Content for TS 23.558 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
5…
6…
6.2a…
6.2b…
6.3…
6.4…
7…
8…
8.3…
8.3.3…
8.3.3.3…
8.4…
8.4.3…
8.4.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.6.3…
8.6.4…
8.6.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.8.2.5…
8.8.2A…
8.8.3…
8.8.4…
8.8.5…
8.9…
8.14…
8.14.3…
8.15…
8.17…
8.17.3…
8.17.4…
8.18…
8.19…
8.20…
9…
A…
A.4…
A.5…
B…
E…
8.8.3 Procedures
8.8.3.1 General
8.8.3.2 Discover T-EAS
8.8.3.3 Retrieve T-EES procedure
8.8.3.4 ACR launching procedure
8.8.3.5 ACR information subscription
8.8.3.5.1 General
8.8.3.5.2 Subscribe
8.8.3.5.3 Notify
8.8.3.5.4 Subscription update
8.8.3.5.5 Unsubscribe
8.8.3.6 EELManagedACR procedure
8.8.3.6.1 General
8.8.3.6.2 Procedure
8.8.3.7 Selected T-EAS declaration
8.8.3.8 ACR status update procedure
8.8.3.9 ACR parameter information procedure
8.8.3.10 Selected EES declaration
8.8.3.11 ACR event subscription and notification procedure
...
...
8.8.3 Procedures p. 189
8.8.3.1 General p. 189
Void
8.8.3.2 Discover T-EAS p. 189
Figure 8.8.3.2-1 illustrates the procedure for fetching T-EAS information. This procedure may be utilized by a S-EAS, which undertakes the transfer of application context information to a T-EAS directly, or can be invoked by the S-EES itself on deciding to execute ACR.
T-EAS discovery procedure also supports EAS retrieval which enables a S-EAS to obtain T-EAS(s) serving the application group so that the S-EAS can start communication with obtained EAS(s) for EAS content synchronization.
Pre-conditions:
- Information related to the EES is available with the S-EAS, if the procedure is triggered by the S-EAS.

Step 1a.
The S-EAS sends the EAS discovery request to the S-EES or the S-EES decides to execute the ACR. The EAS discovery request from the S-EAS includes the requestor identifier [EASID] along with the security credentials and includes EAS discovery filter matching its EAS profile. If target DNAI is available at the S-EAS via User Plane Path change event, the S-EAS provides the S-EES with the target DNAI. If target tunnel information is available at the S-EAS via User Plane Path change event, the S-EAS provides the S-EES with the target tunnel information. The S-EAS also includes an EAS service continuity support indicator indicating that the S-EAS decided ACR according to clause 8.8.2.4 is to be used for the ACR. The S-EAS includes the bundle ID and bundle type indicating the proxy bundle case to which the S-EAS belongs to. The request may include prediction expiration time.
The EAS may send EAS discovery request with EAS ID, Application Group ID and EAS content synchronization support, which indicates the request to obtain EAS(s) currently serving the Application Group ID with the requested EAS ID in order to perform EAS content synchronization.
The Application group ID is included in the EAS discovery request if the S-EAS wants to discover a common T-EAS for UE in the group due to UE's movement.
If the EAS discovery request is triggered by S-EAS due to overload or maintenance reason for the Application Group, the S-EAS also includes list of UE IDs in the EAS discovery request.
Step 1b.
The S-EES either receive the target DNAI and/or target tunnel information for T-EES discovery from the step 1a or by the user plane management event notification from the core network.
Step 2.
If the request is received from the S-EAS, the S-EES checks whether the requesting EAS is authorized to perform the discovery operation.
If Application Group ID and EAS content synchronization support in EAS characteristics are received and the ECS-ER is available, the S-EES checks with the ECS-ER with the received EAS ID and Application Group ID and obtains a list of EAS(s) supporting EAS content synchronization and serving the application group for the desired application service identified by the EAS ID as described in clause 8.20. Step 2 to step 4 are skipped.
