Content for TS 33.127 Word version: 19.1.0
0…
5…
5.4…
5.6…
5.7…
6…
6.2.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.5…
6.3…
6.3.3…
6.3.4…
6.4…
7…
7.3…
7.4…
7.4.7…
7.5…
7.6…
7.7…
7.8…
7.9…
7.10…
7.11…
7.12…
7.13…
7.14…
7.15…
7.16…
8…
A…
A.2…
A.3…
A.4…
B…
D…
E…
7.16 LI at EES
7.16.1 Background
7.16.2 Architecture
7.16.3 Target identities
7.16.4 IRI events
7.17 LI at 5GMS AF
7.17.1 Background
7.17.2 Architecture
7.17.3 Target identities
7.17.4 IRI events
7.18 LI at NWDAF
7.18.1 Background
7.18.2 Architecture
7.18.3 Target identities
7.18.4 IRI events
7.19 LI at eP-CSCF for WebRTC access to the IMS
...
...
7.16 LI at EES p. 147
7.16.1 Background p. 147
Edge computing is a concept, described in TS 23.501, that enables operator and 3rd party services to be hosted close to the UE's access point of attachment, to achieve an efficient service delivery through the reduced end-to-end latency and load on the transport network. An Edge Computing Service Provider (ECSP) is a mobile network operator or a 3rd party service provider offering edge computing service. Details of edge hosting environment, are outside the scope of 3GPP (see clause 4.1 of TS 23.558).
For edge computing, it is essential that the Application Clients (ACs) are able to locate and connect with the most suitable application server available in the Edge Data Network (EDN), depending on the needs of the application. The edge enabler layer exposes APIs to support such capabilities. The edge computing capabilities supported by 3GPP are defined in TS 23.558. Figure 4.1-1 in clause 4.1 of TS 23.558 gives an overview of 3GPP edge computing.
The EES (see clause 6.3.2 of TS 23.558) is a component of the edge enabler layer which facilitates communication between the Application Clients running on the UE and the EAS deployed on the EDN. This includes EAS discovery by the UE and application context transfer between EASs for service continuity. The ECS (Edge Configuration Server) is another component of the edge enabler layer providing supporting functions needed for the EEC to connect with an EES. Figure 6.2-1 in clause 6.2 of TS 23.558 shows the general architecture for enabling edge applications using a service-based representation.
Figure 7.16.1-1 shows an edge computing network, where EDN owned/managed by a ECSP (Edge Computing Service Provider) is communicating with the PLMN operator mobile network, and connected via UPF. The EDN contains EAS, EES and ECS. The PLMN operator is responsible for the deployment of NG-RAN, 5GC including AMF, SMF, UPF and NEF. Other models such as where the PLMN operator is the ECSP are possible.
The ECSP can have service agreement with one or more PLMN operators and may request the PLMN operators to connect EAS and EES with 5GC network functions.

7.16.2 Architecture p. 149
The EES shall provide the IRI-POI function. Figure 7.16.2-1 gives a reference point representation of the LI architecture with EES as a CP NF providing the IRI-POI function for edge computing.
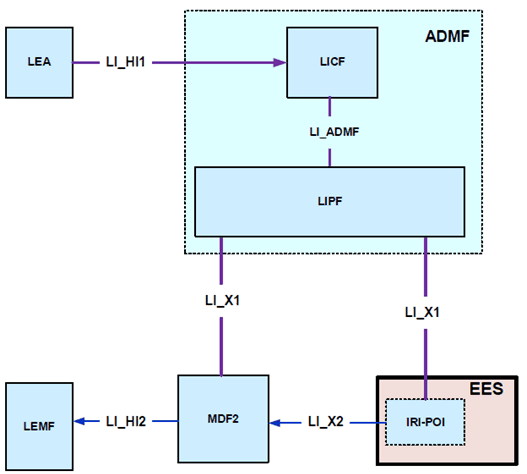
Figure 7.16.2-1: LI architecture for Edge Computing showing LI at EES
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
7.16.3 Target identities p. 149
The LIPF present in the ADMF provisions the intercept information associated with the following target identities to the IRI-POI present in the EES:
- GPSI.
- EECID.
7.16.4 IRI events p. 149
The IRI-POI in the EES shall generate xIRI when it detects the following specific events or information in both roaming and non-roaming situations:
- EEC registration (see clause 8.4.2 of TS 23.558).
- EAS discovery (see clause 8.5.2.2 of TS 23.558).
- EAS discovery subscription (see clause 8.5.2.3 of TS 23.558).
- EAS discovery notification (see clause 8.5.2.3 of TS 23.558).
- Application context relocation (see clause 8.8.3.4 of TS 23.558).
