Content for TS 38.305 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
5…
6…
6.5…
6.7…
7…
7.3A…
7.4…
7.6…
7.11…
7.12…
8…
8.1.2.1a…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
A…
7.4 General RRC procedures for UE Positioning
7.4.1 NR RRC Procedures
7.4.1.0 General
7.4.1.1 Location Measurement Indication
7.4.1.2 UE Positioning Assistance Information
7.4.2 LTE RRC Procedures
7.4.2.0 General
7.4.2.1 Inter-frequency RSTD measurement indication
7.5 Procedures for Broadcast of Assistance Data
7.5.1 General
7.5.2 Broadcast Procedures
...
...
7.4 General RRC procedures for UE Positioning p. 56
7.4.1 NR RRC Procedures p. 56
7.4.1.0 General |R18| p. 56
NR RRC supports the following positioning related procedures:
- Location Measurement Indication;
- UE Positioning Assistance Information.
7.4.1.1 Location Measurement Indication p. 57
The location measurement indication procedure is used by the UE to request measurement gaps for OTDOA RSTD measurements, for subframe and slot timing detection for inter-RAT E-UTRA RSTD measurements, or for NR DL-PRS measurements.

Precondition:
The UE served by a gNB has received a LPP message from an LMF requesting inter-RAT RSTD measurements for OTDOA positioning or NR DL-PRS measurements.
Step 1.
If the UE requires measurement gaps for performing the requested location measurements while measurement gaps are either not configured or not sufficient, or if the UE needs gaps to acquire the subframe and slot timing of the target E-UTRA system before requesting measurement gaps for the inter-RAT RSTD measurements (see TS 38.133, the UE sends an RRC Location Measurement Indication message to the serving gNB. The message indicates that the UE is going to start location measurements, or that the UE is going to acquire subframe and slot timing of the target E-UTRA system, and includes information required for the gNB to configure the appropriate measurement gaps. When the gNB has configured the required measurement gaps the UE performs the location measurements or timing acquisition procedures.
Step 2.
When the UE has completed the location procedures which required measurement gaps, the UE sends another RRC Location Measurement Indication message to the serving gNB. The message indicates that the UE has completed the location measurements or timing acquisition procedures.
7.4.1.2 UE Positioning Assistance Information |R17| p. 57
The UE Positioning Assistance Information procedure is used by UE to report the UE Positioning Assistance Information for UL-TDOA. The UE reports the association between UL-SRS resources for positioning and the UE Tx TEG ID, and the margin value for UE Tx TEGs.

Precondition:
The serving gNB of a UE has received a NRPPa message from an LMF requesting the TxTEG of the UE for NR UL-TDOA positioning.
Step 1.
The serving gNB may send a RRC Reconfiguration message to the UE, requesting the UE to provide the association information of UL SRS resources for positioning with Tx TEGs to the serving gNB if the UE supports UE Tx TEG reporting. Based on the request from the LMF, the RRC Reconfiguration message from the serving gNB to the UE indicates the UE should provide either a single report or a periodic report of UE TxTEG association to the serving gNB.
Step 2.
When the UE receives the request via RRC Reconfiguration message, the UE sends a UE Positioning Assistance Info message to the serving gNB to report the UE TxTEG information, including all the changes of the UE TxTEG during the report period if the UE is required to report UE Tx TEG periodically. The UE will report all the UE TxTEG at the time when the RRC Reconfiguration message is received if the UE is only required to report the one-shot UE TxTEG information. For each UE Positioning Assistance Info message, only a single margin value can be reported.
7.4.2 LTE RRC Procedures p. 58
7.4.2.0 General |R18| p. 58
LTE RRC supports the following positioning related procedures:
- Inter-frequency RSTD measurement indication.
7.4.2.1 Inter-frequency RSTD measurement indication p. 58
The Inter-frequency RSTD measurement indication procedure is used by the UE to request measurement gaps for OTDOA RSTD measurements.