If the UE location is not known to the S-EES or provided by the S-EAS request, then the S-EES may interact with 3GPP core network to retrieve the UE location. If the S-EES decided to execute the ACR or when the requesting EAS is authorized, the S-EES checks if there exists a T-EAS information (registered or cached) that can satisfy the requesting EAS information, target DNAI, target tunnel information, additional query filters and the Expected AC Service KPIs and the Minimum required AC Service KPIs if received from the EEC during the EAS discovery or from the S-EAS in step 1. In this case, the S-EES may collect Edge load performances from ADAES or OAM to find T-EAS(s) that satisfies the Expected AC service KPIs or the Minimum required AC Service KPIs. The S-EES may determine the use of statistics or prediction for evaluating KPIs based on the situation of the T-EAS discovery. If target tunnel information is received, the S-EES additionally takes the target tunnel information into consideration in identifying T-EAS(s). For instance, the IP address(es) of identified T-EAS(s) needs to be topologically close to the IP address of the target tunnel server. The S-EES also considers resource consumption needs for the list of UEs (e.g. received in step 1a) when identifying T-EAS(s). If Application Group ID is not received and if the S-EES finds the T-EAS(s) in the cached or registered information, the flow either continues with step 5 for the S-EAS triggered discovery or stops for the S-EES decided ACR execution, else the S-EES retrieves the T-EES address from the ECS as specified in clause 8.8.3.3 and continues with step 3.
If UE ID list is available in the S-EES (e.g. received in step 1a or known by the S-EES via other means):
Step 3.
- for UE(s) not in the overlapping EDN area (e.g. UE is not in the common S-EAS service area), the S-EES tries to identify a T-EAS within locally registered EAS(s) based on UE location, EAS discovery filters and application group profile.
- for UE(s) in the overlapping EDN area, the S-EES checks if there is available common S-EAS in each EDN which has overlapping EDN area with the current UE related EDN by using procedure described in clause 8.20.2.2 when common EAS information is available at S-EES or ECS-ER. If any common EAS is found, the S-EES decides whether to select an available common EAS or locally registered T-EAS as common EAS considering UE location, EAS discovery filters, application group profile, and E2E response time and continues with step 5; otherwise, the S-EES tries to identify a T-EAS within locally registered EAS(s).
The S-EES invokes the EAS discovery request on the T-EES retrieved from the ECS. The EAS discovery request includes the requestor identifier [EESID] along with the security credentials and includes EAS discovery filter. In the EAS discovery filter, the S-EES may include prediction expiration time, the Expected AC Service KPIs and the Minimum required AC Service KPIs if received from the EEC during the EAS discovery or from the S-EAS in step 1. If target tunnel information is available at the S-EES (e.g. received from S-EAS in step 1a or by the user plane management event notification from the core network), the S-EES provides the T-EES with the target tunnel information.
The S-EES also includes the EEC service continuity support indicator received from the EEC during EAS discovery. If in step 1 the S-EES received an EAS service continuity support indicator from the S-EAS, then the S-EES includes this EAS service continuity support indicator and its own EES service continuity support indicator indicating the ACR scenarios supported by the EES. If in step 1 the S-EES decided to execute the ACR, the S-EES includes the EAS service continuity support indicator received from the S-EAS during EAS registration and includes an EES service continuity support indicator indicating that the S-EES executed ACR according to clause 8.8.2.5 is to be used for the ACR.
Upon receiving the request, the T-EES may trigger the ECSP management system to instantiate the T-EAS that matches with EAS discovery filter IEs (e.g. ACID) as in clause 8.12.
Step 4.
The T-EES discovers the T-EAS(s) and responds with the discovered T-EAS information to the S-EES. To filter T-EAS(s), the T-EES utilizes the discovery filters (e.g. Expected AC Service KPIs and the Minimum required AC Service KPIs) and the indications which ACR scenarios are supported by the AC, the EEC, the T-EES and the S-EAS. If T-EES gets the Expected AC service KPIs or the Minimum required AC Service KPIs, the T-EES may collect edge load analytics from ADAES (as specified in clause 8.8.2 of TS 23.436) or performance data from OAM to find T-EAS(s) that satisfies the Expected AC service KPIs or the Minimum required AC Service KPIs. The T-EES may determine the use of statistics or prediction for evaluating KPIs based on the situation of the T-EAS discovery. The S-EES may cache the T-EAS information.
