Content for TS 23.237 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
5…
5.4…
6…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.3.2…
6.3.2.1.3…
6.3.2.1.7…
6.3.2.1.9…
6.3.2.2…
6.3.2.3…
6.3.2.3.6…
6.3.3…
6.4…
6a…
6a.3…
6a.4…
6a.4.3…
6a.4.5…
6a.4.7…
6a.4a…
6a.5…
6a.6…
6a.7…
6a.8…
6a.9…
6a.10…
6a.11…
6c…
7…
A…
B…
C…
6.3.2.1.3 Subsequent Access Transfers
6.3.2.1.4 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio
6.3.2.1.4a PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio with Session State Information
6.3.2.1.4b PS to CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio; using I1 reference point
6.3.2.1.4c PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, incoming voice or video call in pre-alerting or alerting phase
6.3.2.1.4d PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, outgoing voice or video call in pre-alerting state or in alerting phase
6.3.2.1.4e PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, voice and video
6.3.2.1.5 PS - CS Access Transfer for voice and video, Dual Radio
6.3.2.1.6 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Dual Radio, mid-call service with an active speech and video session
...
...
6.3.2.1.3 Subsequent Access Transfers p. 57
Procedures for subsequent Access Transfers to CS and PS access are the same as procedures for initial Access Transfers specified in clause 6.3.2.1.1 for PS to CS access and clause 6.3.2.1.2 for CS to PS access.
6.3.2.1.4 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio p. 57
Figure 6.3.2.1.4-1 PS-CS: PS to CS - Single Radio, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of media flow(s) of an IMS session in PS to CS direction for Access Transfers within 3GPP access networks as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user is active or inactive in an IMS originating or terminating session; procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer. It further requires that the MSC Server assisted mid-call feature as described in clause 6.3.2.1.4a is not used.
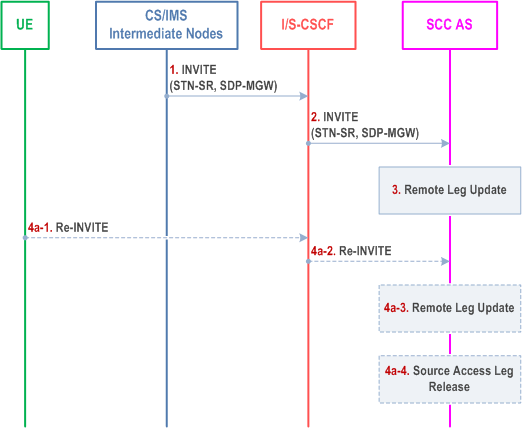
Step 1.
If the MSC Server above (located in the box labelled "CS/IMS Intermediate Nodes") is enhanced for ICS as defined in TS 23.292, then it performs IMS registration after the transfer of the session is completed successfully i.e. after step 3. Registration is performed only if the ICS flag is received via the Sv reference point as specified in TS 23.216 or as determined to by the procedure specified in clause 7.2.1.1 in TS 23.292.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216 result in an INVITE to be sent with an STN-SR indicating use of SRVCC procedures for Access Transfer to CS access. The MSC Server enhanced for SRVCC includes the C-MSISDN as calling party number. If SRVCC with priority is supported, MSC Server enhanced for SRVCC also includes a priority indication if received.
Step 2.
Standard procedures are used at I/S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS uses the STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer using SRVCC is requested. The SCC AS may retrieve the C-MSISDN from the HSS. The SCC AS is able to identify the correct anchored session. The SCC AS determines if the state of the session to be transferred is active or inactive based on the session state information in the source Access Leg. The SCC AS proceeds with the Access Transfer of the session with bi-directional speech for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 4a.
If the Gm reference point is retained upon PS handover procedure then
Step 4a-1.
The UE sends a Re-INVITE via the PS access to update the remaining non-voice media flow(s) associated with the recently added active session. If the UE is using ICS capabilities, this Re-INVITE also adds Gm service control to the active session and the UE subsequently sends Re-INVITEs for any remaining inactive bi-directional speech sessions that are to be transferred.
