Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
6.3.3 Media Adding/Deleting
6.3.3.1 Local End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing CS session
6.3.3.2 Local End Initiation case: Incorporating existing CS media in new IMS Session and Gm Service Control
6.3.3.3 Local End Initiation case: Adding PS media to IMS session with CS media
6.3.3.4 Remote End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing CS session
6.3.3.5 Remote End Initiation case: Incorporating existing CS media in new IMS Session and Gm Service Control
6.3.3.6 Remote End Initiation case: Adding PS media to IMS session with CS media
6.3.3.7 Local End Initiation case - Removing media from split CS and PS sessions
6.3.3.8 Remote End Initiation case - Removing media from split CS and PS sessions
6.3.3.9 Local End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing PS session
6.3.3.10 Remote End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing PS session
6.3.3.11 Local End Initiation case: Removing media from split PS sessions
6.3.3.12 Remote End Initiation case: Removing media from split PS sessions
6.3.5 Service continuity for ICS UE using MSC Server assisted mid-call feature while maintaining CS media
...
...
6.3.3 Media Adding/Deleting p. 94
6.3.3.1 Local End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing CS session p. 94
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.1-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 adds PS media flow(s) (e.g. video) to an existing multimedia session that only contains CS media. As a post condition the UE-1 has an ongoing CS call and a related IMS session with the remote end.
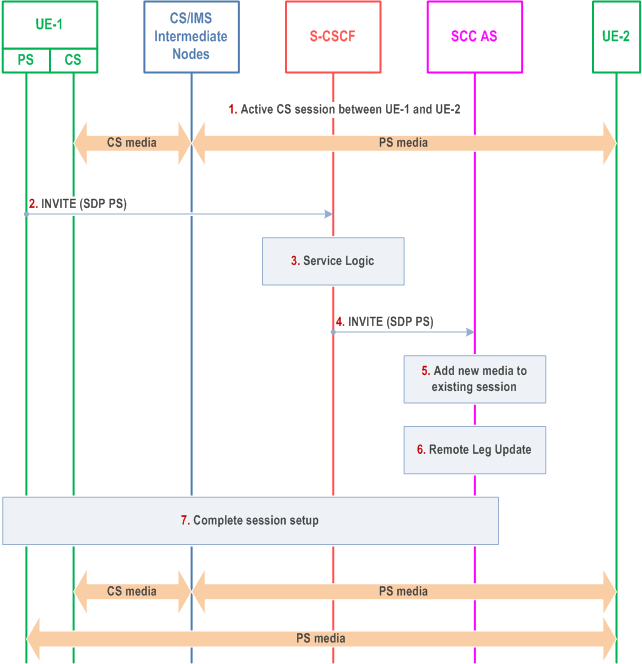
Step 1.
A multimedia session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.1 and 7.4.2.1 of TS 23.292, respectively, i.e. UE-1 is not using the ICS capability and therefore not using the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
UE-1 requests to add one or more PS media component(s) to the existing CS Call by sending an INVITE containing description of the new PS media towards SCC AS to establish a new Access Leg. UE-1 provides description of the new media and the information necessary for the SCC AS to identify the existing session.
Step 3.
The S-CSCF executes any service logic as appropriate.
Step 4.
The S-CSCF sends the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 5.
The SCC AS determines that the INVITE is related to an existing session using the information provided by UE-1 and decides to add the new media flow to the session.
Step 6.
The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg Update using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 7.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE-1 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.2 Local End Initiation case: Incorporating existing CS media in new IMS Session and Gm Service Control p. 95
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.2-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 adds PS media component(s) (e.g. video) and Gm Service Control Signalling Path to an existing multimedia session that only contains CS media. Following this scenario the session is controlled using ICS capability.
