Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
5.4 Signalling and bearer paths for IMS Service Continuity
5.4.1 General
5.4.2 Sessions with PS media flow(s)
5.4.2a Sessions with PS media flow(s) using ATCF
5.4.3 Sessions with CS media
5.4.3a Sessions with CS media flow(s) using ATCF
5.5 IUT Collaborative Sessions
5.6 Reference Architecture for SRVCC emergency session
...
...
5.4 Signalling and bearer paths for IMS Service Continuity p. 30
5.4.1 General p. 30
The SCC AS is inserted in the signalling path of all the IMS user's sessions; the SCC AS behaves as a SIP-AS as described in TS 23.228 to set up a 3pcc to control the bearer path of the session for enablement and execution of Session Transfer.
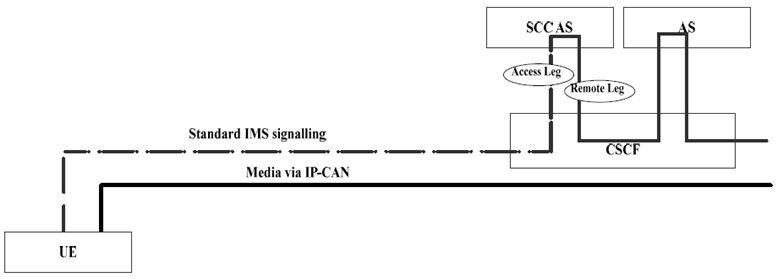
5.4.2 Sessions with PS media flow(s) p. 30
Figure 5.4.2-1 shows 3pcc at the SCC AS, for enablement and execution of Session Transfers, when the media flow(s) for the Access Leg is established via IP-CAN.
The Figure is for illustration of the 3pcc at the SCC AS and its use for Session Transfer; hence it only shows the signalling and bearer components relevant to the enablement and execution of Session Transfers.
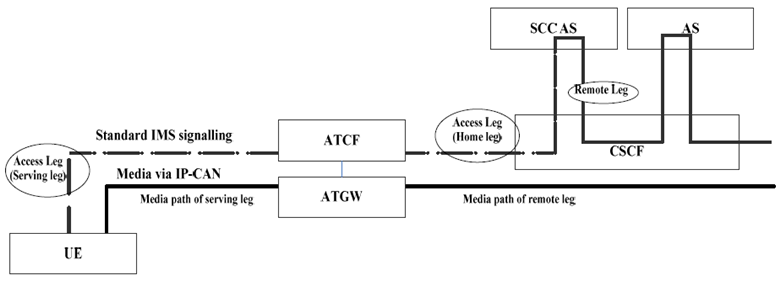
5.4.2a Sessions with PS media flow(s) using ATCF |R10| p. 30
Figure 5.4.2a-1 shows 3pcc at the ATCF and SCC AS, for enablement and execution of Access Transfers, when the media flow(s) for the Access Leg is established via IP-CAN.
The Figure is for illustration of the 3pcc at the ATCF and SCC AS and its use for Access Transfer; hence it only shows the signalling and bearer components relevant to the enablement and execution of Access Transfers.
5.4.3 Sessions with CS media p. 31
For details of signalling and bearer paths when the media for the Access Leg is established via the CS access, see clause 7.1.1 of TS 23.292. For illustration of 3pcc at the SCC AS, for enablement and execution of Session Transfers, with use of the Gm reference point, the I1 reference point and when not using Gm or I1 for service control signalling respectively, refer to Figure 7.1.1-1, Figure 7.1.1-2 and Figure 7.1.2-1, in clause 7.1 of TS 23.292.