Precondition:
The UE served by an ng-eNB has received a LPP message from an LMF requesting inter-frequency RSTD measurements for OTDOA positioning.
Step 1.
If the UE requires measurement gaps for performing the requested inter-frequency RSTD measurements for OTDOA positioning while measurement gaps are either not configured or not sufficient, the UE sends an RRC Inter-frequency RSTD Measurement Indication message to the serving ng-eNB. The message indicates that the UE is going to start inter-frequency RSTD measurements and includes information required for the ng-eNB to configure the appropriate measurement gaps. When the ng-eNB has configured the required measurement gaps the UE performs the inter-frequency RSTD measurements.
Step 2.
When the UE has completed the inter-frequency RSTD measurements which required measurement gaps, the UE sends another RRC Inter-frequency RSTD Measurement Indication message to the serving ng-eNB. The message indicates that the UE has completed the inter-frequency RSTD measurements.
7.5 Procedures for Broadcast of Assistance Data |R16| p. 58
7.5.1 General p. 58
Positioning assistance data can be included in positioning System Information Blocks (posSIBs) as described in TS 36.331, TS 38.331 and TS 36.355. The posSIBs are carried in RRC System Information (SI) messages. The mapping of posSIBs (assistance data) to SI messages is flexibly configurable and provided to the UE in SIB1 for NG-RAN node TS 36.331, TS 38.331.
The UE may request posSI by means of on-demand SI request in RRC_IDLE/RRC_INACTIVE and also request posSIBs by means of on-demand SI request in RRC_CONNECTED as described in TS 38.331. U2N Remote UE may also request posSIB via a U2N Relay UE as described in TS 38.331. The U2N relay UE forwards the posSIB transparently to the U2N Remote UE.
For each assistance data element, a separate posSIB-type is defined in TS 36.355. Each posSIB may be ciphered by the LMF using the 128-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm (with counter mode) as described in TS 36.355, either with the same or different ciphering key. The posSIBs which exceed the maximum size limit defined in TS 36.331, TS 38.331 shall be segmented by the LMF.
7.5.2 Broadcast Procedures p. 59
The general procedures for broadcast of positioning assistance data and delivery of ciphering keys to UEs is described in TS 23.273. This clause defines the overall sequences of operations that occur in the LMF, NG-RAN node and UE.
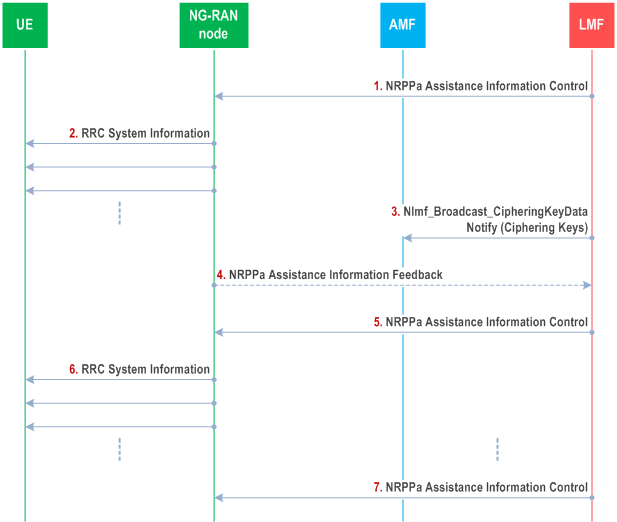
Step 1.
The LMF sends an NRPPa Assistance Information Control message to the NG-RAN node with an indication to start broadcasting assistance information. The message includes one or more System Information groups, where each group contains the broadcast periodicity and one or more posSIB types together with meta data to be scheduled in the same SI message. Each posSIB type may be ciphered and/or segmented at the LMF. The meta data may include an indication whether the posSIB type in the System Information group is ciphered or not, as well as an indication of an applicable GNSS type.
Step 2.
The NG-RAN node includes the received System Information groups in RRC System Information Messages and corresponding scheduling information in SIB1 as described in TS 36.331, TS 38.331. The UE applies the system information acquisition procedure according to TS 36.331, TS 38.331 for acquiring the assistance data information that is broadcasted.
Step 3.
If the posSIB types were ciphered by the LMF, the LMF invokes the Nlmf_Broadcast_CipheringKeyData Notify service operation towards the AMF carrying one or more ciphering keys. For each ciphering key, the LMF includes a ciphering key value, a ciphering key identifier, a validity period, a set of applicable tracking areas, and a set of applicable posSIB types. The AMF may then distribute successfully stored ciphering keys and their validity times and validity areas to suitably subscribed UEs using a mobility management message as described in TS 23.273. The LMF repeats this procedure whenever a ciphering key changes.
Step 4.
At any time after Step 1, the NG-RAN node may send a NRPPa Assistance Information Feedback message to the LMF providing feedback on assistance information broadcasting. The message may include an assistance information failure list indicating that certain posSIB types could not be configured for broadcasting by the NG-RAN node.
Step 5.
If the assistance information in a System Information group changes, the LMF provides updated information in a NRPPa Assistance Information Control message.
Step 6.
The NG-RAN node replaces the previously stored System Information groups with the new information received at Step 5 and includes the new System Information groups in RRC System Information Messages.
Step 7.
If the LMF wants to abort the broadcast of a System Information Group, it sends a NRPPa Assistance Information Control message to the NG-RAN node including an indication to stop broadcasting the assistance information.