Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
6c Procedures and flows for SRVCC Emergency Session
6c.1 IMS Emergency origination flow for PS to CS SRVCC
6c.2 SRVCC session transfer of IMS emergency session for PS to CS
6c.2.1 SRVCC session transfer of an active IMS emergency session for PS to CS (single EATF instance)
6c.2.2 SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS (single EATF instance)
6c.2.3 SRVCC session transfer of an active IMS emergency session for PS to CS when multiple EATF instances are deployed
6c.2.4 SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS when multiple EATF instances are deployed
6c.3 SRVCC Support for UEs in Normal Mode
6c.4 SRVCC Support for UEs in Limited Service Mode
6d Procedures and flows for DRVCC Emergency Session for WLAN
6d.1 IMS Emergency origination flow for PS to CS DRVCC
6d.2 DRVCC session transfer of IMS emergency session for PS to CS
...
...
6c Procedures and flows for SRVCC Emergency Session |R9| p. 169
6c.1 IMS Emergency origination flow for PS to CS SRVCC p. 169
Figure 6c.1-1 provides flow for an emergency session established in IMS, illustrating how the emergency session is anchored in the EATF.
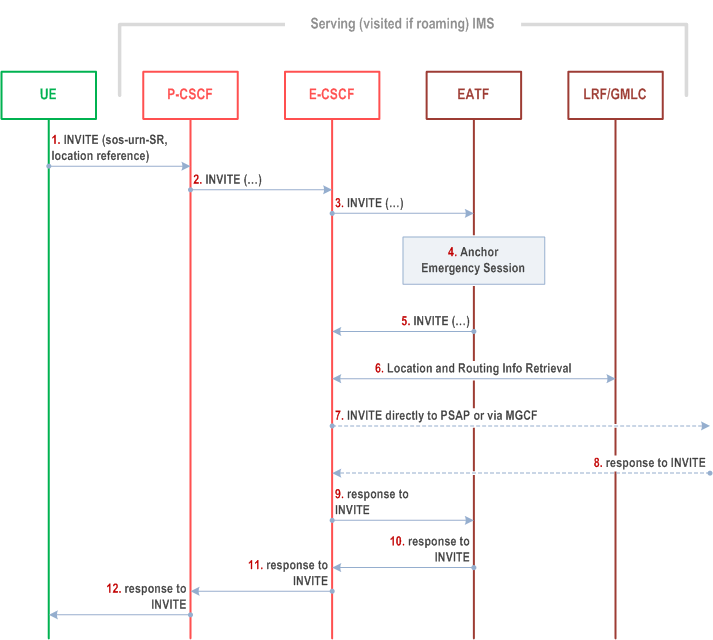
Step 1.
The UE initiates an IMS emergency session over NG-RAN (see TS 23.501), EPS or GPRS and the procedures defined in TS 23.167. This involves the UE generating a SIP INVITE containing the UE's location information and the equipment identifier.
For IMS emergency call over EPS (e.g. after transfer from NG-RAN, see TS 23.501) or GPRS, if the UE supports the UE procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS as described in the clause 6c.2.2, the UE includes in the SIP INVITE an indication of support of the UE procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS.
Step 2.
The P-CSCF selects an E-CSCF and forwards the INVITE to the E-CSCF.
Step 3.
The E-CSCF sends the INVITE to the EATF.
Step 4.
The EATF (acting as a routing B2BUA) anchors the emergency session, i.e. the EATF is inserted in the signalling path which invokes a 3pcc for enablement of Access Transfers for the call as specified in clause 6.3.1.3.
Step 5.
The EATF creates a new INVITE and sends it back to E-CSCF.
Step 6.
For this optional procedure, refer to TS 23.167.
Step 7.
The E-CSCF uses the routing information to format the INVITE message, and it sends it directly to the PSAP, or to the PSAP via the MGCF.
Step 8.
The E-CSCF receives a response to the INVITE.
Step 9.
The E-CSCF forwards to the EATF the response to the INVITE.
Step 10.
The EATF forwards to the E-CSCF the response to the INVITE. If the network supports the network procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS as described in the clause 6c.2.2, and the INVITE request received in step 3 included an indication of support of the UE procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS, then the EATF includes in the response to the INVITE an indication of support of the network procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS.