Step 4a-2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the Re-INVITE(s) to the SCC AS.
Step 4a-3.
The SCC AS processes the Re-INVITE(s) and updates the Remote Leg if needed.
Step 4b.
If the Gm reference point is not retained upon PS handover procedure, e.g. because there was no other media flow(s) in the IMS session than the voice which was transferred to the target access, then the Source Access Leg is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.1.4a PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio with Session State Information |R10| p. 58
Figure 6.3.2.1.4a-1 PS-CS: PS to CS - Single Radio with Session State Information, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of media of an IMS session in PS to CS direction for Access Transfers within 3GPP access networks as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user has an active IMS originating or terminating session, together with at least one more IMS originating or terminating session (active and/or inactive), and that the use of network capabilities to support MSC Server assisted mid-call feature during Access Transfer is possible; procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer.
The flow is not applicable in case ICS UE capabilities can be used.
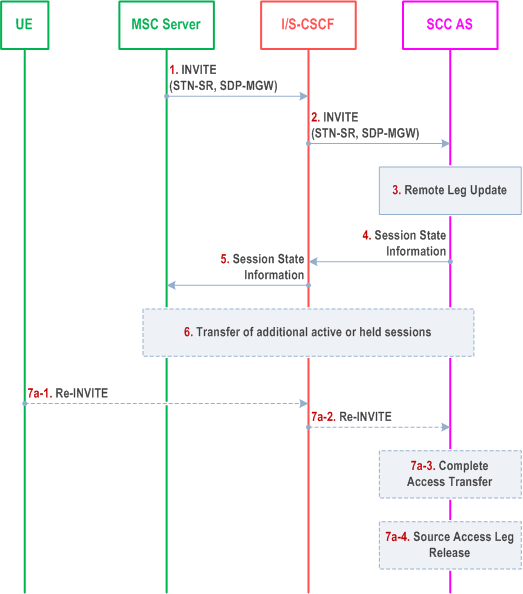
Step 1.
If the MSC Server above is enhanced for ICS as defined in TS 23.292, then it performs IMS registration after the transfer of all sessions is completed successfully i.e. after step 6. Registration is performed only if the ICS flag is received via the Sv reference point as specified in TS 23.216 or as determined to by the procedure specified in clause 7.2.1.1 in TS 23.292.
After completion of this procedure, the UE uses procedures as defined in TS 24.008 to perform service control.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216, result in an INVITE to be sent with an STN-SR indicating use of Single Radio VCC procedures for Access Transfer to CS access. If the user is not IMS registered by the MSC Server, the MSC Server enhanced for SRVCC includes the C-MSISDN as calling party number. If the user is registered in the IMS by the MSC Server, then the MSC Server includes the GRUU into the Access Transfer request. The MSC Server indicates its capability to support MSC Server assisted mid-call feature during Access Transfer.
Step 2.
Standard procedures are used at I/S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 3.
The SCC AS uses the STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer using Single Radio VCC is requested. The SCC AS may retrieve the C-MSISDN from the HSS. The SCC AS identifies the correct anchored session and proceeds with the Access Transfer of the recently added active session or, if there is no active session, the inactive session which was active most recently, with bi-directional speech for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 4.
The SCC AS provides Session State Information on the transferring-in leg. If there are more than two sessions with speech media before session transfer in the source Access Leg, the SCC AS performs the following:
If there are no active sessions, the SCC AS performs the following:
Step 5.
- includes the information that the session is inactive in the transfer response sent to the MSC Server;
- besides the inactive session already handled in step 3, releases all other remaining inactive sessions;
- skips following handling of step 4, 5 and 6 in the information flow.
- if there are two or more active sessions, selects the second-most recently active session, puts it on hold and releases all remaining active sessions;
- selects the held session that has been most recently made inactive. Any other inactive sessions are released;
- the Session State Information of the selected inactive session is sent to the MSC Server.
