Content for TS 23.060 Word version: 18.0.0
1…
5…
5.3.8…
5.4…
5.4.2…
5.4.9…
5.6…
5.6.2
5.6.3…
5.6.3.7…
5.7…
6…
6.3…
6.5…
6.6…
6.8…
6.9…
6.9.1.3
6.9.2…
6.9.2.2…
6.9.2.2.2
6.9.2.2.3…
6.9.2.2.5…
6.9.3…
6.10…
6.12…
6.13…
6.13.1.2…
6.13.2…
6.13.2.2
6.14…
8…
8.2
9…
9.2.2…
9.2.2.2
9.2.2.3…
9.2.3…
9.2.3.2…
9.2.3.3…
9.2.4…
9.2.4.2…
9.2.5…
12…
12.5…
12.6…
12.7…
12.8…
13…
14…
15…
15.3…
16…
16.2…
A…
B…
5.6.3.7 Core Network Node - Core Network Node
5.6.3.8 GGSN - HLR
5.6.3.9 S4-SGSN - HSS
5.6.3.10 Gn/Gp-SGSN - CSS
5.6.3.11 S4-SGSN - CSS
5.6.3.12 SGSN - RCAF (Iu mode)
...
...
5.6.3.7 Core Network Node - Core Network Node p. 68
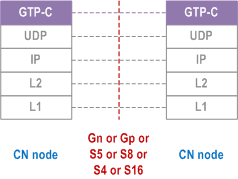
Legend:
- GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for the control plane (GTP-C): This protocol tunnels signalling messages between SGSNs and GGSNs (Gn or Gp), between SGSNs and S-GWs (S4), between S-GWs and P-GWs (S5 or S8) and between SGSNs in the backbone network (Gn or S16).
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP): This protocol transfers signalling messages between GSNs. UDP is defined in RFC 768.
5.6.3.8 GGSN - HLR p. 68
This optional signalling path allows a GGSN to exchange signalling information with an HLR. There are two alternative ways to implement this signalling path:
- If an SS7 interface is installed in the GGSN, the MAP protocol can be used between the GGSN and an HLR.
- If an SS7 interface is not installed in the GGSN, any GSN with an SS7 interface installed in the same PLMN as the GGSN can be used as a GTP-to-MAP protocol converter to allow signalling between the GGSN and an HLR.
5.6.3.8.1 MAP-based GGSN - HLR Signalling p. 68
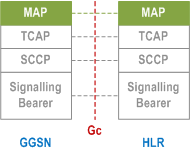
Legend:
- Mobile Application Part (MAP): This protocol supports signalling exchange with the HLR, as described in clause "Network-Requested PDP Context Activation Procedure".
5.6.3.8.2 GTP and MAP-based GGSN - HLR Signalling p. 69
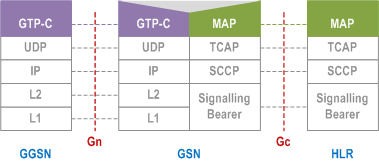
Legend:
- GPRS Tunnelling Protocol for the control plane (GTP-C): This protocol tunnels signalling messages between the GGSN and the protocol-converting GSN in the backbone network.
- Interworking: This function provides interworking between GTP and MAP for GGSN HLR signalling.
5.6.3.9 S4-SGSN - HSS |R8| p. 69
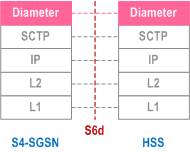
Legend:
- Diameter Base+Apps: Diameter Base Protocol as defined in RFC 3588. The Apps are various Diameter Applications as necessary for the operation between SGSN and HSS.
- SCTP: This protocol guarantees delivery of upper layer packets between SGSN and the HSS with built-in redundancy scheme. SCTP is defined in RFC 4960.
5.6.3.10 Gn/Gp-SGSN - CSS |R11| p. 70
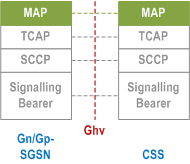
Legend:
- Mobile Application Part (MAP): This protocol supports signalling between Gn/Gp-SGSN and CSS, as defined in clause "Mobility Management Functionality".
5.6.3.11 S4-SGSN - CSS |R11| p. 70
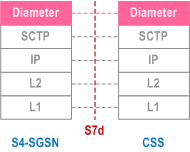
Legend:
5.6.3.12 SGSN - RCAF (Iu mode) |R13| p. 71
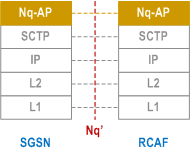
Legend:
- Nq-AP: This application layer protocol supports the APN information retrieval procedure between the RCAF and the SGSN.
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP): This protocol transfers signalling messages. SCTP is defined in RFC 4960.