGSN support of the network requested bearer control. The inclusion of the Negotiated Evolved ARP IE indicates that the SGSN supports the Evolved ARP feature. If the new SGSN did not receive a Negotiated Evolved ARP IE in the SGSN Context Response message from the old SGSN then the new SGSN shall derive this value from the Allocation/Retention Priority of the QoS profile negotiated according to Annex E of TS 23.401. The GGSNs update their PDP context fields and return Update PDP Context Response (TEID, Prohibit Payload Compression, APN Restriction, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action, BCM, Negotiated Evolved ARP). The GGSN sets the Negotiated Evolved ARP based on local policy or PCC. The Allocation/Retention Priority of the QoS Profile Negotiated is derived from the Evolved ARP according to the mapping principles of TS 23.401 Annex E. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this PDP context. User CSG Information includes CSG ID, access mode and CSG membership indication. The SGSN shall apply the Negotiated Evolved ARP if received from the GGSN.
If the new SGSN receives PDP context with SCEF, then the new SGSN updates the SCEF as defined in TS 23.682.
Step 7.
The new SGSN informs the HLR of the change of SGSN by sending Update Location (SGSN Number, SGSN Address, IMSI, IMEISV, UE SRVCC capability, Registration For SMS Request) to the HLR. IMEISV is sent if the ADD function is supported. If the S6d interface is used between S4-SGSN and HSS, a parameter "SMS in SGSN offered" is included in the Update Location message, otherwise this parameter is included in the Insert Subscriber Data Ack (Step 9). "SMS in SGSN offered" indicates that the SGSN supports SMS services via SGSN.
If the MS performs the Routeing Area Update procedure in a VPLMN supporting Autonomous CSG Roaming and the HPLMN has enabled Autonomous CSG Roaming in the VPLMN (via Service Level Agreement) and the SGSN needs to retrieve the CSG subscription information of the MS from the CSS, the SGSN initiates the Update CSG Location Procedure with CSS as described in clause 6.16.
Step 8.
The HLR sends Cancel Location (IMSI, Cancellation Type) to the old SGSN with Cancellation Type set to Update Procedure. If the timer described in step 2 is not running, the old SGSN removes the MM and PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts and an old S4-SGSN releases in addition the S-GW resources when the new SGSN is a Gn/Gp SGSN or when an S-GW change is performed. GTPv1 SGSN context transfer signalling indicates to the old S4-SGSN that the new SGSN is a Gn/Gp SGSN, which does not signal any S-GW change. When the timer described in step 2 is running, the MM and PDP/EPS Bearer Contexts and any affected S-GW resources are removed when the timer expires and the SGSN received a Cancel Location. The old S4-SGSN deletes S-GW bearer resources by sending Delete Session Request (Cause, Operation Indication) messages to the SGW. If ISR is activated the Cause indicates that the old S-GW shall delete the bearer resources on the other old CN node by sending Delete Bearer Request message to the other CN node. The Operation Indication flag is not set by the old S4-SGSN. This indicates to the S-GW that the S-GW shall not initiate a delete procedure towards the PDN-GW.
When the timer described in step 2 expires and no Cancel Location was received the S4-SGSN removes the PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts but preserves the MM context.
The timer started in step 2 allows the old SGSN to complete the forwarding of N PDUs. It also ensures that the MM and PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts are kept in the old SGSN in case the MS initiates another inter-SGSN routeing area update before completing the ongoing routeing area update to the new SGSN. The old SGSN acknowledges with Cancel Location Ack (IMSI).
Step 9.
The HLR sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, Subscription Data) to the new SGSN. The subscription data may contain Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter. If received from the HLR, SGSN stores this Enhanced Coverage Allowed parameter in the SGSN MM context. The new SGSN validates the MS's presence in the (new) RA. If due to regional subscription restrictions or access restrictions the MS is not allowed to be attached in the RA, the SGSN rejects the Routeing Area Update Request with an appropriate cause, and may return an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI, SGSN Area Restricted) message to the HLR. If all checks are successful, the SGSN constructs an MM context for the MS and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack (IMSI, SMS in SGSN offered) message to the HLR. The "SMS in SGSN offered" indicates that the SGSN supports SMS services via SGSN. If the S6d interface is used between S4-SGSN and HSS the messages "Insert Subscriber Data" and "Insert Subscriber Data Ack" are not used. Instead, the Subscription Data is sent by HSS in the message Update Location Ack (Step 10).
Step 10.
The HLR acknowledges the Update Location by sending Update Location Ack (IMSI, GPRS Subscriber Data (only if S6d interface is used)) to the new SGSN.
Step 11.