Step 11.
The E-CSCF forwards to the P-CSCF the response to the INVITE.
Step 12.
The P-CSCF forwards to the UE the response to the INVITE.
6c.2 SRVCC session transfer of IMS emergency session for PS to CS p. 170
6c.2.1 SRVCC session transfer of an active IMS emergency session for PS to CS (single EATF instance) |R15| p. 170
Figure 6c.2.1-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is active session. This applies when a single EATF instance is deployed (see clause 6c.2.3 for multiple EATF instances).
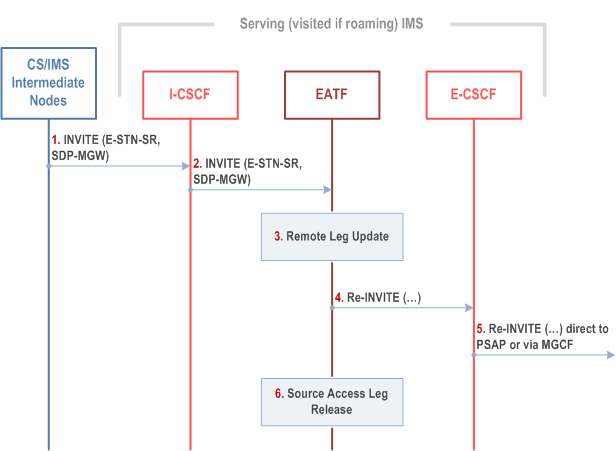
Step 1.
MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The I-CSCF routes the INVITE directly to the EATF via I5 by using similar procedures to that defined in TS 23.228 for PSI based Application Server termination.
Step 3 - 4.
The EATF uses the E-STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer is requested. The EATF proceeds with the Access Transfer of the active session with bi-directional speech for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5. For SRVCC session transfer of an eCall over IMS, the EATF indicates in the reINVITE that the EATF shall exclude INFO requests for any Info Packages related to eCall over IMS as defined in Section 5.2.2 of RFC 6086.
Step 5.
The E-CSCF forwards the Re-INVITE to the MGCF associated with the PSAP if the PSAP is located in the PSTN or CS Domain (the u-plane path is switched between the UE and the MGW) or the Re-INVITE is sent directly to an IP-capable PSAP (the u-plane path between the UE and the PSAP is switched end-to-end).
Step 6.
When session modification procedures complete, the source access leg (i.e. the access leg previously established over IMS) is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6c.2.2 SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS (single EATF instance) |R15| p. 171
Figure 6c.2.2-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is in early dialogue phase. This applies when a single EATF instance is deployed (see clause 6c.2.4 for multiple EATF instances).
This flow assumes that the UE indicated to the EATF the support of the UE procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS and that the EATF indicated to the UE the support of the network procedures for the SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS, as described in clause 6c.1.
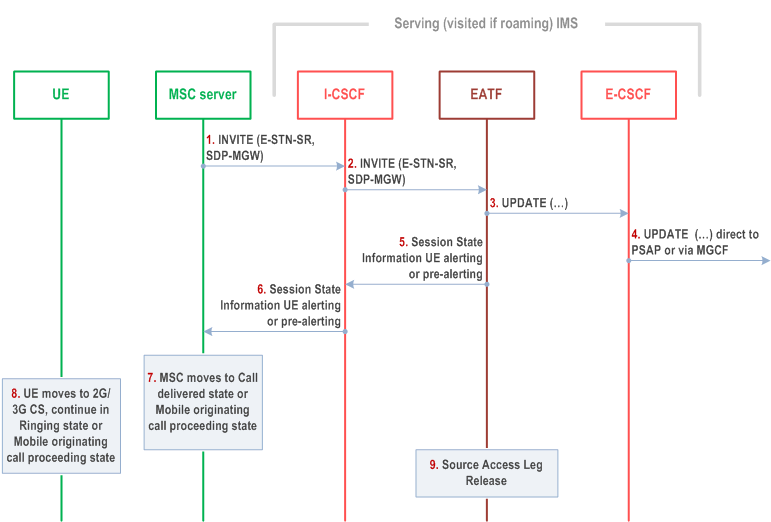
Step 1.
MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The I-CSCF routes the INVITE directly to the EATF via I5 by using similar procedures to that defined in TS 23.228 for PSI based Application Server termination.
Step 3.
The EATF uses the E-STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer is requested. The EATF proceeds with the Access Transfer of the session in early dialogue phase (i.e. pre-alerting or alerting) with bi-directional speech for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 4.
The E-CSCF forwards the UPDATE to the MGCF associated with the PSAP if the PSAP is located in the PSTN or CS Domain (the u-plane path is switched between the UE and the MGW) or the UPDATE is sent directly to an IP-capable PSAP (the u-plane path between the UE and the PSAP is switched end-to-end).
Step 5.
The EATF provides Session State Information on the outgoing speech call in early dialogue phase (e.g., pre-alerting or alerting state).
Step 6.
The E-CSCF forwards the Session State Information to the MSC Server.
Step 7.
The MSC moves to the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Delivered or Mobile Originating Call Proceeding state as specified in TS 24.008.
Step 8.
The UE has received the HO command as described in TS 23.216. The UE determines the local call state in the SIP session, and creates the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Delivered in TS 24.008 for the alerting state, or Mobile Originating Call Proceeding for the pre-alerting state. The UE ensures that the same ring back tone or announcement if any is played to the end user. If the voice+video media is played to the UE in PS domain, and the CS domain does not support video media, only the voice media shall be played to the UE after the call is transferred to CS domain from PS domain, regardless of whether the media is locally generated by the UE or is network-generated to the UE.
Step 9.
When session modification procedures complete and after delivering the Session State Information, the source access leg (i.e. the access leg previously established over IMS) is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6c.2.3 SRVCC session transfer of an active IMS emergency session for PS to CS when multiple EATF instances are deployed |R16| p. 172
6c.2.3.1 Alternative procedure based on forking p. 172
Figure 6c.2.3.1-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is active session and multiple EATF instances are deployed.
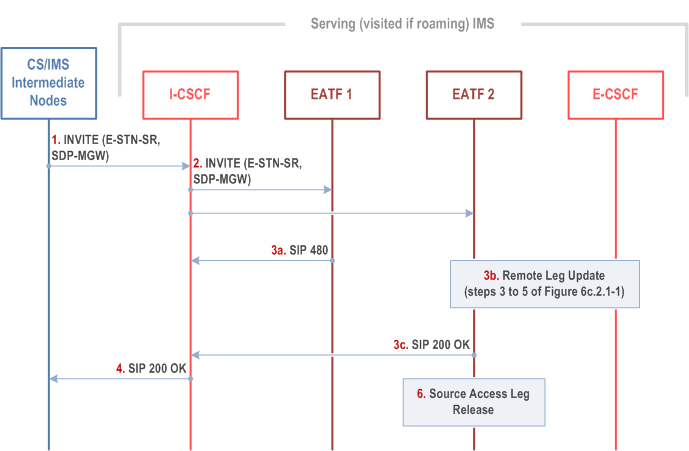
Step 1.
Same as step 1 of Figure 6c.2.1-1: the MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The I-CSCF creates multiple INVITE transactions: one INVITE per configured EATF instance.
Step 3.
Each EATF instance checks whether the equipment identifier matches with any transferable session:
Step 3a.
if no dialog was associated with the domain transfer request, the EATF rejects it (step 3a).
Step 3b, 3c.
if there is a match, the EATF proceeds with the Access Transfer (steps 3 to 5 of Figure 6c.2.1-1) and sends a 200 OK response to the I-CSCF.
Step 4.
The I-CSCF forwards the 200 OK response towards the MSC Server.
Step 6.
Same as step 6 of Figure 6c.2.1-1.
6c.2.3.2 Alternative procedure based on redirection p. 173
The solution is based on the I-CSCF using existing procedures defined in TS 24.229 related to SIP response results to redirect a session to a backup EATF when an EATF has failed.
Figure 6c.2.3.2-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is active session and multiple EATF instances are deployed.
