Content for TS 38.401 Word version: 18.4.0
1…
5…
6…
6.1.4
6.1.5…
6.2…
7…
8…
8.2…
8.2.1.4…
8.2.2…
8.2.3…
8.2.4
8.2.5
8.3…
8.4…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.9…
8.9.4…
8.9.6…
8.9.7…
8.10
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
8.15.2…
8.16…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4
8.18…
8.19…
8.19.2
8.19.3
8.19.4…
8.21…
8.22…
8.23…
8.24…
9…
A…
8.12 IAB-node Integration Procedure
8.12.1 Standalone IAB integration
8.12.2 NSA IAB Integration procedure
8.12.3 Mobile IAB-node integration
...
...
8.12 IAB-node Integration Procedure |R16| p. 90
8.12.1 Standalone IAB integration p. 90
A high-level flow chart for SA-based IAB integration is shown in the Figure 8.12.1-1:
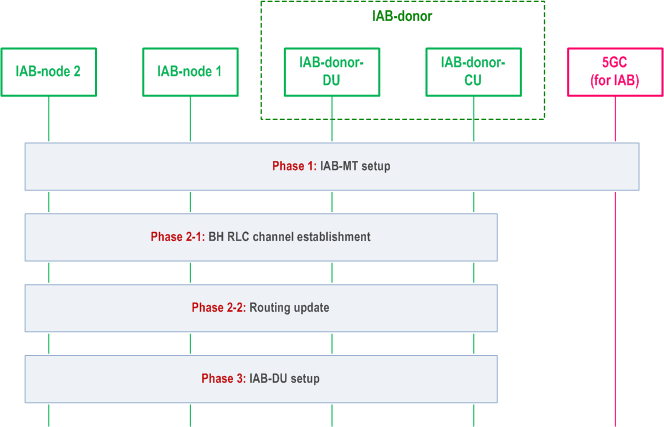
Phase 1:
IAB-MT setup. In this phase, the IAB-MT of the new IAB-node (e.g. IAB-node 2 in Figure 8.12.1-1) connects to the network in the same way as a UE, by performing RRC connection setup procedure with IAB-donor-CU, authentication with the core network, IAB-node 2-related context management, IAB-node 2's access traffic-related radio bearer configuration at the RAN side (SRBs and optionally DRBs), and, optionally, OAM connectivity establishment by using the IAB-MT's PDU session. The IAB-node can select the parent node for access based on an over-the-air indication from potential parent node IAB-DU (transmitted in SIB1). To indicate its IAB capability, the IAB-MT includes the IAB-node indication in RRCSetupComplete message, to assist the IAB-donor to select an AMF supporting IAB.
Phase 2-1:
BH RLC channel establishment. During the bootstrapping procedure, one default BH RLC channel for non-UP traffic e.g. carrying F1-C traffic/non-F1 traffic to and from the IAB-node 2 in the integration phase, is established. This may require the setup of a new BH RLC channel or modification of an existing BH RLC channel between IAB-node 1 and IAB-donor-DU. The IAB-donor-CU may establish additional (non-default) BH RLC channels. This phase also includes configuring the BAP Address of the IAB-node 2 and default BAP Routing ID for the upstream direction.
Phase 2-2:
Routing update. In this phase, the BAP sublayer is updated to support routing between the new IAB-node 2 and the IAB-donor-DU. For the downstream direction, the IAB-donor-CU initiates F1AP procedure to configure the IAB-donor-DU with the mapping from IP header field(s) to the BAP Routing ID related to IAB-node 2. The routing tables are updated on all ancestor IAB-nodes (e.g. IAB-node 1 in Figure 8.12.1-1) and on the IAB-donor-DU, with routing entries for the new BAP Routing ID(s). This phase may also include the IP address allocation procedure for IAB-node 2. IAB-node 2 may request one or more IP addresses from the IAB-donor-CU via RRC. The IAB-donor-CU may send the IP address(es) to the IAB-node 2 via RRC. The IAB-donor-CU may obtain the IP address(es) from the IAB-donor-DU via F1-AP or by other means (e.g. OAM, DHCP). IP address allocation procedure may occur at any time after RRC connection has been established.