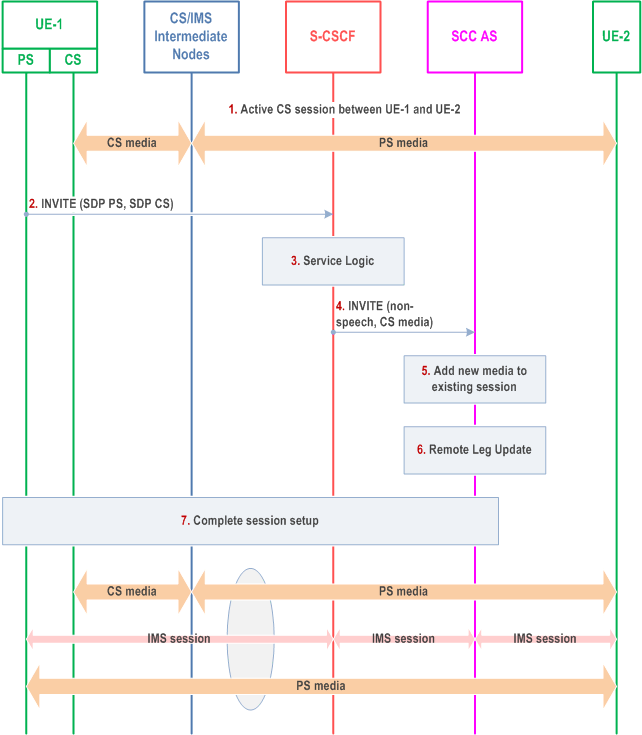
Step 1.
A multimedia session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.1 and 7.4.2.1 of TS 23.292, respectively i.e. UE-1 is not using the ICS capability and therefore not using the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
UE-1 requests to add one or more PS media component(s) and to control the CS media using ICS capabilities by an INVITE towards SCC AS to establish a new session. The request contains the description of the new PS media and indicates that control of the existing CS media is transferred to the new session. UE-1 provides information necessary for the SCC AS to identify the existing session and to request addition of the media flow to the existing session.
Step 3.
The S-CSCF executes any service logic as appropriate.
Step 4.
The S-CSCF sends the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 5.
The SCC AS determines that the INVITE is related to an existing session using the information provided by UE-1 and adds the new media flow to the session.
Step 6.
The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg update using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 7.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE-1 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.3 Local End Initiation case: Adding PS media to IMS session with CS media p. 96
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.3-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 adds PS media component(s) (e.g. video) to an existing multimedia session that contains CS media and is controlled using ICS capability.
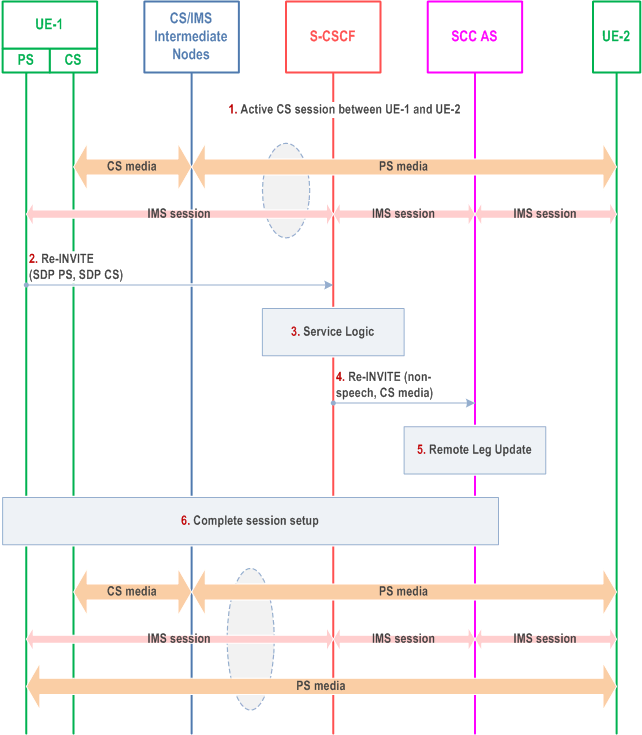
Step 1.
An IMS session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.2.4 and 7.4.2.2.2 of TS 23.292, respectively i.e. UE-1 is using the ICS capability and therefore the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
UE-1 initiates a request to add the PS media flow(s) to the existing IMS session.
Step 3.
The S-CSCF executes any service logic as appropriate.
Step 4.
The S-CSCF sends the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 5.
The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg Update using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 6.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE-1 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.4 Remote End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing CS session p. 97
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.4-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 has an existing CS session with UE-2 and UE-2 adds new media flow(s) to the session and the new media flow is delivered via PS access towards UE-1.
