Content for TS 38.401 Word version: 18.4.0
1…
5…
6…
6.1.4
6.1.5…
6.2…
7…
8…
8.2…
8.2.1.4…
8.2.2…
8.2.3…
8.2.4
8.2.5
8.3…
8.4…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.9…
8.9.4…
8.9.6…
8.9.7…
8.10
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
8.15.2…
8.16…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4
8.18…
8.19…
8.19.2
8.19.3
8.19.4…
8.21…
8.22…
8.23…
8.24…
9…
A…
8.17 IAB Inter-CU Topology Management
8.17.1 IAB Inter-donor-DU Re-routing
8.17.2 IAB Inter-CU Topology Redundancy
8.17.2.1 IAB Inter-CU topological redundancy procedure
...
...
8.17 IAB Inter-CU Topology Management |R17| p. 111
8.17.1 IAB Inter-donor-DU Re-routing p. 111
When an IAB-donor-DU is configured to support inter-donor-DU re-routing, the IAB-donor-DU may identify a re-routed UL IP packet based on the source IP address field of the UL packet, and forwards UL IP packets, whose source IP addresses are anchored at a peer IAB-donor-DU, to this peer IAB-donor-DU via a tunnel. The IAB-donor-DU and the peer IAB-donor-DU may be controlled by the same IAB-donor-CU or by two different IAB-donor-CUs. The inter-donor-DU tunnel may be a GTP-U tunnel. The configuration of the tunnel is up to implementation. At the IAB-donor-DU forwarding the UL IP packets, inter-donor-DU tunnelling may be restricted to only a subset of the IP addresses anchored at the peer IAB-donor-DU. For this purpose, the IAB-donor-CU configures the IAB-donor-DU for forwarding the UL IP packets with a list of TNL addresses and/or prefixes for which tunnelling should be permitted and TNL address filtering should be exempted.
8.17.2 IAB Inter-CU Topology Redundancy p. 112
8.17.2.1 IAB Inter-CU topological redundancy procedure p. 112
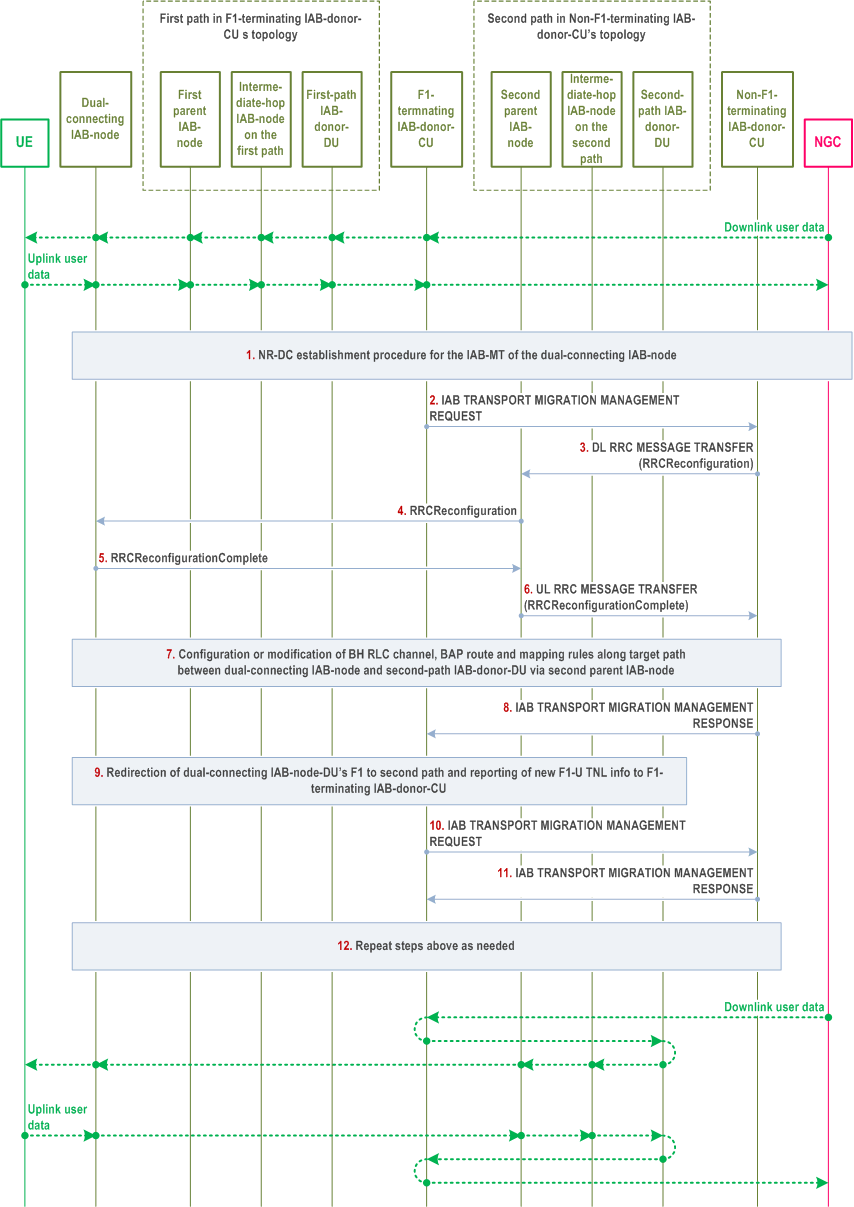
The inter-CU topological redundancy procedure enables the establishment, modification and release of redundant paths in IAB-topologies underneath different IAB-donor-CUs. Since topological redundancy uses NR-DC for the IAB-MT, it is only supported for IAB-nodes operating in the SA mode.