Phase 3:
IAB-DU part setup. In this phase, the IAB-DU of IAB-node 2 is configured via OAM. The IAB-DU of IAB-node 2 initiates the TNL establishment, and F1 setup (as defined in clause 8.5) with the IAB-donor-CU using the allocated IP address(es). The IAB-donor-CU discovers collocation of IAB-MT and IAB-DU from the IAB-node's BAP Address included in the F1 SETUP REQUEST message. After the F1 is set up, the IAB-node 2 can start serving the UEs.
8.12.2 NSA IAB Integration procedure p. 91
The IAB integration procedure for NSA is shown in Figure 8.12.2-1.
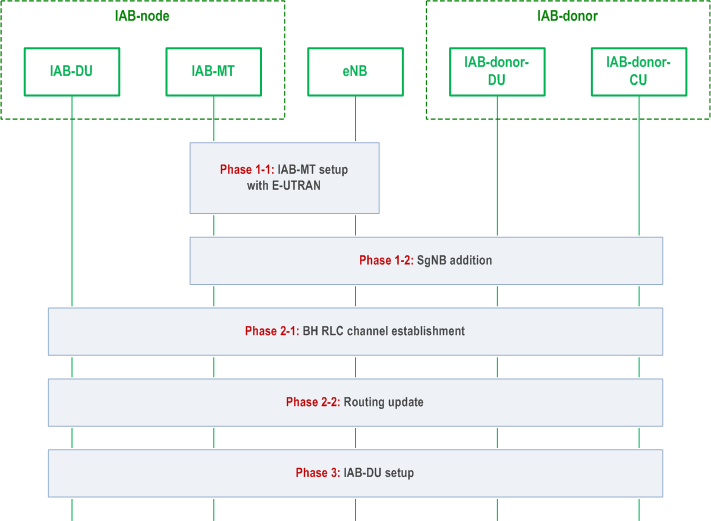
Phase 1-1:
IAB-MT part setup with E-UTRAN. In this phase, the IAB-MT part connects to the LTE network as a UE, by performing RRC connection setup procedure with an eNB, authentication with the EPC, IAB-node's access traffic-related radio bearer configuration at the E-UTRAN side, and optionally, OAM connectivity establishment by using the IAB-MT's PDN connection. The IAB-node can select the IAB-supporting eNB based on an over-the-air indication from eNB (transmitted in SIB1). To indicate its IAB capability, the IAB-MT includes the IAB-node indication in RRCConnectionSetupComplete message, to assist the eNB to select an MME supporting IAB. The eNB then configures the IAB-MT part with an NR measurement configuration in order to perform discovery, measurement and measurement reporting of candidate gNBs. To enable the eNB choose an en-gNB which supports IAB function, the IAB capability of neighbour gNBs can be pre-configured in the eNB (e.g. by OAM).
Phase 1-2:
SgNB addition. In this phase, the IAB-MT part connects to the parent node IAB-DU and IAB-donor-CU via the EN-DC SgNB Addition procedure. The procedure defined in clause 8.4.1 is reused. The eNB includes "IAB Node Indication" in SGNB ADDITION REQUEST message to inform the IAB-donor-CU that the request is for an IAB-node. In addition, SRB3 can be set up for the IAB-MT, to transmit RRC message between the IAB-MT and the IAB-donor-CU via the NR links directly.
Phase 2-1:
BH RLC channel establishment. This phase is the same as Phase 2-1 in the standalone IAB integration procedure (refer to the Phase 2-1 in clause 8.12.1). This step may occur in Phase 1-2.
Phase 2-2:
Routing update. This phase is the same as Phase 2-2 in the standalone IAB integration procedure (refer to the Phase 2-2 in clause 8.12.1), except that the IP traffic on the F1-C interface may be transmitted via the MeNB.