When the T-EES accepts the request and determines to trigger the EAS instantiation, then the response may indicate that the EAS instantiation is in progress so that the detailed EAS profile information will be available later. When S-EES receives the EAS instantiation in progress indication, the S-EES may send EAS discovery subscription request message if not subscribed yet or send EAS discovery request message later to the T-EES for obtaining updated EAS information.
When the bundle EAS information (i.e. list of EASID) is provided and the bundle type indicating the direct bundle, and the S-EES received associated T-EES(s) along with part of EAS ID list in the step2 from the ECS, then the S-EES discover the target direct bundle EAS(s) which belongs to same EDN for all the associated S-EES(s). The request message contains direct bundle EAS(s) information (i.e. list of EASID and direct bundle type). Then the S-EES receives the direct bundle T-EAS(s) information from each associated T-EES(s).
If target tunnel information is received, the T-EES additionally takes the target tunnel information into consideration in identifying T-EAS(s). For instance, the IP address(es) of identified T-EAS(s) needs to be topologically close to the IP address of the target tunnel server.
When the ECS-ER is available and common EAS information corresponding to the Application Group ID (received in step 1a or ACR management event subscription) is not available, then the S-EES identifies one T-EAS for the application group and interacts with the ECS-ER to store the common EAS information as described in clause 8.20.2.3. If common EAS information is already available corresponding to the Application Group ID in the repository, then the ECS-ER returns the common EAS information to the S-EES as described in clause 8.20.2.3.
Step 5.
If the request was received from the S-EAS, the S-EES responds to the S-EAS with the discovered T-EAS Information.
For responding to the S-EAS which is requesting EAS(s) serving the application group for EAS content synchronization purpose, only EAS endpoint and EAS ID are included in EAS profile of Discovered EAS list.
8.8.3.3 Retrieve T-EES procedure p. 191
Figure 8.8.3.3-1 illustrates the procedure for the S-EES to retrieve the T-EES information from the ECS. This procedure is also applicable for the CES to retrieve the T-EES information.
Pre-condition:
- The S-EES has been pre-configured with the address of the ECS; and
- The AC at the UE already has on-going application traffic with the S-EAS.

Step 1.
If the retrieve EES response contains a list of ECS configuration information, the S-EES may initiate retrieve T-EES procedure with one or more ECS(s) listed in the retrieve EES response.
The S-EES sends the Retrieve EES request (UE location information or UE identity, EASID of the S-EAS, bundle ID, bundle type (i.e. proxy bundle case), target DNAI and UE connectivity information) to the ECS in order to identify the T-EES which has an EAS available to serve the given AC in the UE. For obtaining announcement EES list, the Retrieve EES request includes application group id. The request message may also contain the AC, EEC service continuity support information. If target tunnel information is available at the S-EES, then the S-EES provides also the tunnel information to the ECS.
Step 2.
If the request contains the UE identity (e.g. GPSI) but the UE location is not known to the ECS, then the ECS interacts with 3GPP core network to retrieve the UE location. The ECS determines T-EES(s) as per the parameters (e.g. EASID, target DNAI) in the request and the UE location information. If the request message contains the AC, EEC service continuity support information, then the ECS may identify the T-EES taking the AC, EEC, T-EES service continuity support into consideration. The ECS may take the EAS(s) load information corresponding to the EASIDs registered with EES in the EDN(s) or use ADAES Edge load analytics as specified in clause 8.8.2 of TS 23.436) to take EDN load into consideration in identifying T-EES(s). When the bundle ID and is provided and bundle type indicating the proxy bundle case then the ECS can identify the T-EES based on the bundle ID in the EES profile and in the request message to ensure T-EAS is able to invoke the required proxy bundle EAS(s) as the S-EAS does.
If the Prediction expiration time is provided then the ECS may determine whether to identify T-EES with the instantiable but not instantiated EAS based on Prediction expiration time and predicted EAS deployment time information obtained from ADAES as specified in clause 8.11 of TS 23.436 or from local configured maximum EAS deployment time.
If no ECS-ER is available and when the Retrieve EES request includes application group id to the ECS then the request EES list retrieval is for the announcement of common EAS, ECS determines the list of EESs serving the EASs (with same EASID) for the Group ID included in the Retrieve EES request.