The S-CSCF forwards the Session State Information to the MSC Server.
Step 6.
If the MSC Server receives the Session State Information of more than one active or inactive speech sessions, it initiates Access Transfer towards SCC AS for the additional session.
Step 7a.
If the Gm reference point is retained after PS handover procedure completion for non-voice media flows, then:
Step 7a-1.
The UE sends a Re-INVITE via the PS access to update the remaining non-voice media flow associated with the recently added active session.
Step 7a-2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 7a-3.
The SCC AS processes the Re-INVITE and updates the Remote Leg if needed.
Step 7b.
If the Gm reference point is not retained after PS handover procedure completion, e.g. because there was no other media in the IMS session than the voice that was transferred to the target access, then the Source Access Leg is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.1.4b PS to CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio; using I1 reference point |R9| p. 60
Figure 6.3.2.1.4b-1 PS-CS: PS to CS - Single Radio; using I1 reference point, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of media flow(s) of an IMS session in the PS to CS direction for Access Transfers within 3GPP access networks as specified in TS 23.216, and with the use of I1 reference point for service control post transfer to CS.
The flow requires that the UE has indicated ICS capabilities and that the user is active in an IMS originating or terminating session; procedures specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer. The I1 reference point of ICS is used for control of IMS sessions established using CS media and a dynamically assigned STI is associated with each session.
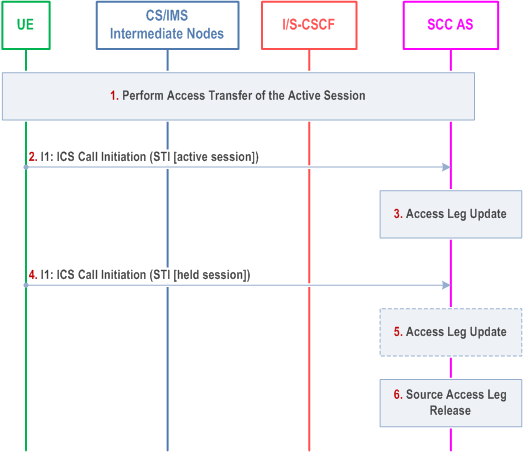
Step 1.
Steps 4 and 5 are repeated for the remaining held sessions.
Access Transfer of the active session with bi-directional speech is performed as defined in clause 6.3.2.1.4, steps 1-3.
Step 2.
The UE sends an I1: ICS Call Initiation via the CS access as specified in TS 23.292 including an STI for continuation of establishment of the Access Leg using Single Radio VCC for the active session.
Step 3.
The SCC AS uses the STI to correlate the Access Transfer request received via the PS access with the Access Transfer request for the active session received via the CS access.
Step 4.
If there are any held sessions present at the time of Access Transfer, the UE proceeds with the Access Transfer of the first held session by sending an I1: ICS Call Initiation via the CS access (as described in TS 23.292) including an STI that identifies the held session.
Step 5.
The SCC AS uses the STI to identify the held session and updates the session information on the Access Leg.
Step 6.
The Source Access Leg is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.1.4c PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, incoming voice or video call in pre-alerting or alerting phase |R10| p. 62
Figure 6.3.2.1.4c-1 PS-CS: PS to CS - Single Radio, incoming call in pre-alerting or alerting phase, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of media of an IMS session in PS to CS direction for Access Transfers as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user is active in a terminating IMS session in pre-alerting or alerting state which the UE has not responded over the access leg and there is no other session (or there is one or more held sessions but mid-call service is not supported); procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer.