Phase 3:
IAB-DU part setup. This phase is the same as Phase 3 in the standalone IAB integration procedure (refer to the Phase 3 in clause 8.12.1), except that the IP traffic on the F1-C interface may be transmitted via the MeNB.
The IAB-donor-CU decides to only configure LTE leg, or only to configure NR leg, or to configure both LTE leg and NR leg, to be used for F1-C traffic transfer. The configuration may be performed before IAB-DU part setup. IAB-donor-CU may also change the configuration after IAB-DU part setup. In case the configuration is not performed before IAB-DU part setup, the IAB node uses the NR leg as the default one. When both LTE leg and NR leg are configured, it is up to the implementation to select the leg for F1-C traffic transfer.
8.12.3 Mobile IAB-node integration |R18| p. 92
During the integration, the mobile IAB-MT and the mobile IAB-DU can connect to the same IAB-donor or two different IAB-donors. The procedure for the latter case is shown in Figure 8.12.3-1.
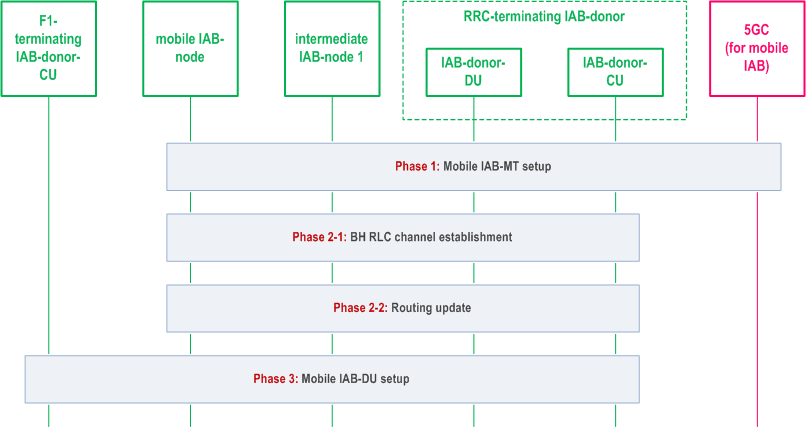
Phase 1:
After the F1 interface is set up, the mobile IAB-node can start serving UEs. The F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU can initiate the IAB Transport Migration Management procedure towards the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU as defined in clause 8.17.3.1. In case the IAB Transport Migration Management procedure is the first XnAP procedure for the mobile IAB-MT, the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU includes the mobile IAB-MT's BAP address in the IAB TRANSPORT MIGRATION MANAGEMENT REQUEST message towards the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU.
Equivalent procedure to Phase 1 of the IAB-node integration in SA mode in clause 8.12.1, where the mobile IAB-node and the RRC-terminating IAB-donor correspond to IAB-node 2 and to the IAB-donor respectively. The mobile IAB-node selects the parent node based on a mobile-IAB-specific over-the-air indication (transmitted in SIB1). The mobile IAB-MT includes a mobile-IAB-node-specific indication in the RRCSetupComplete message to assist the RRC-terminating IAB-donor in selecting an AMF that supports mobile IAB.
Phase 2-1:
Same as Phase 2-1 of procedure in clause 8.12.1.
Phase 2-2:
Same as Phase 2-2 of procedure in clause 8.12.1.
Phase 3:
Mobile IAB-DU part setup. In this phase, the mobile IAB-DU is configured via the OAM. The configured information includes, e.g., the information of the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU, to enable the mobile IAB-DU to initiate the establishment of F1-C to the F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU. The mobile IAB-DU initiates the TNL establishment, and F1 setup (as defined in clause 8.5) with the selected F1-terminating IAB-donor-CU using the default BAP routing ID and default BH RLC channel configured by the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU in Phase 2-1 for upstream traffic. During the F1 setup, the mobile IAB-DU includes the gNB ID of the RRC-terminating IAB-donor-CU and the BAP address of the co-located mobile IAB-MT in the F1 SETUP REQUEST message. The mobile IAB-node determines this gNB ID based on the over-the-air broadcast (SIB1) by the RRC-terminating IAB-donor.