Content for TS 23.435 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4…
5…
7…
9…
9.4…
9.5…
9.6…
9.7…
9.8…
9.9…
9.10…
9.11…
9.12…
9.13…
9.14…
9.15…
9.16…
9.17…
9.18…
A…
9.15 Network slice fault management capability exposure
9.15.1 General
9.15.2 Procedure
9.15.2.1 Procedures on network slice fault management capability exposure
9.15.3 Information flows
9.15.4 APIs
9.15.4.1 General
9.15.4.2 SS_NSCE_FaultDiagnosis API
9.15.4.2.1 General
9.15.4.2.2 Fault_Diagnosis_Subscribe
9.15.4.2.3 Fault_Diagnosis_Notification
...
...
9.15 Network slice fault management capability exposure p. 98
9.15.1 General p. 98
5GS is required to provide suitable APIs to allow a trusted third-party to monitor the network slice used for the third-party according to operator policies. And network diagnostics is of key importance that helps with scanning, diagnosing and identifying problems within a network. Diagnostics includes gathering data and continuously providing sufficient fault diagnosis results that characterize the quality of the network connections and services. Exposure of relevant (and possibly aggregated) performance parameters ensures a quick reaction in case of failure as well as identifying network connectivity, performance and other related problems. Also, the alarm data from different sources (e.g., OAM, VAL server, NSCE client) can be used to help the third-party to diagnose the fault problem of the services, locate the fault causes, and to be aware of the potential fault. In TS 28.545, the fault supervision management services are standardized by which the alarm of the network slice instance from network resource aspects can be subscribed and reported. This alarm information together with the application function's fault report and communication service related knowledge can be utilized by the NSCE to diagnose the cause of the service performance deterioration, locate the fault of the communication services, and expose the fault report to the third-party.
For example, if the status of the required communication is not correct, the SEAL/NSCE derives this alarm information from application functions. In this case, it is the SEAL/NSCE's responsibility to detect whether this fault is caused by the 5GS network or not and exposed the fault report to the third-party. If it is, then the SEAL/NSCE may inform the management functions the location of the fault and ask for the maintenance of the managed functions to clear the fault.
This service provides a possible procedure to illustrate the network slice fault management capability exposed by NSCE server. The performance data and alarm data from multiple sources is helpful to characterize the quality of the network connection.
9.15.2 Procedure p. 98
9.15.2.1 Procedures on network slice fault management capability exposure p. 98
Figure 9.15.2.1-1 illustrates the network slice fault management process to address the key issue 4 of network slice fault management.
Pre-conditions:
- The network slice enabler layer is capable to interact with NEF and OAM system.
- The VAL server has checked the status of application layer.
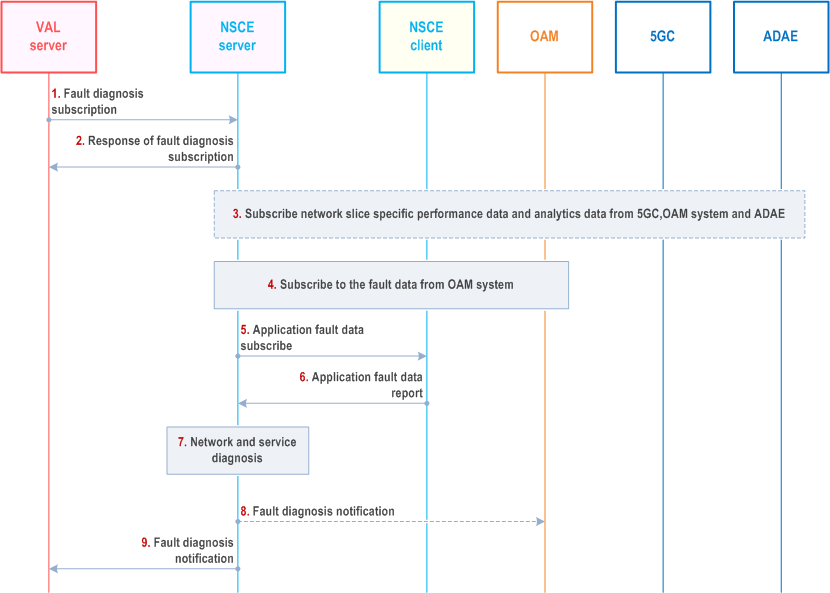
Step 1.
The VAL server sends a subscription to NSCE server to subscribe the fault diagnosis of the applications and networks. This request may be triggered by the errors of the applications detected by the VAL server itself, or the VAL server may periodically collect the fault diagnostic report subscribing to the NSCE.
Step 2.
NSCE server sends the response of the subscription to VAL server.
Step 3.