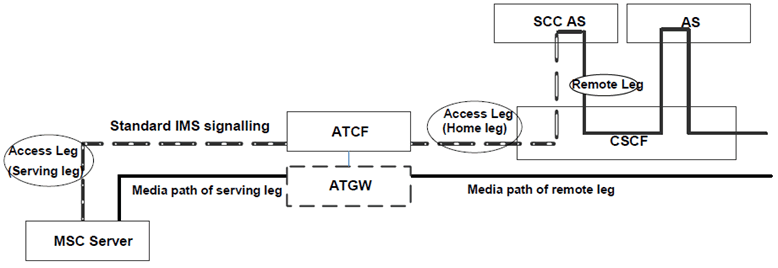
5.4.3a Sessions with CS media flow(s) using ATCF |R11| p. 31
Figure 5.4.3a-1 shows 3pcc at the ATCF and SCC AS, for enablement and execution of CS to PS Access Transfers, when the media flow(s) for the Access Leg is established via CS.
The Figure is for illustration of the 3pcc at the ATCF and SCC AS and its use for Access Transfer; hence it only shows the signalling and bearer components relevant to the enablement and execution of Access Transfers.
5.5 IUT Collaborative Sessions |R9| p. 31
IUT for service continuity allows a multi media session to be split on the local end across two or more UEs that are part of a Collaborative Session. UEs that are part of a single Collaborative Session may belong to different IMS subscriptions under the same operator. Figure 5.5-1: provides signalling and bearer architecture for a Collaborative Session that involves three UEs belonging to two IMS subscriptions.
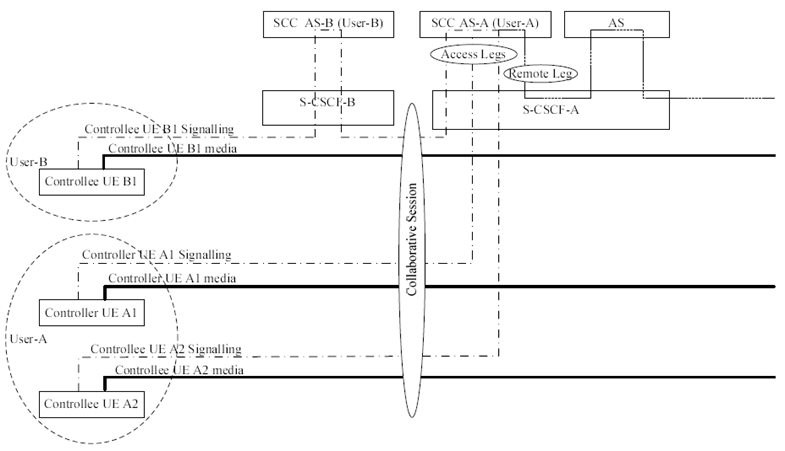
The Controller UE (UE A1) provides the control for a Collaborative Session using IMS signalling on an Access Leg between Controller UE A1 and SCC AS-A. The Controller UE may transfer one or more media flow(s) to one or more target UEs (including itself), by using Collaborative Session control (e.g. in the SDP).
Controllee UE A2 and Controllee UE B1 provide the control for the media established on each respective UE using IMS signalling on the Access Leg associated for the media.
SCC AS-A in this Figure is the Hosting SCC AS of the illustrated Collaborative Session. SCC AS-A combines the media descriptions and Collaborative Session Control on the Access Legs and presents one Remote Leg towards the remote end.
SCC AS-B in this Figure relays service requests associated with the illustrated Collaborative Session towards SCC AS-A using standard IMS signalling. In order for SCC AS-B to determine that it shall simply relay service requests towards the Hosting SCC AS rather than execute them, handling of requests is applied as follows:
- if an SCC AS acts as the Hosting SCC AS of a Collaborative Session, it shall include a piece of service interaction information in the SIP signalling messages sent to other SCC-ASs, indicating that the Service Feature "Collaborative Session" has been performed;
- if an SCC AS receives a SIP message containing indication that the Service Feature "Collaborative Session" has been performed, it shall relay all service requests associated with the Collaborative Session towards the SCC AS that has inserted this indication.
5.6 Reference Architecture for SRVCC emergency session |R9| p. 32
To allow SRVCC or DRVCC for IMS emergency session with PS to CS Access Transfer procedures, an EATF is used for emergency sessions anchoring and transferring. For the overall IMS emergency reference architecture with EATF, refer to the reference architecture in TS 23.167.