Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
6.3.2.1.9 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio using ATCF enhancements
6.3.2.1.9.1 ATCF with media anchored in ATGW
6.3.2.1.9.2 ATCF without media anchored in ATGW
6.3.2.1.9.3 ATCF not included during registration
6.3.2.1.10 PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS - Single Radio
6.3.2.1.10.1 CS to PS - Single Radio procedures with CS media anchored in ATGW
6.3.2.1.10.2 CS to PS - Single Radio procedures without CS media anchored in ATGW
...
...
6.3.2.1.9 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio using ATCF enhancements |R10| p. 76
6.3.2.1.9.1 ATCF with media anchored in ATGW p. 76
This clause describes the main differences with the (v)SRVCC procedures specified in clauses 6.3.2.1.4 and 6.3.2.1.4a for the case when the media is anchored in the ATGW and the ATCF enhancements are used. A pre-requisite for this scenario is that the ATCF has been included during the IMS registration according to clause 6.1.2. Some of the procedures that are not impacted have been left out for clarity of the flow.
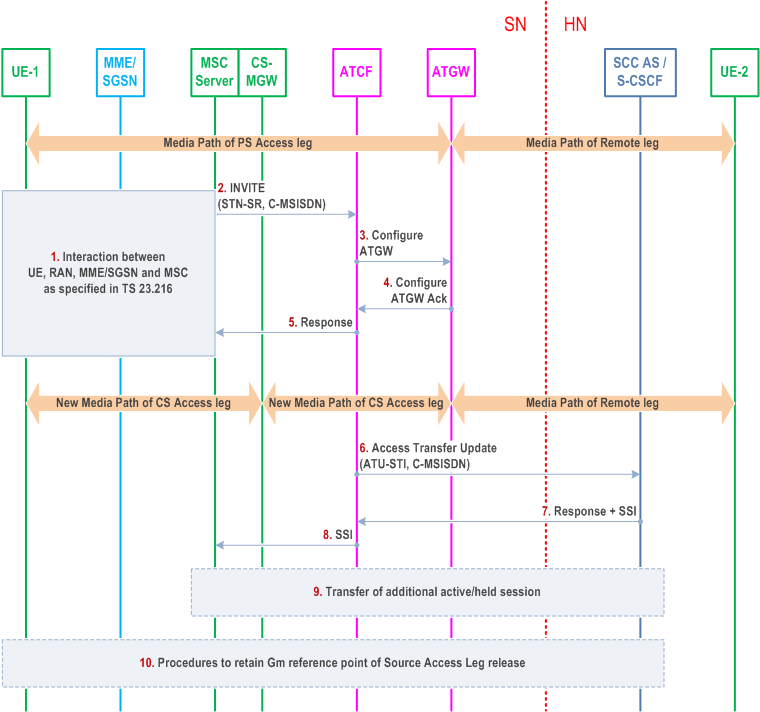
Step 1.
Interaction between UE, RAN, MME/SGSN and MSC Server as specified in TS 23.216. The following step is triggered after the MSC Server has received the PS to CS request from the MME / SGSN and has allocated resources in the RAN.
Step 2.
The MSC Server initiates Access Transfer message, and if supported, the MSC Server indicates its capability to support MSC Server assisted mid-call feature. The MSC Server provides all the supported Codecs for voice or voice and video in the Access Transfer message.
Step 3.
The ATCF receives the Access Transfer message and correlates the transferred session using the C-MSISDN. The ATCF identifies the correct anchored session and proceeds with the Access Transfer of the most recently active speech session. The ATCF updates the ATGW by replacing the existing PS access leg media path information with the new CS access leg media path information, by sending a Configure ATGW message to ATGW. ATCF may provide priority handling if the Access Transfer message contains priority indication.
Step 4.
The ATGW sends Configure ATGW Acknowledgment message back to ATCF.
Step 5.