If the ECS does not identify any suitable EES(s) based on EDN configuration available at the ECS and UE's location, the ECS determines a partner ECS that may satisfy the requirements. Based on ECSP policy, the ECS may use preconfigured or OAM configured information about the partner ECSs or ECS discovery via ECS-ER as specified in clause 8.17.2.3 or both.
If required by the ECSP policies, the ECS may use service provisioning information retrieval procedure as specified in clause 8.17.2.4 to obtain service provisioning information from the partner ECS.
When the bundle EAS information is provided, then if bundle EAS information includes a list of EASIDs, then the ECS identifies the one or more T-EES associated with the same EDN which support all of the EASs within the same EDN based on the EES EDN information obtained in the EES profile.
If tunnel information is received, the ECS additionally takes the tunnel information into consideration in identifying EES(s). For instance, the IP address(es) of identified EES(s) needs to be topologically close to the IP address of the tunnel server.
Step 3.
The ECS sends the Retrieve EES response. If the ECS has determined the EDN configuration information, the retrieve EES response includes the list of EDN configuration information to the S-EES. The list of EDN configuration information includes the EDN details with the endpoint information of T-EES(s) as described in Table 8.3.3.3.3-2. If the ECS has determined suitable partner ECS(s) instead, the retrieve EES response includes a list of ECS configuration information.
The ECS may provide associated T-EES(s) information (one or more T-EES information) to the S-EES in the Retrieve T-EES response along with the bundle EAS information (i.e. list of EASIDs). When S-EES receives multiple associated T-EES(s), then each associated T-EES information is provided along with the part of the EAS ID list.
8.8.3.4 ACR launching procedure p. 193
Figure 8.8.3.4-1 illustrates the ACR launching procedure by the EEC or the S-EAS or the S-EES.
If this procedure is triggered by the EEC, depending on the ACR action indicated in the ACR request, the procedure is used for ACR initiation, ACR determination or ACR modification which is described in clause 8.8.1.4. The procedure of the ACR initiation can be re-sent as described in clause 8.8.1.3 to cancel an ACR.
If this procedure is triggered by the S-EAS, the procedure is used for ACR determination.
If this procedure is triggered by the S-EES to the associated S-EES(s), this procedure is used for the direct bundle EAS case.
Pre-condition:
For EEC as consumer:
- The EEC has been authorized to communicate with the EES as specified in clause 8.11, if the procedure is triggered by the EEC.
- Information related to the S-EES is available with the S-EAS.
- The S-EES obtained the associated S-EES(s) information as specified in clause 8.15.2.2.

Step 1.
In case of re-sending ACR initiation, if serving EES was changed and EEC context was relocated, the T-EES can clean up any relocated EEC context either indicated in the re-sent ACR request for scenario described in clause 8.8.2.6 or upon reception of the ACR status update with failed result from T-EAS for other scenarios.
The EEC or the S-EAS sends an ACR request message to the EES in order to start ACR. The ACR request message may include Predicted/Expected UE location or Expected AC Geographical Service Area to indicate that the EES should detect whether the UE has moves to the Predicted/Expected UE location or Expected AC Geographical Service Area or not in ACR clean-up phase. The ACR request message includes ACR action to indicate either ACR initiation request or ACR determination request. If the procedure is triggered by the S-EAS, the ACR request message is only for ACR determination.
An ACR request for ACR initiation sent by the EEC:
Step 2.
- includes an indication of whether the EEC requests the EES to perform EAS notification; and
- provides information used by EES to perform AF traffic influence as in TS 23.501. The EEC sent ACR request for ACR initiation shall include the simultaneous EAS connectivity information in service continuity (see Table 8.8.4.4-1) if previously received as part of the AC profile.
- includes IDs to identify the ACR that is requested to be modified; and
- includes the ACR parameters to be modified.
- includes direct bundle T-EAS(s) received in step 4 in clause 8.8.3.2 related to the associated S-EES(s) based on the EASID, which EASID of the associated S-EES is corresponding to the direct bundle T-EAS(s) profile.
The EES checks if the requestor is authorized for this operation. If authorized, the EES processes the request and performs the required operations.