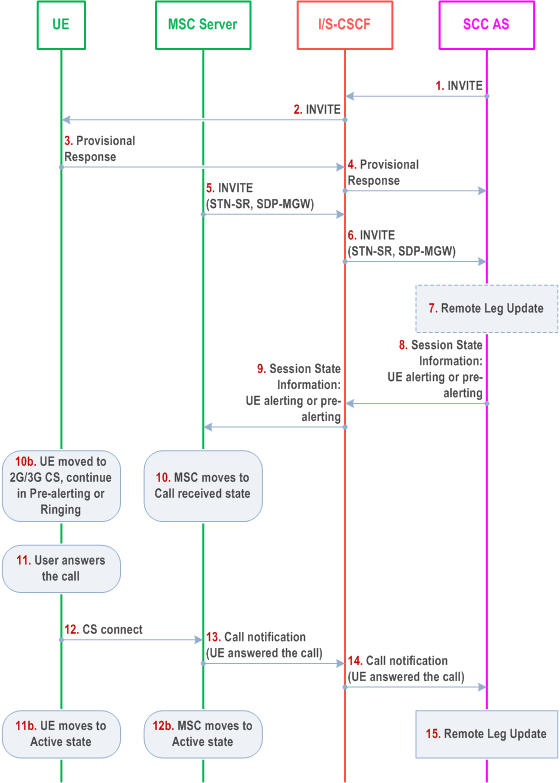
Step 1-4.
Standard procedures are used to initiate a SIP session towards the UE. The UE is either in pre-alerting state or alerting the user for the incoming voice or video-call session. Precondition procedure can be executed in this phase but is not shown in the flow.
Step 5.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216 result in an INVITE to be sent with an STN-SR indicating use of Single Radio VCC procedures for Access Transfer to CS access. The MSC Server enhanced for (v)SRVCC includes the C-MSISDN as calling party number. The MSC Server indicates its capability to support mid-call services during session transfer. For PS-CS transfer for vSRVCC the video Codecs are also included in the session transfer request.
Step 6.
Standard procedures are used at I/S-CSCF for routeing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 7.
The SCC AS uses the STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer using Single Radio VCC is requested. The SCC AS may retrieve the C-MSISDN from the HSS. The SCC AS uses the C-MSISDN to identify the correct anchored session. The SCC AS proceeds with the Access Transfer of the recently added active session with bi-directional speech or bi-directional speech and synchronised video media for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 8.
The SCC AS provides Session State Information on the incoming speech call in pre-alerting state or alerting state.
Step 9.
The S-CSCF forwards the Session State Information to the MSC Server.
Step 10.
The MSC moves to the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Received in TS 24.008.
Step 10b.
In parallel to step 10, the UE has received the HO command as described in TS 23.216. The UE determines the local call state in the SIP session, and creates the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Received in TS 24.008. The UE continues to alert the user for incoming call if it is already in alerting state.
Step 11.
The user answers to the call. For video call the UE may initiate at this stage the H.245 Codec negotiation.
Step 11a.
UE moves to Active state.
Step 12.
The UE uses the standard procedure to send the CS connect message to MSC as e.g. described in TS 24.008.
Step 12b.
The MSC moves to Active state.
Step 13.
The MSC notifies the SCC AS the user has answered the call.
Step 14.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routeing of the notification to the SCC AS.
Step 15.
The SCC AS creates the corresponding SIP request to the remote end, updates the remote leg.
6.3.2.1.4d PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, outgoing voice or video call in pre-alerting state or in alerting phase |R10| p. 63
Figure 6.3.2.1.4d-1 PS-CS: PS to CS - Single Radio, outgoing call in early dialogue phase (i.e. pre-alerting or alerting), provides an information flow for Access Transfer of media of an IMS session in PS to CS direction for Access Transfers as specified in TS 23.216.
The flow requires that the user is active in an outgoing IMS session in early dialogue phase and there is no other session (or there is one or more held sessions but mid-call service is not supported); procedures and capabilities specified in TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer.
