Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
6.3.2.3 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer
6.3.2.3.1 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs not using ICS capabilities
6.3.2.3.2 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS for UEs not using ICS capabilities
6.3.2.3.3 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs with ICS capabilities - Using Gm reference point
6.3.2.3.4 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS for UEs with ICS capabilities - Using Gm reference point
6.3.2.3.5 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: Active/Held sessions - Using Gm reference point
...
...
6.3.2.3 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer p. 86
6.3.2.3.1 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs not using ICS capabilities p. 86
It is required that the UE has a single ongoing IMS session containing speech or speech and video and other media with the remote end. After the Access Transfer, the two sessions are treated as independent sessions on the transferring-in Access Legs for mid-call service (e.g. hold of PS or CS media).
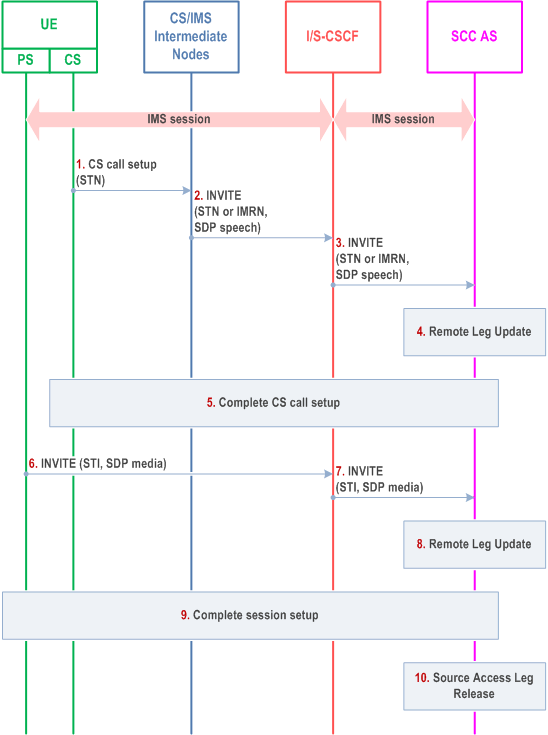
Step 1.
When the UE determines a need for Access Transfer, the UE attaches to CS (if not already attached). It subsequently initiates the PS-CS Access Transfer by sending a CS call setup including the STN to establish the Access Leg via the CS access. A static STN preconfigured to the UE is used.
Step 2.
An INVITE is routed to the I/S-CSCF.
Step 3.
An INVITE is routed to the SCC AS.
Step 4.
The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg update by using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5. The SCC AS updates the speech or speech and video media being transferred in the session towards the Remote Leg.
Step 5.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
Step 6.
The UE initiates registration with IMS via the new PS access (if not already registered) as specified in clause 6.1. It subsequently initiates the PS-PS Access Transfer by sending an INVITE including the SDP for the non-real-time media flow(s) and STI to establish the Access Leg via the PS access. A dynamic STI allocated at the time of IMS session creation is used.
Step 7.
An INVITE is routed to the SCC AS.
Step 8.
The SCC AS identifies the session to be transferred using the STI. The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg update by using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5. The SCC AS updates the non-real-time media flow(s) in the session towards the Remote Leg.
Step 9.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
Step 10.
Source Access Leg Release is performed according to the procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.3.2 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS for UEs not using ICS capabilities p. 88
It is required that the UE has an ongoing CS call and a related IMS session with the remote end.
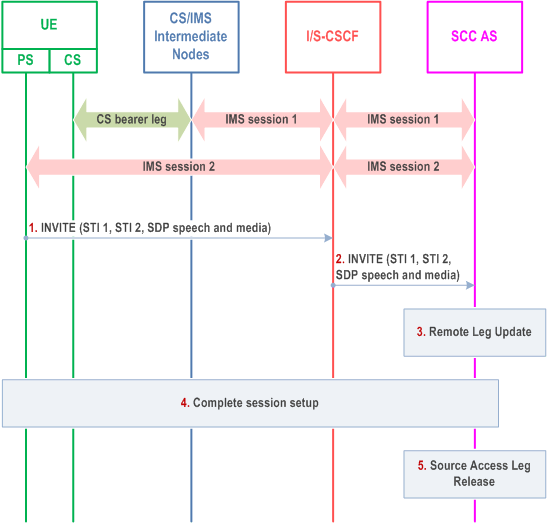
Step 1.