If the request in step 1 is for ACR initiation:
Step 3.
- the EES may use information provided in the request to apply the AF traffic influence with the N6 routing information of the T-EAS in the 3GPP Core Network (if applicable), as described in clause 5.6.7.1 of TS 23.501; and
- if the EAS notification indication in ACR initiation data is provided in the step 1 request and the EAS has subscribed to receive such notification, the EES shall notify the EAS indicated in the ACR initiation data about the need to start ACR by sending an ACR management notification for the "ACT start" event, as described in clause 8.6.3.
- if the previous EAS notification indication is provided in the step 1 request and the EAS has subscribed to receive such notification, the EES shall notify the EAS about the cancellation of the ACR with the previous T-EAS by sending an ACR management notification for the "ACT stop" event, as described in clause 8.6.3.
- The EAS will inform the remote EAS about application context cancellation, which is outside the scope of this specification. The T-EAS sends the ACR status update message to the T-EES which will include failed result with an appropriate cause indicating the reason for the failure.
- the EES identifies the ACR to be modified based on the ID parameters in the request in step 1. If the request in step 1 is to the S-EES, the S-EES performs the ACR parameter information procedure as described in clause 8.8.3.9. If the request in step 1 is to the T-EES, and if the T-EAS has subscribed to receive ACR notifications, the T-EES shall notify the T-EAS by sending an ACR management notification, with "ACT start" event including ACR parameters from the request in step 1, e.g. Prediction expiration time.
The EES responds to the requestor's request with an ACR response message.
8.8.3.5 ACR information subscription p. 195
8.8.3.5.1 General p. 195
Clause 8.8.3.5.2 and clause 8.8.3.5.3 together illustrate the ACR information procedure based on Subscribe/ Notify model.
The ACR information procedure is utilized as a building block for a part of Post-ACR Clean up in clause 8.8.2 and Target information notification.
8.8.3.5.2 Subscribe p. 195
Figure 8.8.3.5.2-1 illustrates the ACR information subscription procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the EES;
- The EEC has received appropriate security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the EES as specified in clause 8.11; and
- The EEC has optionally acquired a Notification Target Address to be used in its subscriptions to notifications.

Step 1.
The EEC sends an ACR information subscription request to the EES. The request from EEC may include the ACIDs to indicate to the EES which ACs are served by the EEC that need to receive ACR information via EEL.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized to subscribe ACR information about the requested EAS(s). If the request is authorized, the EES creates and stores the subscription for ACR information.
Step 3.
The EES sends an ACR information subscription response to the EEC, which includes the subscription identifier and may include the expiration time, indicating when the subscription will automatically expire. To maintain the subscription, the EEC shall send an ACR information subscription update request prior to the expiration time. If an ACR information subscription update request is not received prior to the expiration time, the EES shall treat the EEC as implicitly unsubscribed.
8.8.3.5.3 Notify p. 196
Figure 8.8.3.5.3-1 illustrates the ACR information notification procedure between the EEC and the EES, which can be used by the EES to notify the EEC of the following:
- target information, i.e. the details of the selected T-EAS and, if required, the selected T-EES, during ACR as described in clauses 8.8.2.4 and 8.8.2.5;
- ACR complete events.
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for the ACR information as specified in clause 8.8.3.5.2.

Step 1.
An event (e.g. ACR complete, or Target information notification) occurs at the EES that satisfies trigger conditions for providing ACR information to a subscribed EEC.
Step 2.
The EES sends an ACR information notification to the EEC with the ACR information determined in step 1. The ACR information notification may include ACID to indicate the application context relocation of the AC is complete. If the S-EES has received the successful EEC Context Push response from T-EES, along with registration ID and the registration expiration time in the EEC Context Push relocation procedure, then the ACR information notification towards EEC also includes the registration ID and registration expiration time under EEC context relocation status (for successful status). Upon receiving the target information notification to indicate start of the ACR execution, the EEC avoids triggering a second ACR execution for the same ACR identity (ACID, UE ID, S-EAS endpoint and T-EAS endpoint) until the current ACR execution is completed.