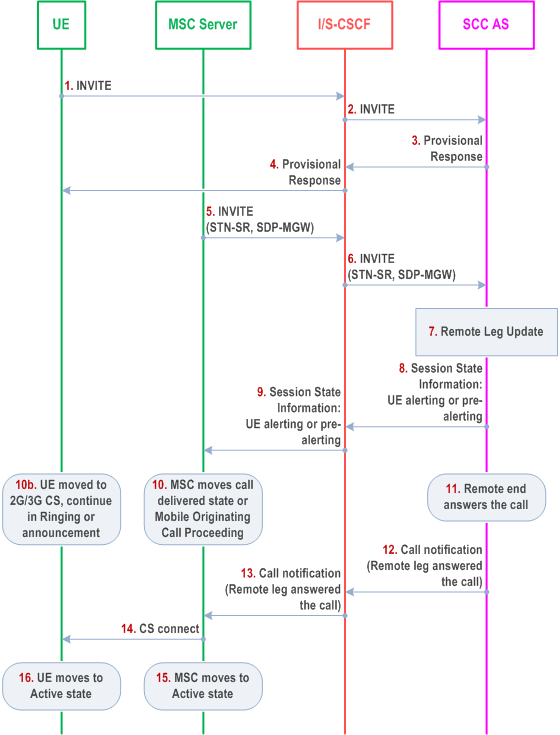
Step 1-4.
Standard procedures are used to initiate a SIP session from the UE towards the remote end. The remote end is either alerting the user for the incoming voice or video-call session or the call is in pre-alerting state and announcements may be played to the UE. Access bearer for voice or video is setup for the UE during this step.
Step 5.
Procedures specified in TS 23.216 result in an INVITE to be sent with an STN-SR indicating use of Single Radio VCC procedures for Access Transfer to CS access. If the user is not IMS registered by the MSC Server, the MSC Server enhanced for (v)SRVCC includes the C-MSISDN as calling party number. If the user is registered in the IMS by the MSC Server, then the MSC Server includes the GRUU into the session transfer request. The MSC Server indicates its capability to support mid-call services during session transfer. For PS-CS transfer for vSRVCC the video Codecs are also included in the session transfer request.
Step 6.
Standard procedures are used at I/S-CSCF for routeing of the INVITE to the SCC AS.
Step 7.
The SCC AS uses the STN-SR to determine that Access Transfer using Single Radio VCC is requested. The SCC AS may retrieve the C-MSISDN from the HSS. The SCC AS identifies the correct anchored session. The SCC AS proceeds with the Access Transfer of the recently added active session with bi-directional speech or bi-directional speech and synchronised video for the UE by updating the Remote Leg with the media description and other information using the Remote Leg Update procedure as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 8.
The SCC AS provides Session State Information on the outgoing speech call in early dialogue phase (e.g., pre-alerting or alerting state).
Step 9.
The S-CSCF forwards the Session State Information to the MSC Server.
Step 10.
The MSC moves to the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Delivered or Mobile Originating Call Proceeding state as specified in TS 24.008.
Step 10b.
In parallel to step 10, the UE has received the HO command as described in TS 23.216. The UE determines the local call state in the SIP session, and creates the corresponding CS call state, e.g. Call Delivered in TS 24.008 for the alerting state, or Mobile Originating Call Proceeding for the pre-alerting state. The UE ensures that the same ring back tone or announcement if any is played to the end user. If the voice+video media is played to the UE in PS domain, and the CS domain does not support video media, only the voice media shall be played to the UE after the call is transferred to CS domain from PS domain, regardless of whether the media is locally generated by the UE or is network-generated to the UE.
Step 11.
The remote end answers to the call.
Step 12.
The SCC AS notifies the MSC the remote end has answered the call.
Step 13.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routeing of the notification to the MSC.
Step 14.
The MSC uses the standard procedure to send the CS connect message to UE as e.g. described in TS 24.008. For video call the UE may initiate at this stage the H.245 Codec negotiation.
Step 15.
The MSC moves to Active state.
Step 16.
The UE moves to Active state.