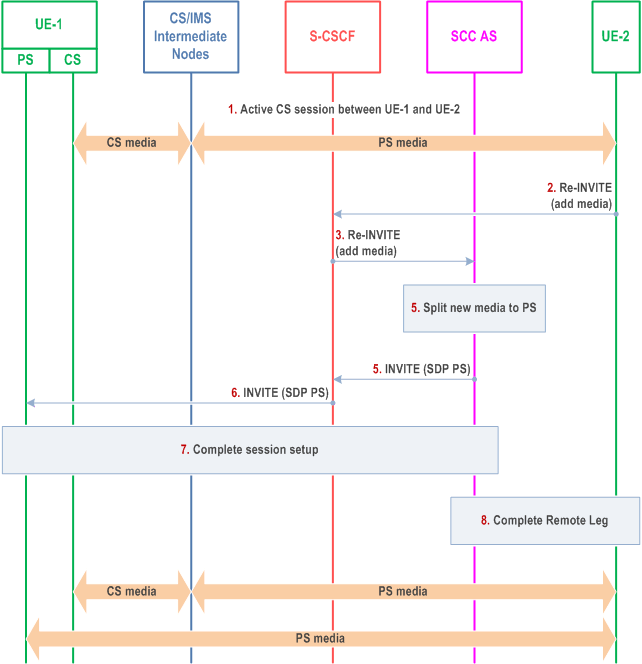
Step 1.
A CS session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.1 and 7.4.2.1 of TS 23.292, respectively, i.e. UE-1 is not using the ICS capability and therefore not using the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
S-CSCF receives a request from UE-2 to add new PS media flow(s) (e.g. video) to the existing session.
Step 3.
S-CSCF forwards the request to SCC AS, which is anchored on the session path.
Step 4.
The T-ADS function in the SCC AS decides that the new media flow is delivered to UE-1 via PS access and therefore splits the session. T-ADS in the SCC AS uses the C-MSISDN for correlation, and then ensures the split session is delivered only to UE-1, and not delivered to other UEs of the user.
Step 5-6.
SCC AS initiates a new session towards UE-1. The request includes the new PS media flow. The SCC AS includes enough information within the session request to allow UE-1 to correlate this new session with the existing CS session.
Step 7.
UE-1 accepts the new session and completes the session setup via PS access.
Step 8.
The SCC AS completes the Remote Leg towards UE-2 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.5 Remote End Initiation case: Incorporating existing CS media in new IMS Session and Gm Service Control p. 98
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.5-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 has an existing CS session with UE-2 and UE-2 adds new media flow(s) to the session. The new media flow(s) is delivered via PS access towards UE-1 and Gm Service Control Signalling Path is added. Following this scenario the session is controlled using ICS capability.
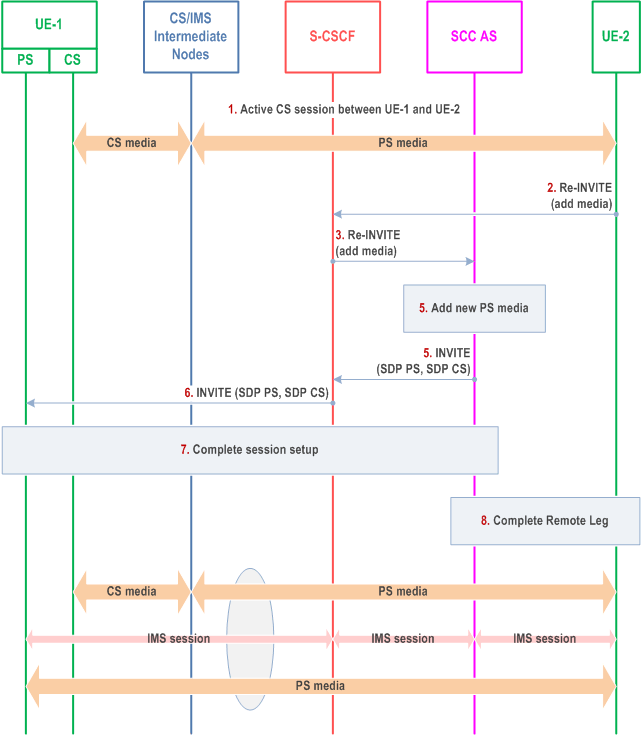
Step 1.
A CS session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.1 and 7.4.2.1 of TS 23.292, respectively, i.e. UE-1 is not using the ICS capability and therefore not using the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
S-CSCF receives a request from UE-2 to add new PS media flow (e.g. video) to the existing session.
Step 3.
S-CSCF forwards the request to SCC AS, which is anchored on the session path.
Step 4.
The T-ADS function in the SCC AS decides that the new media flow is delivered to UE-1 via PS access and therefore initiates a new session using the Gm reference point using ICS capabilities as specified in TS 23.292. SCC AS decides to establish the Gm Service Control Signalling Path together with the media addition using the ICS capability. T-ADS in the SCC AS uses the C-MSISDN for correlation, and then ensures the new session is delivered only to UE-1, and not delivered to other UEs of the user.
Step 5-6.