When the UE determines a need for Access Transfer, the UE initiates registration with IMS via the new PS access (if not already registered) as specified in clause 6.1. It subsequently initiates the Access Transfer by sending an INVITE to establish the Access Leg via the PS access. The INVITE includes the SDP for speech or speech and video and non-real-time media flow(s) and STI-1 and STI-2 respectively for the IMS session using CS and the IMS session using PS to be transferred. For STI-1 a static STI preconfigured to the UE is used. For STI-2 a dynamic STI allocated at the time of IMS session creation is used. STI-1 and STI-2 are never the same.
Step 2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS identifies the session to be transferred using the STI-1 and STI-2. The SCC AS performs the Remote Leg Update by using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5. The SCC AS updates the combined session towards the Remote Leg.
Step 4.
The SCC AS completes the session setup towards UE-1 according to procedures defined in TS 23.228.
Step 5.
Source Access Leg Release is performed according to the procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.3.3 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs with ICS capabilities - Using Gm reference point p. 88
Figure 6.3.2.3.3-1 PS-PS in conjunction with PS-CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs with ICS capabilities, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of real time media flow(s) of an IMS session in PS to CS direction and zero or more non real time media flow(s) in PS to PS direction. The UE may choose to retain some of the non real time media flow(s) in the original PS access.
The flow requires that the user is in an active or inactive IMS originating or terminating session; the Gm reference point of ICS is used for control of IMS sessions that use CS media.
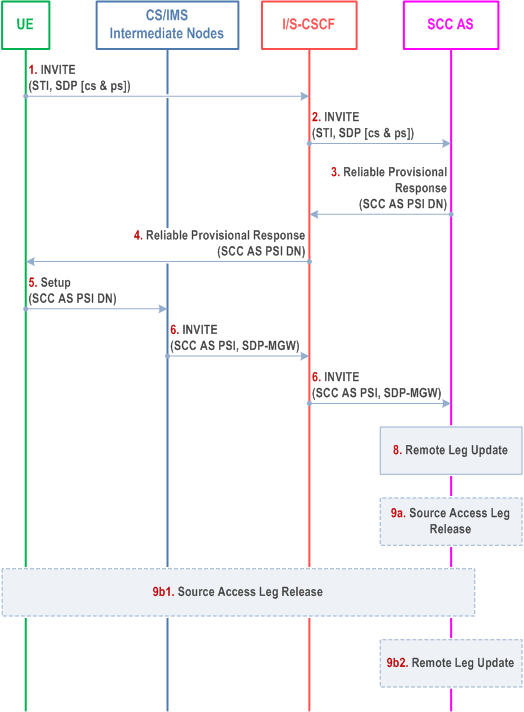
Step 1.
When the UE determines a need for Access Transfer, the UE initiates registration with IMS via the new PS access (if not already registered) as specified in clause 6.1. It subsequently initiates the "Originations with CS media using the Gm reference point" procedure as specified in clause 7.3.2.2.4 of TS 23.292 by sending an INVITE including the STI to establish the Access Leg via the PS access. The INVITE also includes an indication to use a CS bearer for the real time media and a description of non real time media flow(s) that are to be transferred to the new PS access if any non real time media is present at the time of initiation of Access Transfer.
Step 2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS identifies the session to be transferred using the STI and the media flow(s), and continues the "Originations with CS media using the Gm reference point" procedure for completion of the setup of CS media for the Access Leg by allocating a SCC AS PSI DN and sending it in a reliable provisional response to the S-CSCF (see TS 23.292 for SCC AS PSI DN).
Step 4.
The S-CSCF forwards the provisional response (containing the SCC AS PSI DN) to the UE.
Step 5.
The UE continues the "Originations with CS media using the Gm reference point" procedure by sending a Setup message including the SCC AS PSI DN to establish the CS media for the Access Leg.
