Content for TS 23.288 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5A…
6…
6.1.3
6.1.4…
6.1.4.4…
6.1.5…
6.1A…
6.1B…
6.1B.2.3…
6.1C
6.2…
6.2.3…
6.2.6…
6.2.6.2
6.2.6.3…
6.2.6.3.3
6.2.6.3.4
6.2.6.3.5
6.2.6.3.6…
6.2.7…
6.2.8…
6.2.9…
6.2.13…
6.2A…
6.2B…
6.2B.3
6.2B.4…
6.2C…
6.2D…
6.2E…
6.2F…
6.2H…
6.2H.2.2…
6.2H.2.3…
6.2H.2.4…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.7.3…
6.7.4…
6.7.5…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11…
6.12…
6.13…
6.14…
6.16…
6.17…
6.18…
6.19…
6.20…
6.21…
6.22…
6.23…
7…
7.4…
7.7…
7.9…
8…
9…
10…
6.22 Signalling Storm Analytics
6.22.1 General
6.22.2 Input data
6.22.3 Output analytics
6.22.4 Procedures
...
...
6.22 Signalling Storm Analytics |R19| p. 302
6.22.1 General p. 302
This clause specifies how NWDAF supports analytics for network abnormal behaviours (i.e. signalling storm) mitigation and prevention.
The signalling storm analytics provides analytics information (statistics or predictions) regarding the abnormal signalling. Abnormal signalling is a significant deviations from normal conditions indicating a potential signalling storm. The analytics of signalling storm requires the identification of whether the signalling storm is due to signalling from an NF or massive signalling from UE based on the requested analytics ID.
The NWDAF provides statistics and/or prediction analytics to consumer entity (e.g. SCP) or consumer NFs, e.g. AMF, SMF, UDM, PCF, NRF, OAM and AF.
The consumer of these analytics may indicate in the request or subscription:
- Analytics ID = "Signalling Storm";
- Target of Analytics Reporting: a UE or a group of UEs or several groups of UEs identified by internal Group ID or SUPI or SUPI range, a list of NFs which is causing the signalling storm;
- Target Cause ID(s): Indicates specific Cause ID(s) as Analytics Output (e.g. signalling storm caused by UEs, signalling storm caused by NF, or all);
-
Analytics Filter Information:
- NF ID List: instance IDs or NF Set IDs of target NF that signalling storm analytics should be provided for;
- Area of Interest (AoI) and/or S-NSSAI which restricts the scope of signalling storm analytics to the specific area and/or slice.
-
Analytics Reporting Information:
- Expected Report Time: indicates the time limit by which the analytics results need to be received, e.g. 10 seconds, 5 minutes, etc.;
- An Analytics target period indicates the time period over which the statistics or predictions are requested;
- Optionally, preferred level of accuracy of the analytics;
- Signalling frequency threshold: indicates the frequency of the received signalling within the time period;
- UE number threshold: indicates a threshold of the amount of UEs of which the number of one type of request messages meets the frequency of UE requests threshold. For example, if the number of UEs that initiate registration requests exceeds the pre-set rate threshold (10 times per hour) and the number of such UEs exceeding the pre-set rate threshold exceeds 100 (the UE number threshold is set to 100), the NWDAF will provide the analytics.
6.22.2 Input data p. 302
The NWDAF collects the signalling feature data, NF context, AF data and MDAF data as listed in Table 6.22.2-1, Table 6.22.2-2, Table 6.22.2-3, Table 6.22.2-4, Table 6.22.2-5 and Table 6.22.2-6.
The NWDAF can collect UE behavioural information per UE or group of UEs as specified in clause 6.7.5.2.
The NWDAF may use output of abnormal UE behaviour analytics and UE dispersion analytics as specified in clause 6.7.5 and clause 6.10.3 as input data for analytics on signalling storm. This information may be collected from a different NWDAF (e.g. distributed architecture).
The NWDAF may collect the subgroup of input data based on implementation.