- Application context relocation information subscription (see clause 8.8.3.5 of TS 23.558).
- Application context relocation information notification (see clause 8.8.3.5 of TS 23.558).
- EEC context relocation (see clause 8.9 of TS 23.558).
- Start of interception with registered EEC.
7.17 LI at 5GMS AF p. 150
7.17.1 Background p. 150
5G Media Streaming (5GMS) is a concept described in TS 26.501 and is defined as the delivery of time-continuous media as the predominant media. Streaming points to the fact that the media is predominantly sent only in a single direction and consumed as it is received. Additionally, the media content may be streamed as it is produced, referred to as live streaming. If media content being streamed is already produced, it is referred to as on-demand streaming.
The overall 5G Media Streaming Architecture is shown in Figure 4.1.1-2 of clause 4.1 of TS 26.501.
7.17.2 Architecture p. 150
The 5GMS AF shall provide the IRI-POI function. Figure 7.17.2-1 gives a reference point representation of the LI architecture with 5GMS AF as a CP NF providing the IRI-POI function for 5G Media Streaming. A 5GMS AF that is edge-enabled shall support EES functionality. A UE may request edge processing for a streaming session from the EES embedded in the 5GMS AF. EES provides the IRI-POI function as specified in clause 7.16.
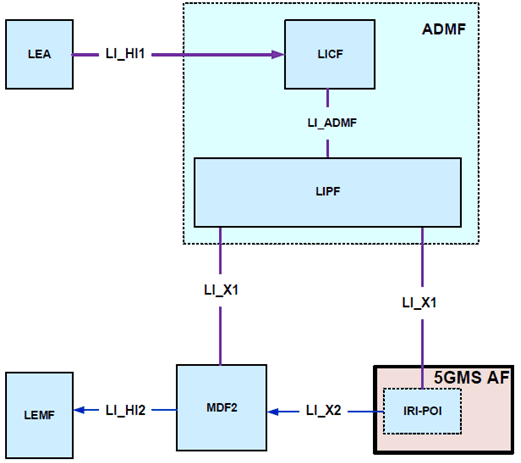
Figure 7.17.2-1: LI architecture for 5G Media Streaming showing LI at 5GMS AF
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
7.17.3 Target identities p. 151
The LIPF present in the ADMF provisions the intercept information associated with the following target identities to the IRI-POI present in the 5GMS AF:
- GPSI.
7.17.4 IRI events p. 151
The IRI-POI in the 5GMS AF shall generate xIRI when it detects the following specific events or information in both roaming and non-roaming situations:
- Service access information (see clause 4.2.3 of TS 26.501).
- Consumption reporting (see clause 5.6 of TS 26.501).
- Metrics reporting (see clause 5.5 of TS 26.501).
- Dynamic policy invocation (see clause 5.7 of TS 26.501).
- Network assistance (see clauses 5.9 and 6.5 of TS 26.501).
- Start of interception with already configured UE.
7.18 LI at NWDAF p. 152
7.18.1 Background p. 152
Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF) is a 5G network function which analyses data collected from network functions, OAM and UEs via AF in the 5G System, and publishes the analytics results to subscribing data analytics consumers. The results could be a summary of statistical/historical data, or an attempt to predict future data values related to UEs which user consent is granted.
NWDAF covers the following data analytics services related to a UE:
- Observed service experience as defined in clause 6.4 of TS 23.288.
- UE mobility as defined in clause 6.7.2 of TS 23.288.
- UE communication as defined in clause 6.7.3 of TS 23.288.
- Abnormal behaviour as defined in clause 6.7.5 of TS 23.288.
- Data volume dispersion as defined in clause 6.10 of TS 23.288.
- Relative proximity as defined in clause 6.19 of TS 23.288.
- PDU session traffic as defined in clause 6.20 of TS 23.288.
7.18.2 Architecture p. 152
The NWDAF shall provide the IRI-POI function. Figure 7.18.2-1 gives a reference point representation of the LI architecture with NWDAF as a CP NF providing the IRI-POI function. NWDAF provides a set of data analytics in the form of statistics and predictions to authorized NF consumers. This LI architecture is valid in non-roaming and roaming situations.
In roaming situation, data analytics may be exchanged between the visited network and home network via NWDAFs with roaming exchange capability.
- For an outbound roaming UE, the NF consumer in the home network can retrieve analytics from the NWDAF present in the visited network.
- For an inbound roaming UE, the NF consumer in the visited network can retrieve analytics from the NWDAF present in the home network.
