Content for TS 38.321 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
5…
5.1.2…
5.2…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.9…
5.18…
5.18.18…
5.19…
5.22…
5.22.1.4…
5.22.2…
5.23…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.3.8…
6.1.3.11…
6.1.3.17…
6.1.3.21…
6.1.3.26…
6.1.3.31…
6.1.3.37…
6.1.3.42…
6.1.3.49…
6.1.3.53…
6.1.3.59…
6.1.3.64…
6.1.3.70…
6.1.3.74…
6.1.3.79…
6.1.4…
6.2…
7…
6.1.4 MAC PDU (transparent MAC)
6.1.5 MAC PDU (Random Access Response)
6.1.5a MAC PDU (MSGB)
6.1.6 MAC PDU (SL-SCH)
...
...
6.1.4 MAC PDU (transparent MAC) p. 310
A MAC PDU consists solely of a MAC SDU whose size is aligned to a TB; as described in Figure 6.1.4-1. This MAC PDU is used for transmissions on PCH, BCH, DL-SCH including BCCH, and SL-BCH.

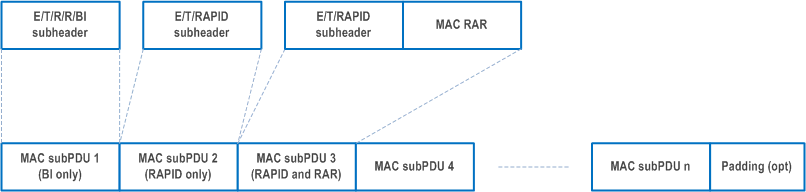
6.1.5 MAC PDU (Random Access Response) p. 310
A MAC PDU consists of one or more MAC subPDUs and optionally padding. Each MAC subPDU consists one of the following:
- a MAC subheader with Backoff Indicator only;
- a MAC subheader with RAPID only (i.e. acknowledgment for SI request);
- a MAC subheader with RAPID and MAC RAR.


6.1.5a MAC PDU (MSGB) |R16| p. 311
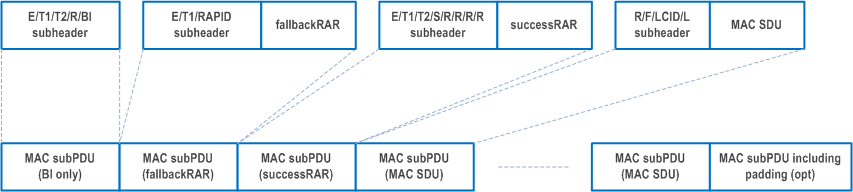
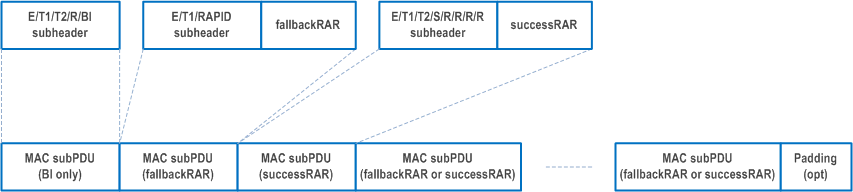
A MAC PDU consists of one or more MAC subPDUs and optionally padding. Each MAC subPDU consists one of the following:
- a MAC subheader with Backoff Indicator only;
- a MAC subheader and fallbackRAR;
- a MAC subheader and successRAR;
- a MAC subheader and MAC SDU for CCCH, DCCH or DTCH;
- a MAC subheader and padding.


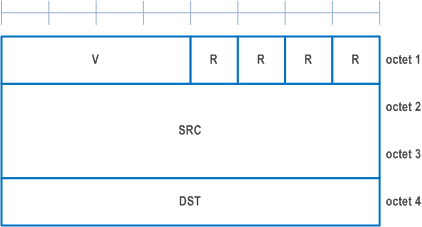
6.1.6 MAC PDU (SL-SCH) |R16| p. 312
A MAC PDU consists of one SL-SCH subheader and one or more MAC subPDUs. Each MAC subPDU consists of one of the following:
- A MAC subheader only (including padding);
- A MAC subheader and a MAC SDU;
- A MAC subheader and a MAC CE;
- A MAC subheader and padding.
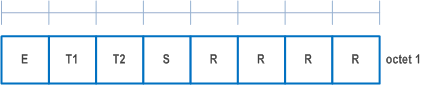
A MAC subheader except for fixed-sized MAC CE and padding consists of the four header fields R/F/LCID/L as depicted in Figure 6.1.2-1 (with 8-bit L field) and Figure 6.1.2-2 (with 16-bit L field). A MAC subheader for fixed-sized MAC CE and padding consists of the two header fields R/LCID as depicted in Figure 6.1.2-3.
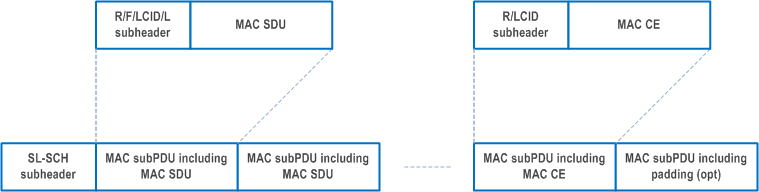
SL MAC subPDU(s) with MAC SDU(s) is placed after the SL-SCH subheader and before the MAC subPDU with a MAC CE and the MAC subPDU with padding in the MAC PDU as depicted in Figure 6.1.6-2. SL MAC subPDU with a MAC CE is placed after all the MAC subPDU(s) with MAC SDU and before the MAC subPDU with padding in the MAC PDU as depicted in Figure 6.1.6-2. The size of padding can be zero.
A maximum of one MAC PDU can be transmitted per TB per MAC entity.