If during the ACR the EES has received the successful EEC Context Push response from the T-EES and the EEC Context Push response includes T-EES selected ACR scenario list in the EEC Context Push relocation procedure, then the ACR information notification towards the EEC includes the list from T-EES as the selected ACR scenario list under EEC context relocation status (for successful status). Upon receiving the ACR complete notification, if the selected ACR scenario list is not available (for successful status), the EEC may either select ACR scenario considering the supported ACR scenarios of AC, EEC, T-EES and T-EAS or request T-EES to select list of ACR scenarios as specified in clause 8.15.
After the ACR complete notification with successful ACR, if the ACR complete notification indicates that EEC context relocation has failed the EEC can trigger EAS Information provisioning procedure to perform a re-selection of the ACR scenarios.
If EEC context does not exist, after the ACR complete notification with successful ACR, the EEC can trigger EAS Information provisioning procedure to select the ACR scenarios.
8.8.3.5.4 Subscription update p. 197
Figure 8.8.3.5.4-1 illustrates the ACR information subscription update procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for the ACR information as specified in clause 8.8.3.5.2.

Step 1.
The EEC sends an ACR information subscription update request to the EES.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized for the operation. If authorized, the EES updates the subscription.
Step 3.
The EES sends an ACR information subscription update response to the EEC.
8.8.3.5.5 Unsubscribe p. 197
Figure 8.8.3.5.5-1 illustrates the ACR information unsubscribe procedure between the EEC and the EES.
Pre-conditions:
- The EEC has subscribed with the EES for the ACR information as specified in clause 8.8.3.5.2.

Step 1.
The EEC sends an ACR information unsubscribe request to the EES.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the EEC, the EES checks if the EEC is authorized for the operation. If authorized, the EES terminates the subscription of the EEC.
Step 3.
The EES sends an ACR information unsubscribe response to the EEC.
8.8.3.6 EELManagedACR procedure p. 198
8.8.3.6.1 General p. 198
This clause introduces a procedure for ACR performed by the Edge Enabler Servers.
When S-EES receives a request for EELManagedACR from S-EAS, the S-EES performs the service operations for the service continuity including detecting the event which may trigger the ACR, making the ACR decision, discovering the T-EAS, accessing and transferring the Application Context to the T-EES/T-EAS, notifying the T-EAS about the available Application Context, notifying the 3GPP network about ACR information, notifying the EEC about the T-EAS information (as per EEC subscription).
The EELManagedACR procedure is designed as an asynchronous operation wherein the S-EES will generate notifications (e.g. failure of any ACR related operation) to the S-EAS while performing the ACR operations.
8.8.3.6.2 Procedure p. 198
8.8.3.6.2.1 General p. 198
This clause describes the procedures for S-EAS to request for EELManagedACR and for T-EAS to subscribe for ACT status notification.
8.8.3.6.2.2 ACR request p. 198
Figure 8.8.3.6.2.2-1 illustrates the procedure for EELManagedACR performed by the Edge Enabler Servers.
Pre-conditions:
- Information related to the S-EES is available with the S-EAS.
- The T-EAS has subscribed to the ACR related event from the T-EES.
- The EEC has subscribed to the ACR related event from the S-EES.

Step 1.
The S-EAS sends an EELManagedACR service request (UE identifier, EAS characteristics for ACR) to request the S-EES to handle all the service operations of the ACR. The S-EAS may initiate this request with S-EES based on different triggers (e.g. when Application Client is connecting to the S-EAS). An address for accessing the Application Context may be provided if available, which allows the S-EES to access the Application Context generated by the S-EAS for ACT.
Step 2.
The S-EES checks whether the requesting EAS is authorized to perform the operation. If it is authorized, the S-EES responds with an EELManagedACR service response. If no address for accessing Application Context is provided by S-EAS in step 1, then the S-EES provides an address for storing the Application Context by S-EAS.
Step 3.
The S-EES determines the EELManagedACR operations to be executed as specified in clause 8.8.2.5.
8.8.3.6.2.3 ACT status subscription p. 199
Figure 8.8.3.6.2.3-1 illustrates the procedure for T-EAS to subscribe for ACT status during EELManagedACR.