6.3.2.1.4e PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Single Radio, voice and video |R11| p. 65
Figure 6.3.2.1.4e-1 describes the information flows for transferring voice and video from PS to CS access single radio.
The flow requires that the user is active in an IMS originating or terminating session with voice and synchronised video media; procedures and capabilities specified in clause 6.2.2.3 of TS 23.216 are used for the switching of access networks at the transport layer.
In this flow, the SCC AS waits for the H.245 negotiation completion before updating Remote Leg.
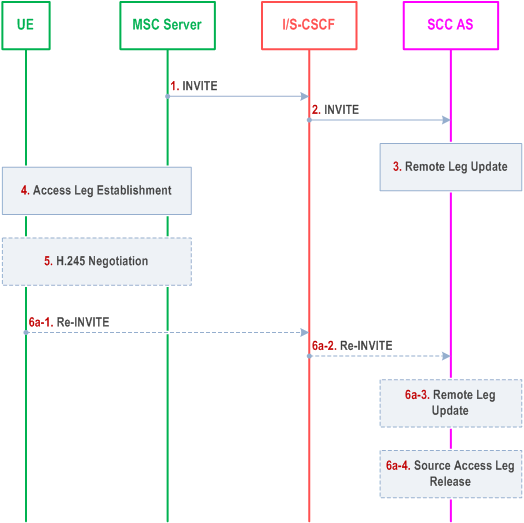
Step 1-2.
See clause 6.3.2.1.4 steps 1 and 2. MSC Server includes the SDP of the voice and video SDP of the predefined Codecs. If vSRVCC with priority is supported, MSC Server enhanced for vSRVCC also includes a priority indication if received. The SCC AS performs the Access Transfer of the most recently added active session for bidirectional voice and synchronised video media. The transfer of the alerting session or during pre-alerting state is described in clause 6.3.2.1.4c and in clause 6.3.2.1.4d.
Step 3.
See clause 6.3.2.1.4 step 3. The SCC AS performs a remote leg update with the media type of the CS access leg for the voice and video session as specified in clause 6.3.1.5.
Step 4.
The MSC Server completes the CS leg establishment with UE-1.
Step 5.
Predefined Codecs for voice and video with specific characteristics are initially used by the UE-1 after it establishes the circuit bearer to the target MSC. The predefined Codecs for voice and video are the default Codecs specified in TS 26.111. If needed, UE-1 and MSC Server may start in band H.245 negotiation right after the UE-1 establishes a circuit bearer to the MSC Server. 3G-324M codec negotiation for the video is executed (refer to TR 26.911 for H.245 signalling optimizations) right after the UE-1 establishes a circuit bearer to the Target MSC.
Step 6a.
If the Gm reference point is retained upon PS handover procedure then:
Step 6a-1.
The UE-1 sends a Re-INVITE via the PS access to update the remaining non-voice and non-voice/non-video media flow(s) associated with the recently added active session. If the UE-1 is using ICS capabilities, this Re-INVITE also adds Gm service control to the active session and the UE-1 subsequently sends Re-INVITEs for any remaining inactive bi-directional speech sessions that are to be transferred.
Step 6a-2.
Standard procedures are used at S-CSCF for routing of the Re-INVITE(s) to the SCC AS.
Step 6a-3.
The SCC AS processes the Re-INVITE(s) and updates the Remote Leg if needed.
Step 6b.
If the Gm reference point is not retained upon PS handover procedure, or if there was no other non-voice and non-voice/non-video media flow(s) in the IMS session than the voice+video which was transferred to the target access, then the Source Access Leg is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.
6.3.2.1.5 PS - CS Access Transfer for voice and video, Dual Radio |R9| p. 67
Figure 6.3.2.1.5-1 describes the information flows for transferring voice and video from PS to CS access.
In this flow, the SCC AS waits for the H245 negotiation completion before updating Remote Leg.