Optionally, on receiving the request from VAL server, NSCE server subscribes the performance data of network slice from 5GS. For OAM system, the APIs defined in clause 11.3 of TS 28.532 is utilized. For CN functions, the APIs of Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo service defined in clause 7.3 of TS 23.288 can be utilized.
The analytics data defined in clause 6.3 to clause 6.14 of TS 23.288, network slice instance related performance data defined in clause 5 of TS 28.552 and network analytics data in clause 8.3 and clause 8.4 of TS 28.104 exposed by OAM system may be acquired. Also, the analytics result of slice-specific performance and slice usage analytics defined in TS 23.436 can be utilized.
Step 4.
NSCE server subscribes the alarms of network slice instances from OAM system via the procedures defined in clause 6.1 of TS 28.545, and the alarms are defined in clause 4.1.1.1 of TS 32.111-1, e.g., the fault of communication, environmental, equipment, processing error, QoS for device/resource/file/functionality/smallest.
Step 5.
NSCE server may subscribe the alarm information (e.g., the 5GS network is not work or the required performance is under the threshold which leads the service's problem) collected by NSCE client if possible. The information collected by the NSCE client depends on the third-parties' requirements and implementation.
Step 6.
NSCE client report the requested fault information to NSCE server.
Step 7.
Every time the notifications from the OAM, NSCE client or ADAEs are received, NSCE server correlates this data, diagnoses the causes of the fault of the applications or services by analysing the fault information from different sources and prepares report for the VAL to be notified about the respective fault event. For example, the RAN function of the slice instance which is utilized to support the service of the smart grid application, for a certain time duration, the smart grid suffered the bad experience caused by Service Availability Failure Events, and in the RAN function is detected continuously to report an alarm of environmental fault in the same time duration, then the environment fault may be the root cause of the Service Availability Failure and should be prioritized to be solved. The fault may be identified with "critical", "major", "minor", "ignore" to show its prioritization.
Step 8.
If the NSCE server detects that the application/service error (reported from NSCE client) is caused by the 5GS, the VAL server may send the fault diagnosis report to OAM system to indicate the server fault which causes the application/service failure by utilizing the NSCE-OAM interface.
Step 9.
NSCE server send a notification to VAL server with the fault diagnostics report prepared in step 7.
9.15.3 Information flows p. 100
9.15.3.1 General p. 100
The following information flows are specified for the network slice fault management capability exposure.
9.15.3.2 Fault diagnosis subscription request p. 100
Table 9.15.3.2-1 describes information elements for fault diagnosis subscription.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VAL server ID | M | The identifier of the VAL server. |
| VAL service ID | M | The identifier of the VAL service for which the request applies. |
| VAL UE ID list | O | The list of VAL UE IDs for which the request applies. |
| Fault diagnosis information | O | Indicate what kind of fault is need for the subscription, e.g., time, specific problem, etc. |
| Network slice related Identifier(s) | O | Identifier(s) of the network slice to be monitored. |
9.15.3.3 Response of fault diagnosis subscription p. 100
Table 9.15.3.3-1 describes information elements for response of fault diagnosis subscription.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription. |
| Result | M | The result of the request (positive or negative acknowledgement). |
9.15.3.4 Fault diagnosis notification p. 100
Table 9.15.3.4-1 describes information elements for fault diagnosis notification.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription. |
| Fault Report ID | M | Identifier of the fault Report. |
| FaultReport | M | The report of the fault diagnosis. |
| > CorrelatedAlarmList | M | The list of the correlated alarms. |
| >> CorrelatedAlarm | M | The correlated alarms. |
| > rootCause | M | The root cause of the fault. |
9.15.4 APIs p. 101
9.15.4.1 General p. 101
Table 9.15.4.1-1 illustrates the APIs for the network slice fault management capability exposure.
| API Name | API Operations | Communication Type | Consumer(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS_ | Fault_Diagnosis_Subscribe | subscription / notification | VAL server |
| Fault_Diagnosis_Notification |
9.15.4.2 SS_NSCE_FaultDiagnosis API p. 101
9.15.4.2.1 General p. 101
API description:
This API enables the VAL server to communicate with the network slice capability enablement server to request the fault diagnosis over NSCE-S.
9.15.4.2.2 Fault_Diagnosis_Subscribe p. 101
API operation name:
Fault_Diagnosis_Subscribe
Description:
The consumer subscribes to the network slice fault diagnosis
Known Consumers:
VAL server
Inputs:
See Table 9.15.3.2-1
Outputs:
See Table 9.15.3.3-1
9.15.4.2.3 Fault_Diagnosis_Notification p. 101
API operation name:
Fault_Diagnosis_Notification
Description:
The consumer notifies the network slice fault diagnosis results
Known Consumers:
VAL server
Inputs:
None
Outputs:
See Table 9.15.3.4-1