The new SGSN validates the MS's presence in the new RA. If due to roaming restrictions or access restrictions the MS, is not allowed to be attached in the SGSN, or if subscription checking fails, the new SGSN rejects the routeing area update with an appropriate cause. If all checks are successful, the new SGSN constructs MM and PDP contexts/EPS Bearer Contexts for the MS. A logical link is established between the new SGSN and the MS. The new SGSN responds to the MS with Routeing Area Update Accept (P-TMSI, P-TMSI Signature, Receive N PDU Number, IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication, SMS-Supported, Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter). Receive N PDU Number contains the acknowledgements for each acknowledged-mode NSAPI used by the MS, thereby confirming all mobile-originated N PDUs successfully transferred before the start of the update procedure. The IMS voice over PS Session Supported Indication is set as described in clause 5.3.8.
ISR Activated is never indicated to the MS in case of inter SGSN RAU as described in TS 23.401. The E-UTRAN capable UE sets its TIN to "P-TMSI" or "RAT related TMSI" as described for Routing Area Update procedures in TS 23.401.
"SMS-Supported" is indicated to the MS when the HSS has indicated "SMS in SGSN Support". It indicates to the MS that it can obtain SMS services via PS domain NAS from the SGSN.
If the MS included support for restriction of use of Enhanced Coverage, the SGSN sends Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter to the MS in the Routeing Area Update Accept message. MS shall store Enhanced Coverage Allowed parameter and shall use the value of Enhanced Coverage Restricted parameter to determine if enhanced coverage feature should be used or not.
In Iu mode, if after step 6 the new SGSN receives a Downlink Data Notification message or any other downlink signalling message while the MS is still connected, the new SGSN may prolong the PS signalling connection with the MS.
If the SGSN decides to enable extended idle mode DRX for an MS that included extended idle mode DRX parameters information element, it includes the extended idle mode DRX parameters information element.
Step 12.
The MS acknowledges the new P-TMSI by returning a Routeing Area Update Complete (Receive N PDU Number) message to the SGSN. Receive N PDU Number contains the acknowledgements for each acknowledged-mode NSAPI used by the MS, thereby confirming all mobile-terminated N PDUs successfully transferred before the start of the update procedure. If Receive N PDU Number confirms reception of N PDUs that were forwarded from the old SGSN, these N PDUs shall be discarded by the new SGSN. LLC and SNDCP in the MS are reset.
C1)
This procedure is called several times: once per PDP context. It returns as result "Continue".
CAMEL_GPRS_PDP_Context_Disconnection, CAMEL_GPRS_Detach and CAMEL_PS_Notification.
They are called in the following order:
C2)
- The CAMEL_GPRS_PDP_Context_Disconnection procedure is called several times: once per PDP context. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- Then the CAMEL_GPRS_Detach procedure is called once. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- Then the CAMEL_PS_Notification procedure is called once. The procedure return as result "Continue".
CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session and CAMEL_PS_Notification.
They are called in the following order:
C3)
- The CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Session procedure is called. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
- Then the CAMEL_PS_Notification procedure is called. The procedure returns as result "Continue".
CAMEL_GPRS_Routeing_Area_Update_Context.
6.9.1.2.2a Inter SGSN Routeing Area Update and Combined Inter SGSN RA / LA Update using S4 |R8| p. 118
The procedures described in figures 33a and 33b show only the steps 2 and 4 for the case when new and old SGSNs are S4-SGSNs and step 6 when the new SGSN is an S4-SGSN. These steps are different from the Gn/Gp variant of the procedure given by clauses 6.9.1.2.2 and 6.9.1.3.2. The ISR function is deactivated in Inter SGSN RAU as defined in TS 23.401.

2)
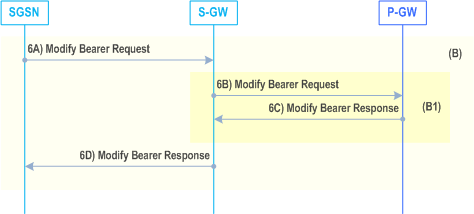 6A)
6A)
The new SGSN sends a Context Request (old RAI, TLLI, old P-TMSI Signature, New SGSN Address) to the old SGSN to get the MM and EPS Bearer contexts for the MS. If the new SGSN provides functionality for Intra Domain Connection of RAN Nodes to Multiple CN Nodes, the new SGSN may derive the old SGSN from the old RAI and the old P-TMSI (or TLLI) and send the Context Request message to this old SGSN. Otherwise, the new SGSN derives the old SGSN from the old RAI. In any case the new SGSN will derive an SGSN that it believes is the old SGSN. This derived SGSN is itself the old SGSN, or it is associated with the same pool area as the actual old SGSN and it will determine the correct old SGSN from the P-TMSI (or TLLI) and relay the message to that actual old SGSN. The old SGSN validates the old P-TMSI Signature and responds with an appropriate error cause if it does not match the value stored in the old SGSN. This should initiate the security functions in the new SGSN. If the security functions authenticate the MS correctly, the new SGSN shall send a Context Request (old RAI, TLLI, MS Validated) message to the old SGSN. MS Validated indicates that the new SGSN has authenticated the MS. If the old P-TMSI Signature was valid or if the new SGSN indicates that it has authenticated the MS, the old SGSN responds with a Context Response (MM Context, EPS Bearer Contexts). MM Context and EPS Bearer Context when used at the S16 interface are defined by clause 13.2.2. If the MS is not known in the old SGSN, the old SGSN responds with an appropriate error cause. The old SGSN starts a timer and stops the transmission of N PDUs to the MS. The new SGSN shall ignore the MS Network Capability contained in MM Context of Context Response only when it has previously received an MS Network Capability in the Routeing Area Request.