The ATCF sends an Access Transfer response to the MSC Server. The media path is switched to CS when receiving SDP information.
Step 6.
After receiving the Access Transfer message, the ATCF re-establishes the communication with the SCC AS and updates the SCC AS that the transfer has taken place by sending an Access Transfer Update message to the SCC AS using the stored ATU-STI. If the MSC server indicated it supported mid-call feature, it also indicates this in the message to the SCC AS. The Access Transfer Update creates a new dialogue between the ATCF and SCC AS. The SCC AS correlates the new dialog with the remote dialog (e.g., using the C-MSISDN). As there is no update in the session description, no remote end update will be performed.
Step 7.
The SCC AS sends confirmation response to the ATCF. If the SCC AS and MSC Server supports mid call feature, the SCC AS provides the SSI according to clause 6.3.2.1.4a.
Step 8.
If the ATCF receives the SSI, it forwards the SSI to the MSC server.
Step 9.
If the MSC Server receives the Session State Information of more than one active or inactive speech sessions, it initiates Access Transfer towards SCC AS for the additional session.
Step 10.
Procedures according to clause 6.3.2.1.4, steps 4a and 4b are used to handle the cases where the Gm reference point is either retained upon PS handover procedure, not retained upon PS handover, or if there was no other media flow(s) in the IMS session.
6.3.2.1.9.2 ATCF without media anchored in ATGW p. 77
This clause describes the main differences with the (v)SRVCC procedures specified in clauses 6.3.2.1.4 and 6.3.2.1.4a for the case when the ATCF is included in the session path, but media has not been anchored in ATGW. Some of the procedures that are not impacted have been left out for clarity of the flow.
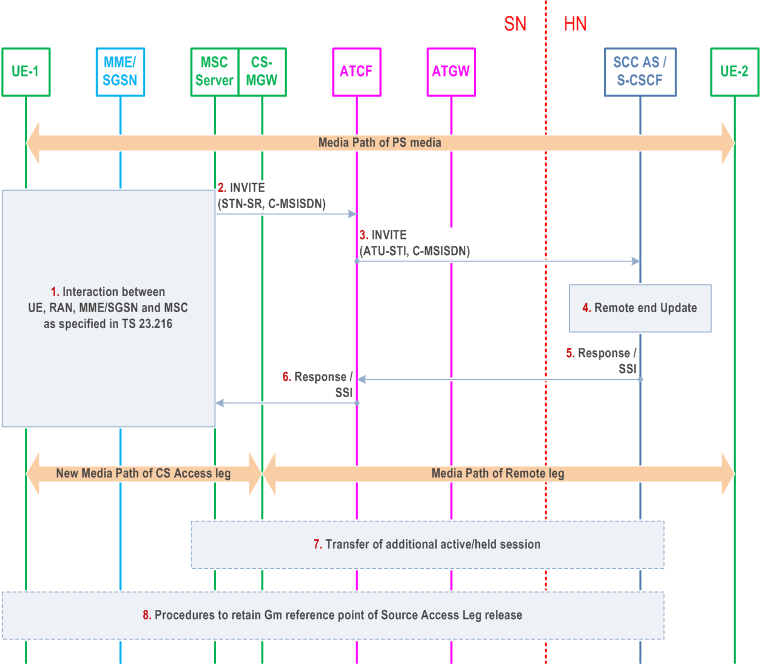
Step 1.
Interaction between UE, RAN, MME/SGSN and MSC Server as specified in TS 23.216. The following step is triggered after the MSC Server has received the PS to CS request from the MME / SGSN and has allocated resources in the RAN.
Step 2.
The MSC Server initiates Access Transfer message and if supported, the MSC Server indicates its capability to support MSC Server assisted mid-call feature. The MSC Server provides all the supported Codecs for voice or voice and video in the Access Transfer message.
Step 3.