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE ID | Identifies a single UE. | |
| Signalling feature data | NF procedures containing signalling exchange information related to a particular UE or session from the Connection, Registration, Mobility and Session Managements procedures (NOTE 1). | |
| > Request type and number from UE/RAN (0..max) | AMF | Request type of N1 or N2 interface (such as received Initial Registration Request, Mobility and Periodic Registration Request, Service Request, etc.) and the number of requests corresponding to the request type. |
| >> Time duration from receiving request from UE/RAN to response to UE/RAN | AMF | Time duration between the request from UE/RAN and response to UE/RAN. |
| >> Number of successful responses of UE/RAN | AMF | Number of successful responses associated to their initial requests, such as Registration Response, etc. |
| >> Number of failed responses of UE/RAN | AMF | Number of failed responses associated to their initial requests, such as Registration Reject, Service Reject, etc. |
| >> Reason of failed responses of UE/RAN | AMF | Reasons of failed responses associated to their initial requests, e.g. reject, no-response, etc. |
| >> A posterior Request type of UE/RAN (0..max) | AMF | A posterior Request types triggered from UE/RAN, for NF Service request, or request to UE/RAN (NOTE 6). |
| > Request type and number from NF (0..max) | NF | Request type received from NF, e.g. Namf_ |
| >> Time duration from receiving request from NF to response to NF | NF | Time duration between the request from NF and response to NF. |
| >> Time duration of transactions related to SCP ingress interface | SCP | Time duration between the received request from consumer NF and response forwarded by SCP to consumer NF (NOTE 4). |
| >> Time duration of transactions related to SCP egress interface | SCP | Time duration between the routed/forwarded request to producer NF and response received from producer NF (NOTE 4). |
| >> Number of successful responses of NF | NF | Number of successful responses associated to their initial requests (NOTE 2). |
| >> Number of failed responses of NF | NF | Number of failed responses associated to their initial requests (NOTE 2). |
| >> Number of successful responses related to SCP egress interface | SCP | Number of successful responses received over the egress interface associated to their initial requests. |
| >> Number of failed responses related to SCP egress interface | SCP | Number of failed responses received over the egress interface associated to their initial requests. |
| >> Reason of failed responses of NF | NF | Reasons of failed responses associated to their initial requests, e.g. reject, no-response, etc. |
| >> Reason of failed responses related to SCP egress interface | SCP | Reasons of failed responses over the egress interface associated to their initial requests, e.g. reject, no-response, etc. (NOTE 5). |
| >> Number of redundant signalling of NF | NF | Number of received redundant signalling. The redundant signalling means the signalling which is transmitted multiple times (NOTE 2) (NOTE 3). |
| >> A posterior Request type of NF (0..max) | NF | A posterior Request types triggered from NF, for NF Service request (NOTE 3) (NOTE 6). |
| > Public Warning information | AMF | Public Warning information as defined in the TS 23.041, such as WRITE-REPLACE WARNING REQUEST, etc. |
| > Frequent Mobility Registration Update | AMF | The number of Mobility Registration Updates N within a period M may be an indication for abnormal ping-pong behaviour, where N and M are operator's configurable parameters. |
| > Number of receiving Session Report from UPFs | SMF | Number of receive Session Report from UPF triggered by DL packet in case of PDU Session is in 5GCM-idle state. |
| UE Context in NF | ||
| > State transition information | AMF, SMF |
UE related state transition information such as transition type, frequency of CM state changes, etc.
State transition identifier:
|
| > timer information | AMF, SMF | Timer information which has been set for the UE, such as timer type, duration. |
|
NOTE 1:
NWDAF can optionally provide transaction dispersion analytic information for MM and SM transactions.
NOTE 2:
This data is provided per time interval that is indicated by the NWDAF.
NOTE 3:
The word "NF" refers here to SCP as well. As a centric routing/proxy entity, SCP might be involved with some signaling that may not be visible to the NF sending the SCP's ingress traffic, such a signaling could be associated with actions such as selection & discovery, retransmissions, re-directions, re-selection, throttling, etc.
NOTE 4:
e.g. average time duration of a transaction (averaged over all of the transactions handled by the SCP within the requested time interval).
NOTE 5:
Distribution of the failed responses, e.g. how many time-outs vs how many server errors vs how many consumer errors.
NOTE 6:
A posterior request is a request sent from NF1 to NF2 (or from NF2 to NF1) that was triggered by a previous request received by NF1. For example, in clause 4.3.2.2 of TS 23.502, the request sent by AMF in step 3 and the request sent by SMF in step 11 are both posterior requests of the request received by the AMF in step 1. These posterior requests can be collected by NF1 (the AMF in this example).