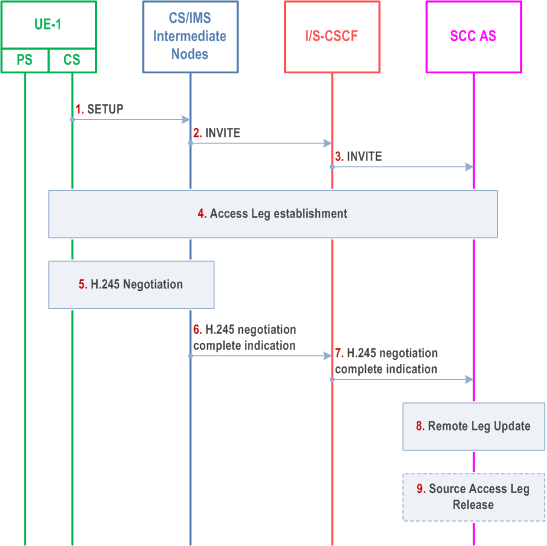
Step 1-3.
UE-1 starts Access Transfer of multimedia session from PS to CS as specified in steps 1-3 of clause 6.3.2.1.1. The media types of voice and video, included in the INVITE message with STN in step 3, instruct the SCC AS to wait for H.245 negotiation complete to perform the Remote Leg update in step 8.
Step 4.
The SCC AS completes the CS leg establishment with UE-1.
Step 5.
UE-1 and CS/IMS intermediate node starts in band H.245 negotiation.
Step 6-7.
After the H.245 negotiation is done, CS/IMS intermediate node sends H.245 negotiation completion indication towards SCC AS.
Step 8.
On receipt of the H.245 negotiation complete indication, the SCC AS updates the Remote Leg as specified in step 4 of clause 6.3.2.1.1
Step 9.
The SCC AS may release the Source Access Leg as specified in step 5 of clause 6.3.2.1.1.
6.3.2.1.6 PS - CS Access Transfer: PS to CS - Dual Radio, mid-call service with an active speech and video session |R9| p. 68
Figure 6.3.2.1.6-1 PS to CS with one active speech and video session, using SCUDIF, provides an information flow for Access Transfer of multiple IMS sessions in PS to CS direction. The flow requires that the user is active in an IMS originating or terminating speech and video session using PS media at the time of initiation of Access Transfer to CS and that the use of network capabilities to support mid-call services during session transfer is possible. It also requires that SCUDIF feature is supported by the UE and the CS network.
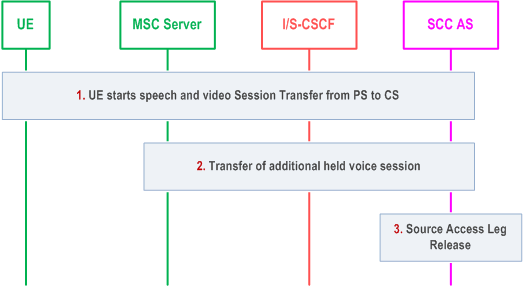
Step 1.
Subsequently, the UE can switch between the speech and video session and the voice session with different bearer capabilities activated using SCUDIF feature as specified in TS 23.292.
If SCUDIF is not supported, the transfer can be performed as Figure 6.3.2.1.6-1 with the differences that in step 1 the UE initiates Access Transfer not using SCUDIF, and after the transfer video channel is closed via H.245 negotiation if the voice session is to be activated.
Standard procedure as specified in clause 6.3.2.1.5 PS - CS Access Transfer for voice and video is used for transferring the active speech and video session. The UE indicates SCUDIF support and provides two bearer capabilities (voice and multimedia) with multimedia preferred when initiating the transfer. Also, the SCC AS provides session state information on the inactive voice session including needed STI on the transferring-in leg to the MSC Server.
Step 2.
The MSC Server initiates session transfer towards SCC AS for the additional inactive voice session on behalf the UE.
Step 3.
The Source Access Leg associated with the inactive voice session is released as specified in clause 6.3.1.6.