The ATCF receives the Access Transfer message and correlates the transferred session using the C-MSISDN. As the media flow has not been anchored in the ATGW, the ATCF forwards the Access Transfer message along with priority indication if received to the SCC AS using the stored ATU-STI. If the MSC server indicated it supported mid-call feature, it also indicates this in the message to the SCC AS.
Step 4.
The SCC AS correlates the incoming Access Transfer message. As the Session Description has changed, a remote end update is initiated according to clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 5.
The SCC AS sends an Access Transfer response to the MSC Server, and in the case MSC Server assisted mid-call feature is supported and used, the SCC AS provides Session State Information (SSI) according to clause 6.3.2.1.4a.
Step 6.
The ATCF forwards the response to the MSC server.
Step 7.
If the MSC Server receives the Session State Information of more than one active or inactive speech sessions, it initiates Access Transfer towards SCC AS for the additional session according to clause 6.3.2.1.4a.
Step 8.
Procedures according to clause 6.3.2.1.4, steps 4a and 4b are used to handle the cases where the Gm reference point is either retained upon PS handover procedure, not retained upon PS handover, or if there was no other media flow(s) in the IMS session.
6.3.2.1.9.3 ATCF not included during registration p. 79
If the decision by the ATCF during registration was not to be included at all, the SRVCC procedures will fall back to procedures according to clauses 6.3.2.1.4 and 6.3.2.1.4a.
6.3.2.1.10 PS - CS Access Transfer: CS to PS - Single Radio |R11| p. 79
6.3.2.1.10.1 CS to PS - Single Radio procedures with CS media anchored in ATGW p. 79
Figure 6.3.2.1.10-1 PS-CS: CS to PS - Single Radio, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of a CS speech media flow in CS to PS direction for Access Transfers within 3GPP access networks as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user is active or inactive in a CS originating or terminating speech session; procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer. It further requires that the UE has an active IMS registration prior the transfer take place.
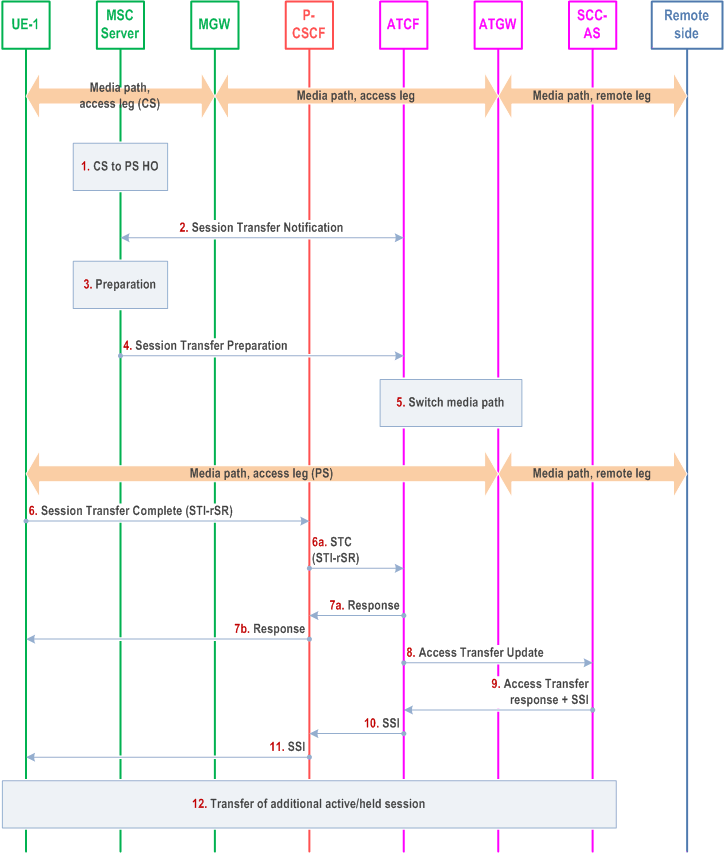
Step 1.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216 result in that the MSC Server receives a CS to PS HO request.