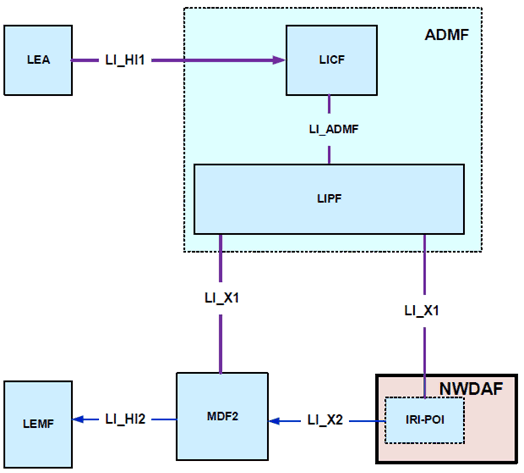
Figure 7.18.2-1: LI architecture for 5G data analytics showing LI at NWDAF
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
7.18.3 Target identities p. 153
The LIPF present in the ADMF provisions the intercept information associated with the following target identities to the IRI-POI present in the NWDAF:
- SUPI.
7.18.4 IRI events p. 153
The IRI-POI in the NWDAF shall generate xIRI when it detects the following specific events or information:
- Events subscription (see clauses 7.2.2 and 7.2.3 of TS 23.288).
- Events notification (see clause 7.2.4 of TS 23.288).
- Analytics info query (see clause 7.3.2 of TS 23.288).
- Roaming analytics subscription (see clauses 7.7.2 and 7.7.3 of TS 23.288).
- Roaming analytics notification (see clause 7.7.4 of TS 23.288).
7.19 LI at eP-CSCF for WebRTC access to the IMS p. 154
7.19.1 Background p. 154
Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) adds real-time communication to the browser with a focus on peer-to-peer communication. It enables multimedia interaction capabilities in web browsers on any platform without installing a specific plug-in or using a third-party application. WebRTC leaves the signalling plan to service developers, who are free to implement any call control protocol, e.g. SIP over secure WebSocket, XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) over WebSocket, etc. The only requirement is that the session negotiation data be represented by the SDP (Session Description Protocol). WebRTC clients may have access to IMS through mediation functions for signalling and media. The enhanced P-CSCF (eP-CSCF) is the endpoint for the signalling connection from the WebRTC IMS Client (WIC) and is located in the operator network. The enhanced IMS-AGW (eIMS-AGW) is the endpoint for the media connection from the WIC.
Figure U.1.2-1 of TS 23.228 gives an overview of WebRTC IMS architecture.
The WebRTC Web Server Function (WWSF) is the initial point of contact in the Web that controls access to the IMS communications services for the user. It provides a web page, which is the user interface (UI) for the user. The WebRTC Authorisation Function (WAF) creates an authentication token for the user and deliver it to the WWSF. The WAF is used in the case of IMS registration scenario using Web Authentication and is not used in the case of IMS registration scenario using IMS Authentication.
7.19.2 Architecture p. 154
The WWSF and eP-CSCF shall provide the IRI-POI function. Figure 7.19.2-1 gives a reference point representation of the LI architecture with WWSF and eP-CSCF as CP NFs providing the IRI-POI function for WebRTC access to the IMS. This LI architecture is valid in non-roaming situations.
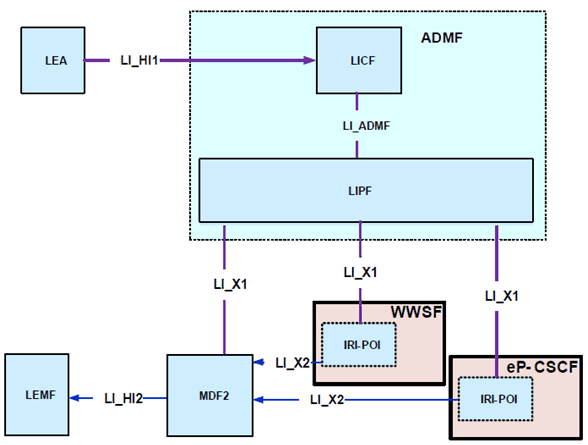
The eP-CSCF shall adhere to all LI requirements pertaining to the P-CSCF in addition to the LI requirements pertaining to the support of WebRTC access to IMS.
The IMS-AGW of the IMS LI architecture detects the media to be intercepted and generates the associated xCC.
7.19.3 Target identities p. 155
The LIPF present in the ADMF provisions the intercept information associated with the following target identities to the IRI-POI present in the WWSF:
- IMPU.
- IMPI.
- NAI (i.e. Web Identity).
- IMPU.
- IMPI.
7.19.4 IRI events p. 156
The IRI-POI in the WWSF shall generate the following xIRIs:
- WIC authorization.
- Start of interception with already authorized WIC.
- Encapsulated signalling message.