8.8.3.6.2.4 ACT status notification p. 199
Figure 8.8.3.6.2.4-1 illustrates the procedure for T-EES to notify the T-EAS about the status of ACT during EELManagedACR.
Pre-conditions:
- ACT between the S-EES and T-EES has been completed.

Step 1.
The T-EES sends ACT status notification to the T-EAS, notifying about the status of the ACT between the Application Context received from the S-EES.
Step 2.
On receiving a notification about successful ACT, the T-EAS may initiate the ACR status update procedure as described in clause 8.8.3.8.
8.8.3.7 Selected T-EAS declaration p. 200
Figure 8.8.3.7-1 illustrates the interactions between the S-EAS and the S-EES for the selected T-EAS declaration.
Pre-conditions:
- The S-EAS has discovered and selected the T-EAS as described in clause 8.8.3.2.

Step 1.
The S-EAS sends Selected target EAS declaration request message to the S-EES. The request includes the information of the selected T-EAS and may include ACID to indicate which AC the T-EAS is intended for.
Step 2.
The S-EES checks whether the requesting EAS is authorized to perform operation. If authorized, the S-EES responds to the received request with Selected target EAS notification declaration response message. The S-EES also determines the selected T-EES based on the declared T-EAS selection, then S-EES checks whether the EEC (serving the ACs) has subscribed for ACR related information.
8.8.3.8 ACR status update procedure p. 200
Figure 8.8.3.8-1 illustrates the procedure for ACR status update, which is triggered by the S-EAS or the T-EAS. In the post-ACR clean up phase of service continuity scenarios described in clause 8.8.2, this procedure may be used by EAS to indicate the status of ACT to their registrar EESs; or used by the T-EAS to update the notification target address and allow the T-EES to indicate the status of EDGE-3 subscription relocation to the T-EAS including subscription ID update for EDGE-3 subscriptions; or both.
Pre-condition:
- The ACT procedure between the S-EAS and the T-EAS is either successfully completed or failed.

Step 1.
The EAS sends ACR status update request message to the EES, the request may include the ACT result (success or failure). When sent by the T-EAS, the request may include a list of EDGE-3 subscription ID(s) and Notification Target Address for which the T-EAS wants to update. In case of EELManagedACR, the ACT result is not included by the T-EAS.
Step 2.
If the request is authorized by the EES, the EES processes the request. When sent by the T-EAS, if the EDGE-3 subscriptions are available in the T-EES or were successfully relocated during the EEC context relocation procedure, the T-EES updates the Notification Target Address if provided by the T-EAS and may update the list of EDGE-3 subscription ID(s) for the EDGE-3 subscriptions.
When the ACR status update request message of step 1 includes the ACT result, it shall also include the UEID and endpoint information of the other EAS involved in the ACT. The EES uses UEID and EAS endpoint information to identify the corresponding ACR. In cases where the ACT result indicates failure of the ACR (i.e. failure with a cause indicating cancellation of the ACR), the T-EES which receives the ACR status update request message removes the transferred EEC context.
Step 3.
The EES responds with ACR status update response message to the EAS.If the EEC context has been established and during the ACR the T-EES has provided the Selected ACR Scenario list to the S-EES as a result of a successful push context response as per clause 8.9.2.3, after the successful ACR the T-EES updates the Session Context IE within the EEC Context in Table 8.2.8-1 by replacing Selected ACR scenario list with the Selected ACR Scenario list in the push context response. The T-EES may send the ACR Selection notification to the T-EAS if the T-EAS has subscribed to such a notification.
8.8.3.9 ACR parameter information procedure |R18| p. 201
Figure 8.8.3.9-1 illustrates the procedure for sending ACR parameters from S-EES to the T-EES and T-EAS. The procedure may be used by the S-EES at the beginning of the ACR execution to provide ACR parameters, e.g. prediction expiration time, to the T-EES and T-EAS. The procedure may also be used during an ongoing ACR to update ACR parameters. This procedure is also applicable for the CES to send ACR parameter information to the T-EES.
Pre-condition:
- The ACR has been launched to the S-EES.

Step 1.
The S-EES sends the ACR parameter information request to the T-EES.
Step 2.