Figure 8.17.2.1-1 shows an example of the inter-CU topological redundancy procedure, where a second backhaul path is established for a dual-connecting IAB-node via a separate IAB-topology that is not controlled by the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU. The dual-connecting IAB-DU retains the F1 connection with the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU. Since the dual-connecting IAB-MT also maintains an RRC connection with the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, this procedure renders the dual-connecting IAB-node as a boundary IAB-node.
Step 1.
The traffic offload for descendant nodes follows the same procedure as defined for the partial migration in clause 8.17.3.2.
The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may request full or partial release of the offloaded traffic from the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU by initiating the IAB Transport Migration Management procedure towards the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU (e.g., for the purpose of revoking, or in case UE bearers are released).
The traffic offload for the dual-connecting IAB-node and the descendent nodes can be partially or fully revoked, resulting in the return of the offloaded traffic back to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU's topology. Full or partial traffic revoking can be initiated by the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU by initiating the IAB Transport Migration Management procedure towards the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU. The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU can request partial or full revoking of traffic offload from the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU by initiating the IAB Transport Migration Modification procedure towards the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
The NR-DC establishment procedure is performed for the IAB-MT of the dual-connecting IAB-node as described in clause 10.2 of TS 37.340. This procedure can be conducted before or after establishment of the F1 interface between the IAB-DU and an IAB-donor-CU.
Step 2.
The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends an IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT REQUEST message to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU to provide the context of the traffic to be offloaded.
Step 3.
The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends a DL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message to the second parent IAB-DU, which includes an RRCReconfiguration message for the dual-connecting IAB-MT. The RRC configuration includes a BAP address for the boundary node, pertaining to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU's topology. The RRC configuration may include new TNL address(es) for the dual-connecting IAB-node, anchored at the second-path, i.e., at the IAB-donor-DU under the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU. In case IPsec tunnel mode is used to protect the F1 and non-F1 traffic, the new TNL address refers to the outer IP address.
Step 4.
The second parent IAB-DU forwards the received RRCReconfiguration message to the dual-connecting IAB-MT.
Step 5.
The dual-connecting IAB-MT responds to the second parent IAB-DU with an RRCReconfigurationComplete message.
Step 6.
The second parent IAB-DU sends an UL RRC MESSAGE TRANSFER message to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, to convey the received RRCReconfigurationComplete message.
Step 7.
The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may configure or modify BH RLC channels and BAP-sublayer routing entries on the second path between the dual-connecting IAB-node and the second-path IAB-donor-DU, as well as DL mappings on the second-path IAB-donor-DU for the dual-connecting IAB-node's second path. The DL mappings may be based on the TNL address(es) allocated to the dual-connecting IAB-node in step 3. These configurations may support the transport of UP and non-UP traffic on the second path.
Step 8.
The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU responds with an IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT RESPONSE message to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, to provide the mapping information for the traffic to be offloaded as indicated in step 2. The message includes the L2 info necessary to configure the dual-connecting IAB-node with the UL mappings for this traffic. The message includes the DSCP/IPv6 Flow Label values to be used for the DL traffic to be offloaded.
Step 9.
The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU updates the boundary node with the UL BH information received from the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU in Step 8 for the traffic to be offloaded. This step may also update UL FTEID and DL FTEID associated with individual GTP-tunnel(s). The affected GTP tunnel(s) will be switched to use the dual-connecting IAB-node's new TNL address(es). This step may use non-UE associated signaling in E1 and/or F1 interface to provide updated UP configuration for F1-U tunnels of multiple connected UEs or child IAB-MTs. Implementation must ensure the avoidance of potential race conditions, i.e., that no conflicting configurations are concurrently performed using UE-associated and non-UE-associated procedures.
The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may also provide UL BH information associated with non-UP traffic. New TNL addresses for F1-C traffic configured in step 3, if any, can be added to the dual-connecting IAB-DU's F1-C association(s) with the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
If new TNL addresses for F1-C traffic are configured, new SCTP association(s) between the dual-connecting IAB-node and the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may be established using the new TNL address information of the dual-connecting IAB-node. The dual-connecting IAB-node sends an F1AP gNB-DU CONFIGURATION UPDATE message to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, which may include new (outer) IP addresses and corresponding new (inner) IP address for offloaded F1-U traffic.
Step 10.
The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU sends an IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT REQUEST message to the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, to modify the context of the dual-connecting IAB-node's offloaded traffic. The message may include the DL TNL address information used for the offloaded traffic and reported by the boundary node in step 9. The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may use this information to configure DL mappings on the second-path IAB-donor-DU.
Step 11.
The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU responds with an IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT RESPONSE message to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
Step 12.
The steps above, may be repeated, except step 1, if needed, for the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU to request addition, modification, or release of the offloaded traffic. The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU can fully or partially reject the addition or modification requested by the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may request the modification of the L2 transport for the offloaded traffic in the non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU's topology using the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MODIFICATION REQUEST message. The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU reconfigures UL BH mappings accordingly and acknowledges the modification via the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MODIFICATION RESPONSE message. The non-F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU may further reconfigure the TNL addresses of the dual-connecting IAB-node via RRC.