An SCP can collect a posterior request between NF1 and NF2 only if it routes incoming requests to NF1 as well as route requests between NF1 and NF2.
|
||
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NF ID | NF instance ID. | |
| > NF profile | NRF | NF Profile information such as allowed NF information for the NF and NF Service(s). |
| > NF load status information | NRF, SCP | Load information indicates the current load of the NF and NF Service(s), e.g. CPU, memory, and/or percentage of load information (NOTE 1). |
| > Capacity and priority information of NFs and NF Services | NRF, SCP | Capacity and priority information of the registered NF and NF Service(s) (NOTE 1). |
| NF heart-beat related information | NF | NF heart-beat related information such as responding time, Number of retransmissions, heart-beat intervals. |
| heart-beat related information | SCP | heart-beat related information such as responding time, Number of retransmissions, heart-beat intervals between the NF and NRF and/or between SCP and NRF. |
| > Unexpected operational status indicator | NF, OAM | The parameter indicates unexpected operational status occurs. It is an indication of deviation from the normal operations, based on thresholds or rules configured by operator at the NF or OAM (e.g. for energy consumptions, loads, etc.). |
|
NOTE 1:
If this information is not available in the NRF, it can be obtained from the OAM.
|
||
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NF ID | NF instance ID. | |
| > Usage information of UE IP address resources | SMF | Usage information of UE IP address resources (dynamic and static, V4, V6, etc.) for CP or UP allocation, such as number, usage, number of UE IPs, which prohibit allocation during certain time interval, etc. This parameter is valid for SMF only. |
| > Load information of connected UPFs | SMF | Load information of connected UPFs such as using PFCP Load Control Information. This parameter is valid for SMF only. |
| SCP Signalling statistics | SCP | The number of different types of signalling received and sent by SCP during a target time period, etc. This parameter is valid for SCP only. |
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application ID | AF | Identifies the application providing this information. |
| User activation time information (1…max) | AF | Information of activation time for the users (e.g. IoT users) per application. |
| > Number of UEs | AF | The total number of UEs. |
| > Active Time | AF | The time stamp of the users per application switch to active, or the start and end time of the users activity per application. |
| > Inactive Time | AF | The time stamp of the users per application switch to inactive, or the start and end time of the users inactivity per application, if applicable. |
| > UE type ID | AF | Identifies a group of UEs, e.g. external group ID, or a list of UE IDs. |
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NRF ID | NRF instance ID. | |
| Number of NF service registration requests | OAM | Number of registration request received at the NRF. |
| > Number of successful NF service registrations | OAM | Number of successful registrations. |
| > Number of failed NF service registrations due to encoding error of NF profile | OAM | Number of failed registrations. |
| > Number of failed NF service registrations due to NRF internal error | OAM | Number of failed registrations. |
| Number of NF service update requests | OAM | Number of update request received at the NRF. |
| > Number of successful NF service updates | OAM | Number of successful updates. |
| > Number of failed NF service updates due to encoding error of NF profile | OAM | Number of failed updates. |
| > Number of failed NF service updates due to NRF internal error | OAM | Number of failed updates. |
| Number of NF discovery requests | OAM | Number of discovery request received at the NRF. |
| > Number of successful NF discoveries | OAM | Number of successful discovery attempts. |
| > Number of failed NF service discoveries due to unauthorized NF Service consumer | OAM | Number of failed discovery attempts. |
| > Number of failed NF discoveries due to input errors | OAM | Number of failed discovery attempts. |
| > Number of failed NF discoveries due to NRF internal error | OAM | Number of failed discovery attempts. |
|
NOTE 1:
If this information is not available in the OAM, it can be obtained from the NRF if available.
|
||
| Information | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| affectedObject | MDAF | Indication of 5GC NFs where congestion issues occurred or potentially may occur. |
| cPCongestionIssueID | MDAF | This field holds the ID of the control plane congestion issue which is reported. |
6.22.3 Output analytics p. 308
The output analytics of signalling storm provided by NWDAF is defined in Table 6.22.3-1, and Table 6.22.3-2. The Table 6.22.3-3 gives examples of NF/SCP actions for solving each risk. The final mitigation or prevention operations are based on operator's policy/configuration and NF/SCP implementation.