SCC AS initiates a new session towards UE-1. The request includes the new PS media and indicates that the existing CS media is moved to and controlled over this session.
Step 7.
UE-1 accepts the new session and completes the session setup via PS access.
Step 8.
The SCC AS completes the Remote Leg towards UE-2 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.6 Remote End Initiation case: Adding PS media to IMS session with CS media p. 99
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.6-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 has an existing session that contains CS media and Gm Service Control Signalling Path with UE-2 and UE-2 adds new media to the session. The new media is delivered together with the Gm Service Control Signalling Path towards UE-1.
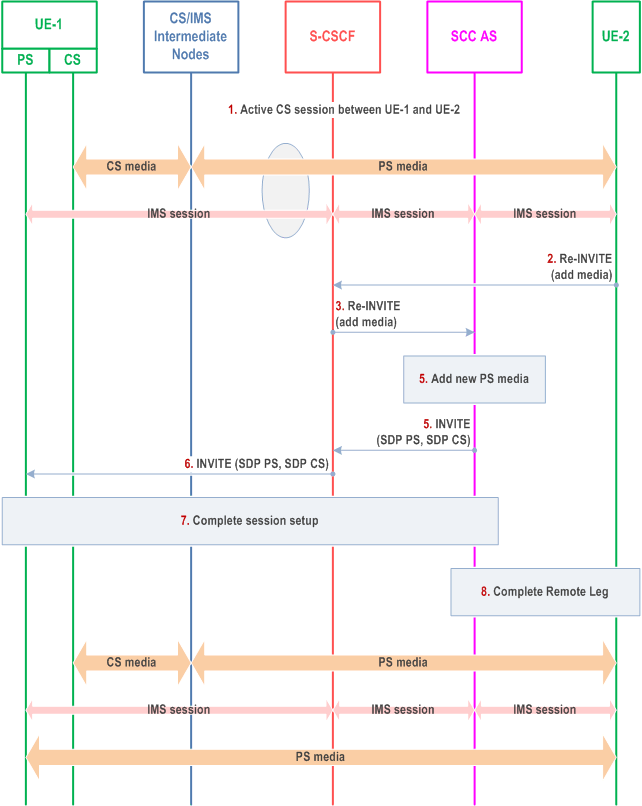
Step 1.
A CS session between UE-1 and UE-2 is established as either originated or terminated session with CS media as described in clauses 7.3.2.2.4 and 7.4.2.2.2 of TS 23.292, respectively i.e. UE-1 is using the ICS capability and therefore the Gm reference point during the session establishment.
Step 2.
S-CSCF receives a request from UE-2 to add new PS media flow(s) (e.g. video) to the existing session.
Step 3.
S-CSCF forwards the request to SCC AS, which is anchored on the session path.
Step 4.
The T-ADS function in the SCC AS decides that the new media flow is delivered to UE-1 via PS access. The SCC decides to add the PS media to the existing Service Control Signalling Path that is established via Gm.
Step 5-6.
SCC AS initiates a request to add the PS media to the existing Service Control Signalling Path towards UE-2.
Step 7.
UE-1 accepts the new session and completes the session setup via PS access.
Step 8.
The SCC AS completes the Remote Leg towards UE-2 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
6.3.3.7 Local End Initiation case - Removing media from split CS and PS sessions p. 100
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.7-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 has a CS call and an IMS multimedia session with the remote end in a manner that they are presented to UE-2 as one IMS session by the SCC AS and then removes PS media flow(s) by releasing the PS Access Leg.
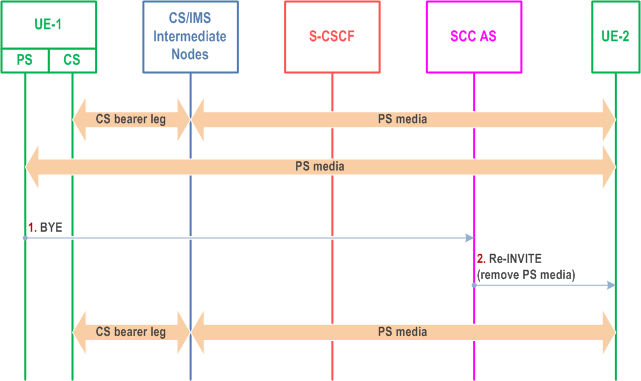
Step 1.
UE-1 uses standard IMS procedures defined in TS 23.228 to remove one or more PS media flows from the session.
Step 2.
