Content for TS 38.401 Word version: 18.4.0
1…
5…
6…
6.1.4
6.1.5…
6.2…
7…
8…
8.2…
8.2.1.4…
8.2.2…
8.2.3…
8.2.4
8.2.5
8.3…
8.4…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.9…
8.9.4…
8.9.6…
8.9.7…
8.10
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
8.15.2…
8.16…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4
8.18…
8.19…
8.19.2
8.19.3
8.19.4…
8.21…
8.22…
8.23…
8.24…
9…
A…
8.24 Timing resiliency service
8.24.1 RAN TSS reporting towards the CN
8.24.2 RAN TSS reporting towards the UE
...
...
8.24 Timing resiliency service |R18| p. 151
The following clauses describe the overall procedures for RAN Timing Synchronisation Status (TSS) reporting involving gNB-CU/gNB-DU.
8.24.1 RAN TSS reporting towards the CN p. 151
The signaling flow for RAN TSS reporting towards the CN is shown in Figure 8.24.1-1. This procedure is used when the TSCTSF subscribes to RAN TSS reporting at the AMF as described in TS 23.502.
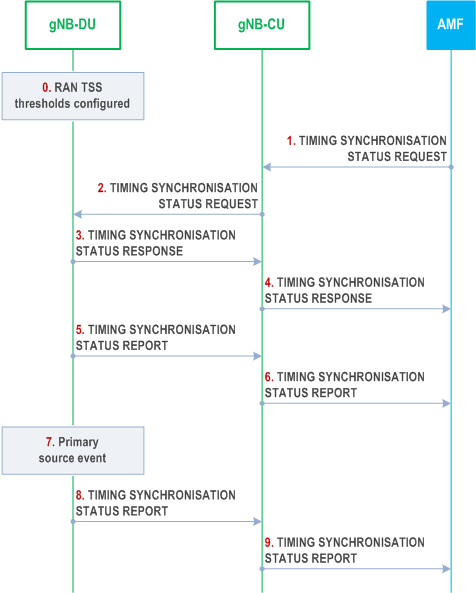
Step 0.
The gNB-DU is pre-configured with a threshold for each RAN TSS attribute it supports. The gNB-DU does not report RAN TSS attribute values better than the pre-configured thresholds, i.e. if a RAN TSS attribute has a value better than the pre-configured threshold, the gNB-DU reports the threshold value to the gNB-CU instead.
Step 1.
The AMF requests RAN TSS reporting by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REQUEST message to the gNB-CU.
Step 2.
The gNB-CU requests RAN TSS reporting from at least one gNB-DU by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REQUEST message to the gNB-DU.
Step 3.
The gNB-DU replies to the gNB-CU by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS RESPONSE message.
Step 4.
The gNB-CU replies to the AMF by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS RESPONSE message. If the gNB-CU does not receive a successful response from at least one gNB-DU, the gNB-CU replies to the AMF by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS FAILURE message and the flow stops at this step.
Step 5.
Upon sending the response to the gNB-CU, the gNB-DU provides a first RAN TSS report to the gNB-CU by sending the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REPORT message.
Step 6.
The gNB-CU sends the TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REPORT message to the AMF. The message contains the RAN TSS attributes received from the gNB-DU and the RAN TSS Scope IE to indicate whether the scope of the RAN TSS report is "RAN node level" or "cell list level".
Step 7.
Later, the gNB-DU detects a primary source event:
Step 8.
- a RAN TSS attribute cannot meet a pre-configured threshold (i.e. status is degraded);
- a RAN TSS attribute meets the pre-configured threshold again (i.e. status is no longer degraded);
- event a) occurred and b) has not yet been reached for a RAN TSS attribute, and either an implementation-dependent time interval has passed or a previously reported value can no longer be met.
Upon detecting the primary source event, the gNB-DU provides an updated RAN TSS report to the gNB-CU by sending a TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REPORT message.
Step 9.
Same as step 6.
8.24.2 RAN TSS reporting towards the UE p. 153
The signaling flow for RAN TSS reporting towards the UE in RRC_CONNECTED state is shown in Figure 8.24.2-1.
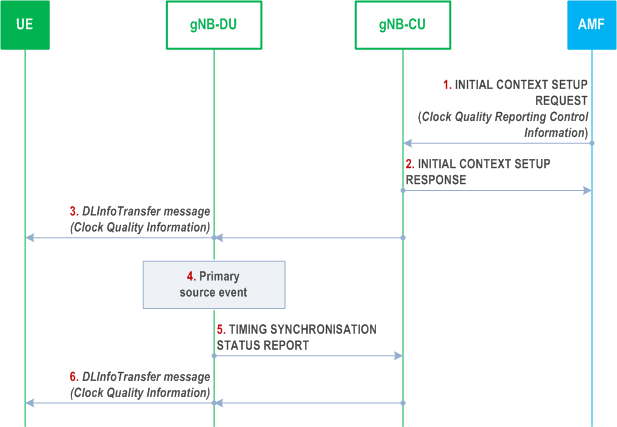
Step 1.
The AMF sends the INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP REQUEST message to the gNB-CU, containing the Clock Quality Reporting Control Information IE within the Time Synchronization Assistance Information IE. The clock quality reporting control information indicates the clock quality detail level to provide to the UE, i.e. "metrics" or "acceptable/not acceptable indication". If clock quality detail level equals "acceptable/not acceptable indication", the clock quality reporting control information also contains the clock quality acceptance criteria.
Step 2.
The gNB-CU replies to the AMF by sending the INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP RESPONSE message.
Step 3.
The gNB-CU sends the latest clock quality information to the UE by sending the DLInformationTransfer message. The clock quality information provided to the UE depends on the clock quality detail level received in step 1 (i.e., "metrics" or "acceptable/not acceptable indication").
Step 4.
Later, the gNB-DU detects a primary source event:
Step 5.
- a RAN TSS attribute cannot meet a pre-configured threshold (i.e. status is degraded);
- a RAN TSS attribute meets the pre-configured threshold again (i.e. status is no longer degraded);
- event a) occurred and b) has not yet been reached for a RAN TSS attribute, and either an implementation-dependent time interval has passed or a previously reported value can no longer be met.
Upon detecting the primary source event, the gNB-DU provides an updated RAN TSS report to the gNB-CU by sending a TIMING SYNCHRONISATION STATUS REPORT message.
Step 6.
Same as step 3.