For RAU between two S4-SGSNs, the old SGSN shall include the Change Reporting Action and CGI/SAI/RAI change support indication in the Context Response message.
If the new SGSN supports CIoT GSM Optimization, CIoT GSM Optimization support indication is included in the Context Request indicating support for various CIoT Optimisations (e.g. support for Non-IP data, SCEF, etc.).
Based on the CIoT GSM Optimization support indication, old SGSN only transfers the PDP Context(s) that the new SGSN supports. If the new SGSN does not support CIoT GSM Optimization, Non-IP PDP Context(s) are not transferred to the new SGSN. If the PDP Context(s) has not been transferred, the old SGSN deactivate that PDP Context(s). Any buffered data in the old SGSN is discarded.
4)
The new SGSN sends a Context Acknowledge message to the old SGSN. The old SGSN marks in its context that the MSC/VLR association and the information in the GWs and the HSS are invalid. This triggers the MSC/VLR, the S-GW, the P-GW and the HSS to be updated if the MS initiates a routeing area update procedure back to the old SGSN before completing the ongoing routeing area update procedure. If the security functions do not authenticate the MS correctly, then the routeing area update shall be rejected, and the new SGSN shall send a reject indication to the old SGSN. The old SGSN shall continue as if the Context Request was never received.

If the S-GW does not change, the new SGSN updates these EPS Bearer contexts by sending Modify Bearer Request (SGSN Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, EPS Bearer ID(s), SGSN Address for Control Plane, SGSN Address(es) and TEID(s), PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP-based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, serving network identity, CN Operator Selection Entity, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication). The SGSN puts the according NSAPI in the field of EPS Bearer ID. If ISR is activated on the S-GW that is updated by a new SGSN then this S-GW deletes the bearer resources on the other old CN node by sending Delete Session Request message(s) to that CN node.
If the S-GW changes or if an S-GW needs to be allocated (Gn/Gp to S4-SGSN RAU) the SGSN selects an S-GW and sends a Create Session Request message (APN-AMBR) with the content as described for the Modify Bearer Request message to the S-GW.
For Gn/Gp to S4-SGSN RAU, the new S4-SGSN provides APN-AMBR to the Serving GW. Details on mapping MBR to APN-AMBR are specified in Annex E of TS 23.401.
If the new SGSN receives the PDP context with SCEF, then the new SGSN updates the SCEF as defined in TS 23.682.
6B)
If the S-GW has changed, or if an S-GW needs to be allocated (Gn/Gp to S4-SGSN RAU), or the RAT type has changed, or the S-GW received CGI/SAI from the S4-SGSN, the S-GW sends Modify Bearer Request (EPS Bearer ID(s), serving network identity, CN Operator Selection Entity, CGI/SAI, User CSG Information, RAT type, MS Info Change Reporting support indication, APN-AMBR) messages to the P-GWs involved.
6C)
The P-GWs acknowledge by sending Modify Bearer Response (TEID, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action, Default bearer id, APN-AMBR) messages to S-GW. The Prohibit Payload Compression indicates that the SGSN should negotiate no data compression for this PDP/EPS Bearer context. The default bearer id is included if the UE moves from a Gn/Gp SGSN to an S4-SGSN.
6D)
The S-GW acknowledges the user plane switch to the new SGSN via the message Modify Bearer Response (Cause, Serving GW Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for Control Plane, Serving GW Address for Control Plane, PDN-GW addresses and TEIDs (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP-based S5/S8) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic, Prohibit Payload Compression, MS Info Change Reporting Action, CSG Information Reporting Action, default bearer id, APN-AMBR). If the SGSN sent a Create Session Request message the S-GW sends a Create Session Response message with the content as described for the Modify Bearer Response message to the SGSN.
If there are active GBR bearers with maximum bit rate set to 0, the S4-SGSN should use the SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure using S4 (as defined in clause 9.2.4.2) to deactivate the PDP Context.
When the SGSN receives the Modify Bearer Response message, the SGSN checks if there is a "Notify-on-available-after-DDN-failure" monitoring event or a "UE Reachability" monitoring event configured for the UE in the SGSN and in such a case sends an event notification according to TS 23.682.