Step 2.
The MSC Server initiates a Session Transfer Notification towards the ATCF, which indicates to the ATCF that it should prepare for the transfer of media to PS. The ATCF responds with information required for the transfer, including allocated media IP/ports for UL direction and UE's port for DL direction and voice codec information allocated in the ATGW.
Step 3.
The MSC Server performs the CS to PS HO preparation procedures by interacting with target MME/SGSN to initiate the handover according to TS 23.216.
Step 4.
When the target MME/SGSN have reserved appropriate resources in the target network, the MSC Server sends a Session Transfer Preparation request to the ATCF to instruct the ATCF that media should be switched to the target access and also triggers the UE to hand over to the target according to TS 23.216.
Step 5.
The ATCF switches the media path in the ATGW from the source access to target access.
Step 6.
The UE initiates a Session Transfer Complete request to the ATCF to move the session control to the PS access. If mid-call and alerting is supported, the UE will include this in the request.
Step 7.
The ATCF sends a Session Transfer Complete response to the UE and releases the Source Access Leg toward the MSC Server.
Step 8.
After receiving the Session Transfer Complete message, the ATCF re-establishes the communication with the SCC AS and updates the SCC AS that the transfer has taken place by sending an Access Transfer Update message to the SCC AS using the stored ATU-STI and C-MSISDN. If the UE indicated it supported mid-call feature and/or alerting, it also indicates this in the message to the SCC AS. The Access Transfer Update creates a new dialogue between the ATCF and SCC AS. The SCC AS correlates the new dialog with the remote dialog (e.g., using the C-MSISDN). As there is no update in the session description, no remote end update will be performed.
Step 9.
The SCC AS sends confirmation response to the ATCF. If the SCC AS and UE supports mid-call feature and/or alerting, the SCC AS provides the Session State Information (SSI) according to clause 6.3.2.1.2a. The Session State Information includes the additional held session with speech media including dynamic STI needed for the held session on the transferring-in leg.
Step 10-11.
If the ATCF receives the SSI, it forwards the SSI to the UE.
Step 12.
If the UE receives the Session State Information of the held session, it initiates a Access Transfer request towards the SCC AS using the dynamic STI for the held session.
6.3.2.1.10.2 CS to PS - Single Radio procedures without CS media anchored in ATGW p. 80
Figure 6.3.2.1.10-2 PS-CS: CS to PS - Single Radio, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of a CS speech media flow in CS to PS direction for Access Transfers within 3GPP access networks as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user is active or inactive in a CS originating or terminating speech session; procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer. It further requires that the UE has an active IMS registration prior the transfer take place.
