Content for TS 38.321 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
5…
5.1.2…
5.2…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.9…
5.18…
5.18.18…
5.19…
5.22…
5.22.1.4…
5.22.2…
5.23…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.3.8…
6.1.3.11…
6.1.3.17…
6.1.3.21…
6.1.3.26…
6.1.3.31…
6.1.3.37…
6.1.3.42…
6.1.3.49…
6.1.3.53…
6.1.3.59…
6.1.3.64…
6.1.3.70…
6.1.3.74…
6.1.3.79…
6.1.4…
6.2…
7…
6 Protocol Data Units, formats and parameters
6.1 Protocol Data Units
6.1.1 General
6.1.2 MAC PDU (DL-SCH and UL-SCH except transparent MAC and Random Access Response)
...
...
6 Protocol Data Units, formats and parameters p. 210
6.1 Protocol Data Units p. 210
6.1.1 General p. 210
A MAC PDU is a bit string that is byte aligned (i.e. multiple of 8 bits) in length. In the figures in clause 6, bit strings are represented by tables in which the most significant bit is the leftmost bit of the first line of the table, the least significant bit is the rightmost bit on the last line of the table, and more generally the bit string is to be read from left to right and then in the reading order of the lines. The bit order of each parameter field within a MAC PDU is represented with the first and most significant bit in the leftmost bit and the last and least significant bit in the rightmost bit.
A MAC SDU is a bit string that is byte aligned (i.e. multiple of 8 bits) in length. A MAC SDU is included into a MAC PDU from the first bit onward.
A MAC CE is a bit string that is byte aligned (i.e. multiple of 8 bits) in length.
A MAC subheader is a bit string that is byte aligned (i.e. multiple of 8 bits) in length. Each MAC subheader is placed immediately in front of the corresponding MAC SDU, MAC CE, or padding.
The MAC entity shall ignore the value of the Reserved bits in downlink MAC PDUs.
6.1.2 MAC PDU (DL-SCH and UL-SCH except transparent MAC and Random Access Response) p. 210
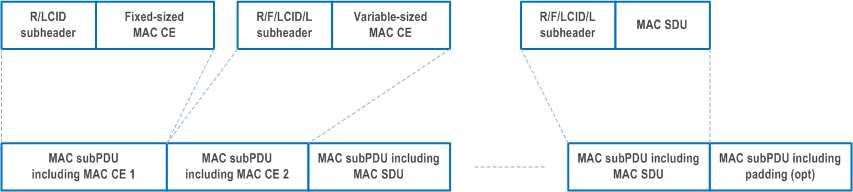
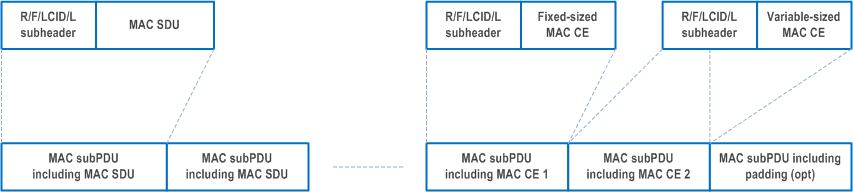
A MAC PDU consists of one or more MAC subPDUs. Each MAC subPDU consists of one of the following:
- A MAC subheader only (including padding);
- A MAC subheader and a MAC SDU;
- A MAC subheader and a MAC CE;
- A MAC subheader and padding.
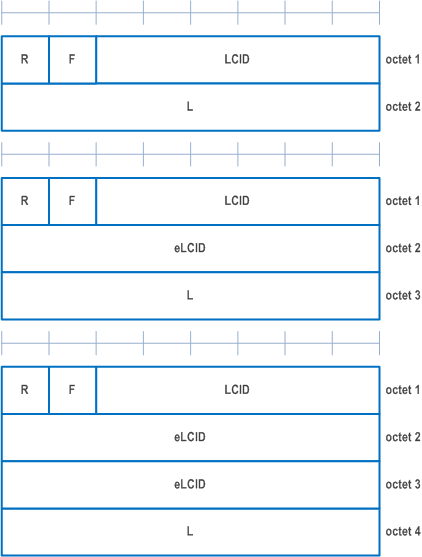
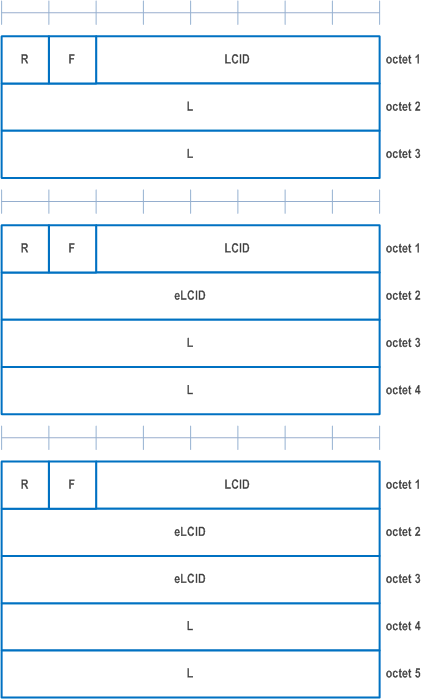
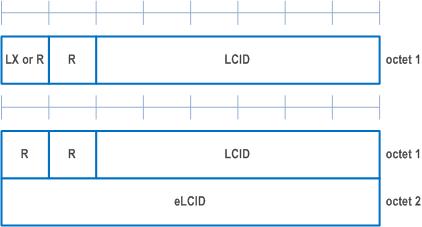
MAC CEs are placed together. DL MAC subPDU(s) with MAC CE(s) is placed before any MAC subPDU with MAC SDU and MAC subPDU with padding as depicted in Figure 6.1.2-4. UL MAC subPDU(s) with MAC CE(s) is placed after all the MAC subPDU(s) with MAC SDU and before the MAC subPDU with padding in the MAC PDU as depicted in Figure 6.1.2-5. The size of padding can be zero.
A maximum of one MAC PDU can be transmitted per TB per MAC entity.