SCC AS sends a re-INVITE to UE-2 to remove the associated PS media flow(s) from the session. The SCC AS terminates the Source Access Leg as defined in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.3.8 Remote End Initiation case - Removing media from split CS and PS sessions p. 101
The call flow in Figure 6.3.3.8-1 presents a scenario where UE-1 has a CS call and an IMS multimedia session with the remote end in a manner that they are presented to UE-2 as one IMS session by the SCC AS and where as a result of UE-2 requesting to remove PS media flow(s), the SCC AS terminates the Access Leg associated with the PS media flow(s).
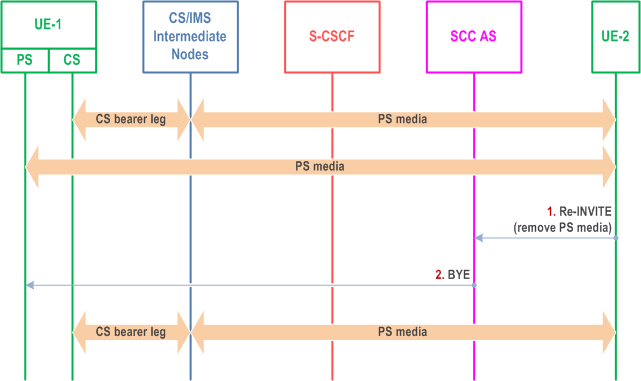
Step 1.
UE-2 uses standard IMS procedures defined in TS 23.228 to remove one or more PS media flow(s) from the session.
Step 2.
SCC AS identifies the session from UE-2 as being split into two legs to UE-1. It determines the appropriate Access Leg over which to send the updated session information from UE-2. Since there is only a single PS media flow associated with the session, the SCC AS terminates the Access Leg associated with the PS media flow.
6.3.3.9 Local End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing PS session p. 102
This clause covers the scenario where UE 1 adds PS media flow(s) (e.g. video) over a new IP-CAN, IP-CAN2, to an existing multimedia session that uses PS media over IP-CAN1. As a post condition the UE 1 has an ongoing multimedia session with the remote end.
The call flow is the same as in Figure 6.3.3.3-1 except that both the original media and the added media are on PS accesses and no CS intermediate nodes are involved.
6.3.3.10 Remote End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing PS session p. 102
This clause covers the scenario where UE 1 has an existing PS session with UE 2 using PS media over IP-CAN1 and UE 2 adds new media to the session and the new media flow is delivered using PS media over IP-CAN2 towards UE-1.
The call flow is the same as in clause 6.3.3.4 Remote End Initiation case: Adding new PS media to existing CS session, except that both the original media flow and the added media flows are on PS accesses and no CS intermediate nodes are involved. Consequently:
- in step 4. of the call flow, the T-ADS function in the SCC AS decides that the new media is delivered to UE 1 via PS through the access networks type corresponding to IP-CAN2;
- in step 5. of the call flow, the SCC AS includes enough information within the session request to ensure that the S-CSCF establishes the new session via the selected access networks type.
6.3.3.11 Local End Initiation case: Removing media from split PS sessions p. 102
This clause covers the scenario where local end UE-1 removes media flows from split PS sessions. As a precondition, UE-1 has an IMS multimedia session with the remote end. As a post-condition, UE-1 removes the PS session over one IP-CAN and continues IMS multimedia session with the remote end over the other IP-CAN.
The call flow is the same as in Figure 6.3.3.7-1 except that all the media components are on PS accesses and no CS intermediate nodes are involved.
6.3.3.12 Remote End Initiation case: Removing media from split PS sessions p. 102
This clause covers the scenario where remote end UE-2 removes media flow(s) from split PS sessions. As a precondition, UE-1 has an IMS multimedia session with the remote end. As a post-condition, the PS session over one IP-CAN is removed and UE-1 continues IMS multimedia session with the remote end over the other IP-CAN.
The call flow is the same as in Figure 6.3.3.8-1 except that all the media components are on PS accesses and no CS intermediate nodes are involved.
6.3.4 Void
6.3.5 Service continuity for ICS UE using MSC Server assisted mid-call feature while maintaining CS media |R10| p. 102
If the SCC AS detects that the ICS UE is not reachable over Service Control Signalling Path and if the UE and the network support the MSC Server assisted mid-call feature and the CS Bearer Control Signalling Path was established using the MSC Server enhanced for ICS, the same procedure as in clause 6.3.2.1.4a steps 4-6 are performed.
After completion of this procedure, the UE uses procedures as defined in TS 24.008 to perform service control.