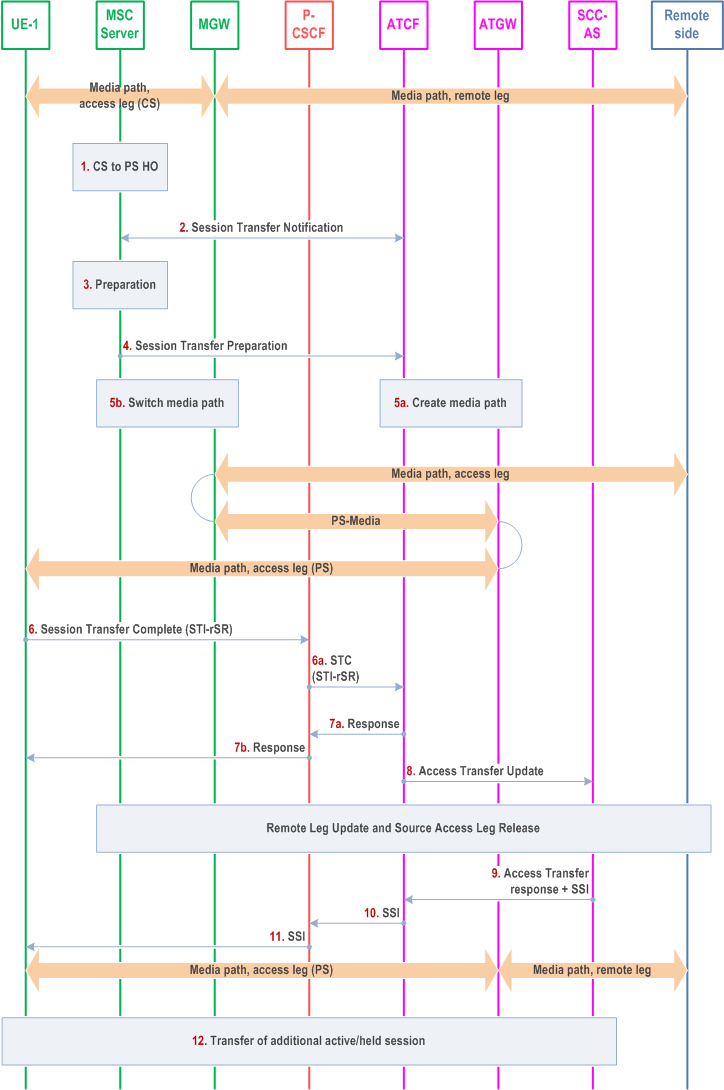
Step 1.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216 result in that the MSC Server receives an CS to PS HO request.
Step 2.
The MSC Server initiates a Session Transfer Notification towards the ATCF, which indicates to the ATCF that it should prepare for the transfer of media to PS. The ATCF responds with information required for the transfer, including allocated media IP/ports for UL direction and UE's port for DL direction and voice codec information allocated in the ATGW.
Step 3.
The MSC Server performs the CS to PS HO preparation procedures by interacting with target MME/SGSN to initiate the handover according to TS 23.216.
Step 4.
When the target MME/SGSN have reserved appropriate resources in the target network, the MSC Server sends a Session Transfer Preparation request to the ATCF.
Step 5.
When receiving the Session Transfer Preparation request from the MSC Server, the ATCF reserves ATGW resources for the media path connected to MGW and then sends a Session Transfer Preparation response to the MSC Server. Upon receipt of the Session Transfer Preparation response, the MSC Server instructs the MGW to switch the media path from the source access (CS RAN) to the target access (ATGW), and also triggers the UE to hand over to the target according to TS 23.216.
Step 6.
The UE initiates a Session Transfer Complete request to the ATCF to move the session control to the PS access. If mid-call and alerting is supported, the UE will include this in the request.
Step 7.
The ATCF sends an Session Transfer Complete response to the UE.
Step 8.
After receiving the Session Transfer Complete message, the ATCF re-establishes the communication with the SCC AS and updates the SCC AS that the transfer has taken place by sending an Access Transfer Update message to the SCC AS using the stored ATU-STI and C-MSISDN. If the UE indicated it supported mid-call feature and/or alerting, it also indicates this in the message to the SCC AS. The Access Transfer Update creates a new dialogue between the ATCF and SCC AS. The SCC AS correlates the new dialog with the remote dialog (e.g., using the C-MSISDN). As there is update in the session description, Remote Leg Update and Source Access Leg procedures (to release unused resources at the CS MGW) will be performed as specified in 6.3.1.5 and 6.3.1.6 respectively.
Step 9.
The SCC AS sends confirmation response to the ATCF. If the SCC AS and UE supports mid-call feature and/or alerting, the SCC AS provides the Session State Information (SSI) according to clause 6.3.2.1.2a. The Session State Information includes the additional held session with speech media including dynamic STI needed for the held session on the transferring-in leg.
Step 10-11.
If the ATCF receives the SSI, it forwards the SSI to the UE.
Step 12.
If the UE receives the Session State Information of the held session, it initiates an Access Transfer request towards the SCC AS using the dynamic STI for the held session.