The statistics and predictions are provided with a Validity Period, as defined in clause 6.1.3.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Report (1..max) | List of observed signalling storm statistics. |
| > Target NF ID/SCP ID | A list of impacted NFs/SCPs of signalling storm detected by NWDAF. |
| > Cause of the signalling storm | The potential cause of abnormal level of signalling (i.e. massive signalling from UE or NF abnormal signalling). |
| > Source UE/NF | a UE or a group of UEs or several groups of UEs identified by internal Group ID or SUPI or SUPI range, or a list of NFs which cause the signalling storm. |
| > OPTIONAL Time slot entry (1..max) | List of time slots during the Analytics target period. |
| >> Time slot start | Time slot start within the Analytics target period. |
| >> Duration | Duration of the time slot. If a Temporal granularity size was provided in the request or subscription, the Duration is greater than or equal to the Temporal granularity size. |
| >> Received Signalling Analytics | Information of signalling received by the target NF(s). |
| >>> Total number of received signalling | Indicates the statistics on the number of signalling messages received by the target NF(s) in the time slot. |
| >>> Growth rate of received signalling | Difference between the number of signalling messages received by the NF in the time slot and the number of signalling messages received by the target NF(s) in the previous time slot. |
| >>> Signalling analytics of UE | Indicates the statistics on the number of signalling messages received from UEs within the time slot (NOTE 1). |
| > OPTIONAL Timer List | The list of timer information per source UE(s) (NOTE 1). |
| >> Type of timer | The type of timer which has been set. |
| >> Timer duration | The timer duration that has be selected for the source UE(s). |
|
NOTE 1:
Only available when Cause of signalling storm is massive signalling from UEs, and there exists Source UE(s).
|
|
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Report (1..max) | List of predicted signalling storm analytics. |
| > Target NF ID/SCP ID | A list of impacted NFs/SCPs signalling storm predicted by NWDAF. |
| > Cause of the signalling storm | The potential cause of abnormal level of signalling (i.e. massive signalling from UE or NF abnormal signalling). |
| > Source UE/NF | a UE or a group of UEs or several groups of UEs identified by internal Group ID or SUPI or SUPI range, or a list of NFs which cause the signalling storm. |
| > OPTIONAL Time slot entry (1..max) | List of time slots during the Analytics target period. |
| >> Time slot start | Time slot start within the Analytics target period. |
| >> Duration | Duration of the time slot. If a Temporal granularity size was provided in the request or subscription, the Duration is greater than or equal to the Temporal granularity size. |
| >> Reference point | The information of the reference point impacted. (e.g. N1, N2) |
| >> Service operation(s) | The information of the service operation(s) impacted. (e.g. Namf_ |
| >> Received Signalling Analytics | Information of signalling received by the target NF(s). |
| >>> Received number of signalling | Received number of signalling of the specific signalling type. |
| >>> Growth rate of received signalling | Difference between the number of signalling messages received by the NF in the time slot and the number of signalling messages received by the target NF(s) in the previous time slot. |
| >>> Signalling analytics of UE | Indicates the statistics on the number of signalling messages received from UEs within the time slot (NOTE 1). |
| > OPTIONAL Timer List | The list of timer information per Source UE(s) (NOTE 1). |
| >> Type of timer | The type of timer. |
| >> Timer duration | The timer duration that commonly is selected for the Source UE(s). |
| > Priority | Priority (relative to other NFs of the same type) of candidate NFs as defined in the TS 29.510. |
| > Capacity | Candidate NF capacity information, expressed as a weight relative to other NF instances of the same type as defined in the TS 29.510. |
| > Confidence | Confidence of this prediction. |
|
NOTE 1:
Only available when Cause of signalling storm is massive signalling from UEs, and there exists Source UE(s).