Step 6.
The "Originations with CS media using Gm reference point procedure" is used at the CS and IMS intermediate nodes, resulting in routing of an INVITE to the I/S-CSCF.
Step 7.
The I/S-CSCF extends the INVITE with the SCC AS PSI and SDP of the MGW as part of the "Originations with CS media using the Gm reference point" procedure.
Step 8.
The SCC AS uses the SCC AS PSI to correlate the incoming session via the CS access with the Access Transfer request previously received via the PS access.
The SCC AS completes the establishment of the Access Leg by combining the description of the media established via the CS access with the description of the media flow(s) established via the PS access for the signalling associated with the Access Leg.
The SCC AS performs the Access Transfer by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information of the newly established Access Leg using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 9a.
If the UE transfers all the non real time media flow(s) to the new PS access, the Source Access Leg (which is the Access Leg previously established over PS access) is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
Step 9b.
If the UE chooses to retain some media flow(s) in the original PS access, then:
Step 9b1.
the UE sends an INVITE to the SCC AS (as part of the existing dialog) to update the session information over the Source Access Leg; and
Step 9b2.
the SCC AS performs the Remote Leg update (if necessary) by using procedures defined in clause 6.3.1.5. The Source Access Leg is not released in this case.
6.3.2.3.4 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS for UEs with ICS capabilities - Using Gm reference point p. 90
The information flow for Access Transfer of real time media of an IMS session in CS to PS direction, and zero or more non real time media flow(s) in PS to PS direction is the same as the information flow for PS-CS Access Transfer: CS to PS access, as specified in clause 6.3.2.1.2.
The flow requires that the user is in an active or inactive IMS originating or terminating session; the Gm reference point of ICS is used for control of IMS sessions that use CS media; and a dynamic STI is associated with each session.
6.3.2.3.5 PS - PS in conjunction with PS - CS Access Transfer: Active/Held sessions - Using Gm reference point p. 90
Figure 6.3.2.3.5-1 PS-PS in conjunction with PS-CS Access Transfer: Active/Held sessions, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of real time media flow(s) of one active and one or more held sessions between PS and CS, any of which may have zero or more non real time media flow(s) which is transferred within the PS access.
The flow requires that the user is in an active IMS originating and/or terminating sessions; the Gm reference point of ICS is used for control of IMS sessions that use CS media; and a dynamic STI is associated with each session.
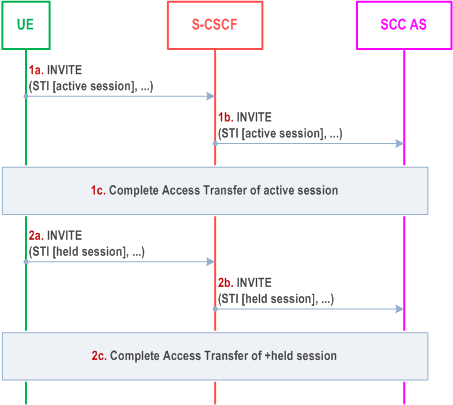
Step 1a, 1b.
Steps 2a, 2b and 2c are repeated for the remaining held sessions.
When the UE determines a need for Access Transfer, the UE initiates the Access Transfer of the active session as specified in clause 6.3.2.3.3 PS-PS in conjunction with PS-CS Access Transfer: PS to CS for UEs with ICS capabilities, or clause 6.3.2.3.4 PS-PS in conjunction with PS-CS Access Transfer: CS to PS for UEs with ICS capabilities, based on the direction of the Access Transfer of the real time media. The STI of the active session is used by SCC AS to identify the active session.
Step 1c.
The UE and the SCC AS complete the Access Transfer of the active session.
Step 2a, 2b.
The UE initiates the Access Transfer of the first held session using the same procedures as identified in steps 1a and 1b with a difference that for transfer to CS access, the CS media is not established for the held session; the media established upon the transfer of the currently active session is reused for the held session when it is resumed. The STI of the held session is used by SCC AS to identify the held session.
Step 2c.
The UE and the SCC AS complete the Access Transfer of the held session.