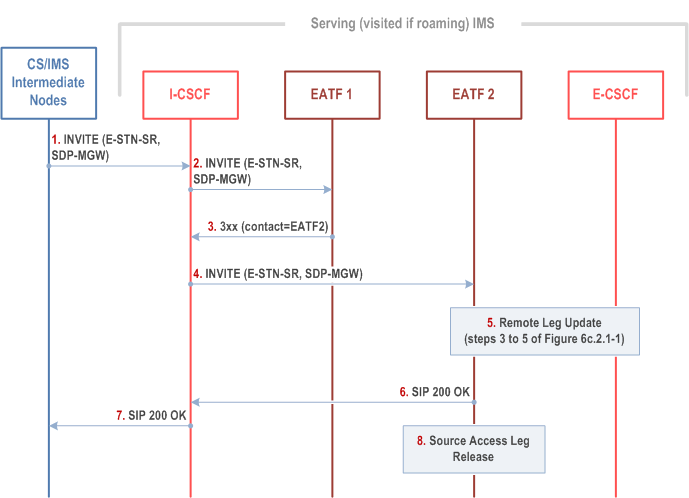
Step 1.
MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The I-CSCF forwards te SIP INVITE to the target EATF instance EATF-1.
Step 3.
The target instance EATF-1 returns a 3xx response and incudes the contact address(es) for redundant instance(s) of EATF(s) that may have anchored the IMS session.
Step 4.
The I-CSCF forwards the SIP INVITE to (one of) the contact(s) in the returned 3xx, EATF-2.
Step 5.
The EATF returns a SIP 200 OK to the I-CSCF.
Step 6.
I-CSCF returns SIP 200 OK response towards the MSC Server.
Step 7.
MSC server returns SIP 200 OK to the UE.
Step 8.
Same as step 6 of Figure 6c.2.1-1.
6c.2.4 SRVCC session transfer of an IMS emergency session in early dialogue phase for PS to CS when multiple EATF instances are deployed |R16| p. 174
6c.2.4.1 Alternative procedure based on forking p. 174
Figure 6c.2.4.1-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is in early dialogue phase.
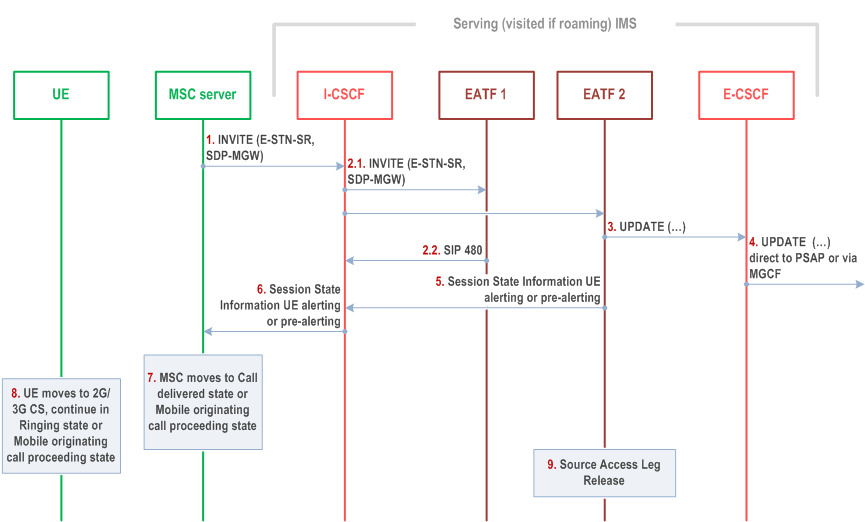
Step 1.
Same as step 1 of Figure 6c.2.2-1: the MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The I-CSCF creates multiple INVITE transactions: one INVITE per configured EATF instance.
Step 2.2.
If no dialog is associated with the domain transfer request, the EATF rejects it.
Step 3 - 9.
Same as corresponding steps in Figure 6c.2.2-1.
6c.2.4.2 Alternative procedure based on redirection p. 174
Figure 6c.2.4.2-1 provides flow for SRVCC for IMS emergency session, when the IMS emergency session is in early dialogue phase.