The T-EES checks if the requestor is authorized for this operation. If authorized, the T-EES processes the request.
Step 3.
If the request is authorized and if the T-EAS has subscribed to receive ACR notifications, the EES shall notify the T-EAS by sending an ACR management notification, with "ACT start" event including ACR parameters from the request in step 1, e.g. Prediction expiration time.
Step 4.
In case of service continuity planning, if the T-EAS had included indication of EAS Acknowledgement within ACR management subscribe request, the T-EAS sends EAS Acknowledgement as a response to the ACR management notification. In the Acknowledgement, the T-EAS indicates the acceptance or rejection of the ACT considering ACR parameters (e.g. prediction expiration time).
Step 5.
The EES responds to the requestor's request with an ACR parameter information response message.
8.8.3.10 Selected EES declaration |R18| p. 202
The selected EES declaration request is triggered when an ACR is performed from EAS to CAS. Figure 8.8.3.10-1 illustrates the interactions between the EES and the CAS for the selected EES declaration.
Pre-conditions:
- A serving EES is selected for the EEC and the serving EES decides to inform CAS. The serving EES is the last EES serving the EEC during the ACR from EAS to CAS.
- AC has requested and forwarded the UE ID as per clause 8.14.2.6 while performing ACR from EAS to CAS as described in clause 8.8.2A or the CAS knows UE ID using procedure defined in clause 8.6.5.

Step 1.
The CAS, after knowing the selected EES for the UE, may subscribe to receive ACT status notifications as described in clause 8.8.3.6.2.3 for EELManagedACR, or trigger service continuity procedures towards the selected EES.
The EES sends Selected EES declaration request message to the CAS. The request includes the information of the selected EES and may include ACID to indicate which AC the EES is intended for.
Step 2.
The CAS checks whether the requesting EES is authorized to perform operation. If authorized, the CAS stores the received information.
Step 3.
The CAS responds the request with Selected EES notification declaration response message.
8.8.3.11 ACR event subscription and notification procedure |R19| p. 203
Figure 8.8.3.11-1 illustrates the procedure for the EES to subscribe ACR event exposure service from the ECS and the procedure for the EES to receive ACR event notification from the ECS.
Pre-condition:
- The EES is registered with the ECS.
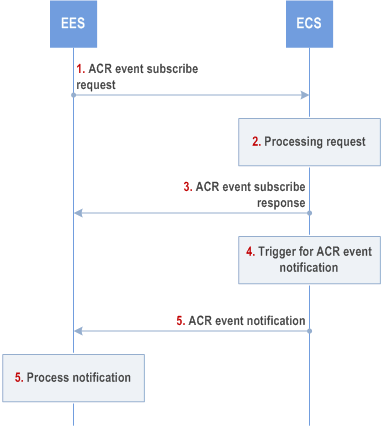
Step 1.
The EES may unsubscribe ACR events by sending an ACR event unsubscribe request to the ECS, then the ECS terminates corresponding subscription and responds with ACR event unsubscribe response.
The EES involved in edge application facilitation (e.g. being informed by EEC with EAS information provisioning with EAS selection) subscribes to ECS provided ACR event exposure service.
For EDN overload event, the EDN information is included for ECS to monitor EDN load.
Step 2.
If the request is authorized, the ECS processes the request.
For EDN overload event, the ECS subscribed to ADAES edge load analytics (statistics or prediction) as specified in clause 8.8.2.1 of TS 23.436) for monitoring EDN load.
Step 3.
The ECS responds the EES with ACR event subscribe response.
Step 4.
An event occurs at the ECS that satisfies trigger conditions for notification.
For EDN overload event, the ECS is notified by the ADAES for EDN load stats information. If the ECS detects that the EDN identified by DNN and DNAI(s) is overloaded, the ECS determines impacted EES(s) of the same EDN. The ECS also determines a relocation ratio that will mitigate the EDN overload situation for the impacted EES(s).
Step 5.
The ECS notifies each impacted EES with EDN overload event in ECS event notification.
Step 6.
Based on the received relocation ratio, the EES determines applications to be relocated and also impacted UEs (and EECs). Further, the EES continues with ACR execution phase as described in clause 8.8.2.5 for each impacted EEC in UE.