|
|
| Cause of the signalling storm | Example actions of NFs |
|---|---|
| massive signalling from UE | AMF sets MM NAS related timer (e.g. back-off, T3512) for a selected set of UEs. |
| massive signalling from UE | SMF sets SM NAS related timer (e.g. back-off) for a selected set of Sessions. |
| massive signalling from UE | AMF/SMF sets suggested N1/N2 interface related ingress/egress threshold, or AMF triggers RAN to initiate overload control for a selected set of UEs in specific slice or priority as defined in clause 8.7.7 of TS 38.413 to start overload control. The AMF may assign a slice under signalling storm conditions to the UEs and initiate overload control for the specific slice. |
| NF abnormal signalling | NRF configures the local policy (e.g. to prevent the source NF with abnormal signalling from being discovered or discovering others, to update the NF profile(s)(e.g. Priority, Capacity) of NF(s) based on the signalling storm statistics and/or predictions and send the updated NF profiles(s) to NF service consumer(s) of the NF(s)(e.g. subscriber of the NF profile as defined in clause 4.17.7 of TS 23.502)). |
| NF abnormal signalling | Source NF configures to (re)select other NFs instead of NF with abnormal signalling and may unsubscribes the NF with abnormal signalling. |
| NF abnormal signalling | Source NF configures to deprioritize the NFs/Services with abnormal signalling from being selected. |
| NF abnormal signalling | Source NF triggers UE Reregistration and/or Session Reestablishments to avoid NF with abnormal signalling. |
| NF abnormal signalling | SCP blocks or throttles messges originating from an NF/service with abnormal signalling. |
| NF abnormal signalling | SCP redirects requests towards an NF service producer with abnormal signalling towards another service producer. |
| NF abnormal signalling | SCP notifies communication peers of an NF with abnormal signalling about abnormal condition, e.g. high load. |
6.22.4 Procedures p. 311
The NWDAF can provide information on network signalling storm as follows (Figure 6.22.4-1).
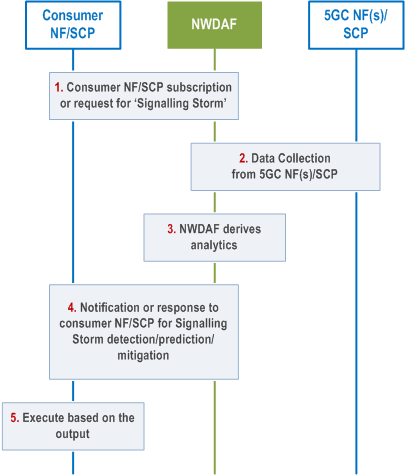
Step 1.
The consumer NF (SCP included) or other entities subscribes to or sends a request to NWDAF for the signalling storm analytics using either Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription_Subscribe or Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo_Request service operation. The request additionally includes thresholds such as confidence level and accuracy of detection:
Step 2.
- The Analytics ID is set to "Signalling Storm analytics". The target for analytics reporting is set to be any NF/SCP or any UE. Analytic filters may be provided as shown in clause 6.22.1.
- The consumer NF can request statistics or/and predictions for a given Analytics target period.
- The consumer NF may also subscribe to "NF load analytics" as depicted in clause 6.5 and trigger the signalling storm analytics based on output of the NF load analytics, e.g. CPU usage is over 80%.
- The consumer NF may also subscribe to "Abnormal behaviour" analytics as depicted in clause 6.7.5 and trigger the signaling storm analytics based on the suspicion of DDoS attack.
- The consumer NF may also subscribe to "Dispersion Analytics" analytics as depicted in clause 6.10 and trigger the signaling storm analytics when the transaction dispersion is above the expected transaction dispersion configurable threshold.
The NWDAF retrieves Input data from NFs and SCPs, using Nnf_EventExposure_Subscribe , or from NRF using Nnrf_NFManagement_NFStatusSubscribe service operation, such as UE and/or NF releated context data, NF context, AF data, MDAF data and UE behavioural information to derive the required analytics as depicted in clause 6.22.2. The NWDAF may optionally request additional data aligned with the analysis target identified in step 1.
The NWDAF may optionally subscribe the abnormal UE behaviour analytics and UE dispersion analytics as specified in clause 6.7.5 and 6.10.3 as input data from other NWDAFs, using Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription_Subscribe or Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo_Request service operation.
Step 3.
The NWDAF derives the required analytics with the collected data described in clause 6.22.2.
Step 4.
The NWDAF invokes Nnwdaf_AnalyticsSubscription_Notify or Nnwdaf_AnalyticsInfo_Request response or response to the consumer NF/SCP for the Output data analytics as depicted in clause 6.22.3.
Step 5.
The consumer upon receiving the detection and/or prediction and/or mitigation may execute based on the example mechanisms as depicted in clause 6.22.3.