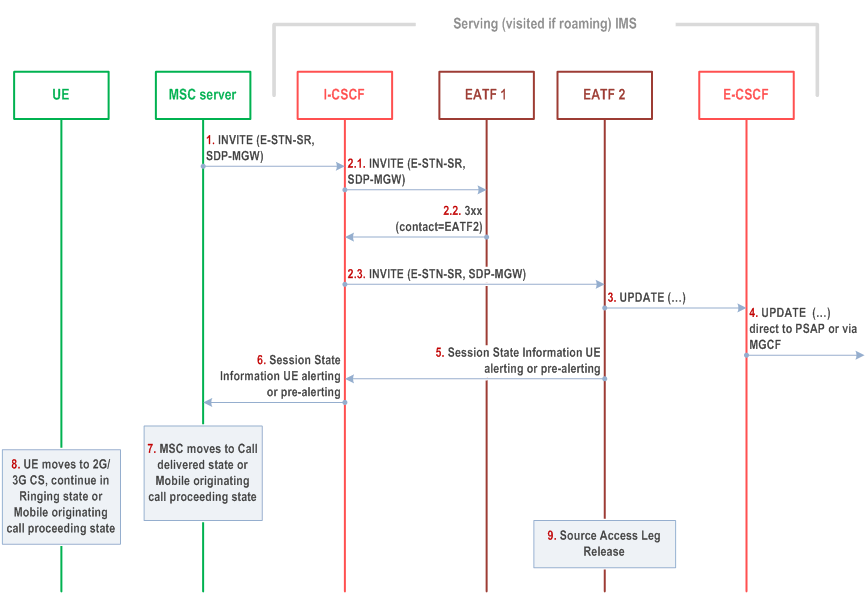
Step 1.
MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-SR and it includes the equipment identifier.
Step 2.1.
The I-CSCF forwards the SIP INVITE to target instance EATF-1.
Step 2.2.
The target instance EATF-1 returns a 3xx response and incudes the contact address(es) for a redundant instance(s) EATF(s) that may have anchored the IMS session.
Step 2.3.
The I-CSCF forwards the SIP INVITE to (one of) the contact(s) in the returned 3xx, EATF-2.
Step 3 - 9.
Same as corresponding steps in Figure 6c.2.2-1.
6c.3 SRVCC Support for UEs in Normal Mode p. 175
If the MSC enhanced for PS to CS SRVCC has a SIP interface, it shall use the mechanism specified in TS 24.229 additionally to carry the equipment identifier to the EATF.
If the MSC Server is enhanced for ICS as defined in TS 23.292, then it performs IMS registration after the transfer of the session is completed successfully.
If the MSC enhanced for PS to CS SRVCC does not have a SIP interface, it shall convey the equipment identifier by using the IAM message to the MGCF. The MGCF shall use the mechanism specified in TS 24.229 additionally to carry the equipment identifier to the EATF.
The EATF can then correlate the call legs according to the equipment identifier.
6c.4 SRVCC Support for UEs in Limited Service Mode p. 175
To support SRVCC procedure for UEs in Limited Service Mode for PS to CS, the MSC enhanced for SRVCC will setup the call leg towards the EATF with the UE's equipment identifier.
If the MSC enhanced for PS to CS SRVCC has a SIP interface, it shall use the mechanism specified in TS 24.229 to carry equipment identifier to the EATF.
If the MSC enhanced for PS to CS SRVCC does not have a SIP interface, it shall convey the equipment identifier by using the IAM message to the MGCF. The MGCF shall use the mechanism specified in TS 24.229 to carry equipment identifier to the EATF.
6d Procedures and flows for DRVCC Emergency Session for WLAN |R14| p. 176
6d.1 IMS Emergency origination flow for PS to CS DRVCC p. 176
This procedure is only applicable if UE uses WLAN access to EPC via s2a or s2b, see TS 23.167.
Figure 6d.1-1 provides flow for an emergency session established in IMS, illustrating how the emergency session is anchored in the EATF.
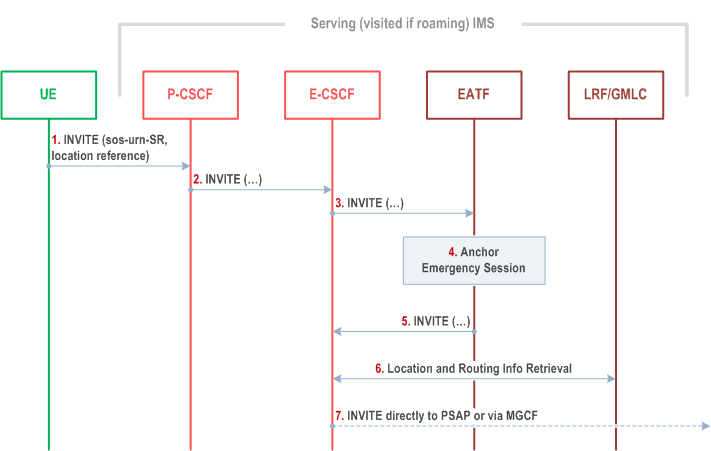
Step 1.
The UE initiates an IMS emergency session over WLAN access to EPC as defined in TS 23.167. This involves the UE generating a SIP INVITE containing the UE's location information and the equipment identifier.
Step 2.
The P-CSCF selects an E-CSCF and forwards the INVITE to the E-CSCF.
Step 3.
The E-CSCF sends the INVITE to the EATF.
Step 4.
The EATF (acting as a routing B2BUA) anchors the emergency session, i.e. the EATF is inserted in the signalling path which invokes a 3pcc for enablement of Access Transfers for the call as specified in clause 6.3.1.3. EATF allocates an E-STN-DR for this session. The INVITE contains information (network provided PANI header) that this call is via WLAN access and this can be used to trigger the E-STN-DR allocation. This E-STN-DR is return back to the UE in the SIP response message to #3.
Step 5.
The EATF creates a new INVITE and sends it back to E-CSCF.
Step 6.
For this optional procedure, refer to TS 23.167.
Step 7.
The E-CSCF uses the routing information to format the INVITE message, and it sends it directly to the PSAP, or to the PSAP via the MGCF.
6d.2 DRVCC session transfer of IMS emergency session for PS to CS p. 177
Figure 6d.2-1 provides flow for DRVCC for IMS emergency session.
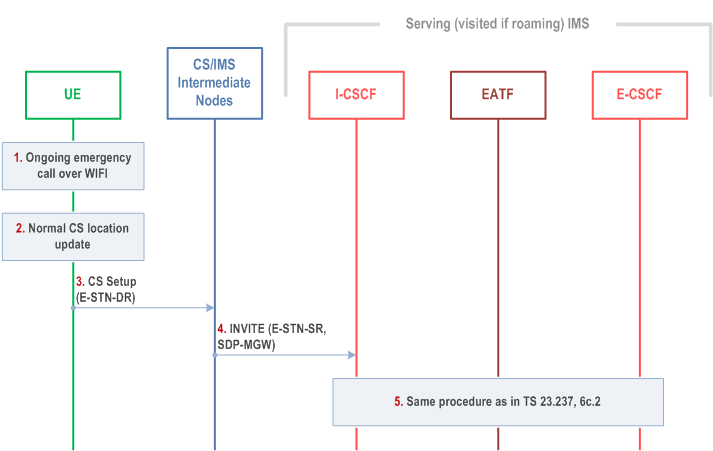
Step 1.
UE has an active emergency session over WLAN and have received E-STN-DR from IMS (EATF) for this session. UE determines that handover to CS RAT is needed (based on UE implementation).
Step 2.
UE performs normal CS location update if it has not yet attached to the CS domain.
Step 3.
While the IMS emergency call is on-going/active, UE starts a normal CS call setup using the E-STN-DR.
Step 4-5.
MSC Server initiates the session transfer with the E-STN-DR and follow the same procedure as defined in clause 6c.2 with the following updates:
- Based on configuration, MSC Sever is aware the E-STN-DR is within a range of numbers that are defined for dual radio emergency session continuity procedure and can trigger priority call handling if needed.
- The EATF uses the E-STN-DR to determine that Access Transfer is requested and for correlating with the source access leg for which the Access Transfer is needed.