Content for TS 38.305 Word version: 18.3.0
1…
4…
5…
6…
6.5…
6.7…
7…
7.3A…
7.4…
7.6…
7.11…
7.12…
8…
8.1.2.1a…
8.1.3…
8.2…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
8.11…
8.12…
8.13…
8.14…
8.15…
A…
7.11 General SLPP procedures for UE Positioning and Ranging
7.11.1 SLPP procedures
7.11.2 SLPP positioning and ranging procedures
7.11.2.1 SLPP capability transfer
7.11.2.2 SLPP assistance data transfer
7.11.2.3 SLPP location information transfer
7.11.2.4 Error handling
7.11.2.5 Abort
7.11.2.6 Sequence of Procedures
...
...
7.11 General SLPP procedures for UE Positioning and Ranging |R18| p. 66
7.11.1 SLPP procedures p. 66
Positioning and Ranging procedures using NR sidelink are modelled as transactions of the SLPP protocol using the procedures defined in this specification. A procedure consists of a single operation of one of the following types:
- Exchange of positioning capabilities;
- Transfer of assistance data;
- Transfer of location information (positioning measurements, ranging measurements, and/or position estimate);
- Error handling;
- Abort.
7.11.2 SLPP positioning and ranging procedures p. 66
7.11.2.1 SLPP capability transfer p. 66
Capabilities in an SLPP context refer to the ability to support different position methods defined for SLPP (e.g., SL-RTT, SL-TDOA, etc.), different aspects of a particular position method (e.g. different types of measurements or assistance data) and common features not specific to only one position method.
The exchange of capabilities between different endpoints may be initiated by a request or sent as "unsolicited" information. If a request is used, an endpoint A sends an SLPP Request Capabilities message to an endpoint B with a request for capability information. The endpoint B sends an SLPP Provide Capabilities message.

The SLPP Capability Indication procedure is used for unsolicited capability transfer.

7.11.2.2 SLPP assistance data transfer p. 67
Assistance data may comprise SL-PRS information (e.g., SL-PRS Sequence ID) or position calculation information (e.g., SL Anchor UE location information) and may be transferred either by request or unsolicited. If a request is used, an endpoint A sends an SLPP Request Assistance Data message to an endpoint B and may indicate the assistance data needed. The endpoint B then responds with an SLPP Provide Assistance Data message.
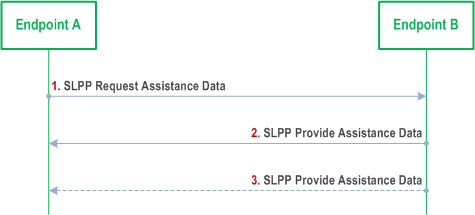
Step 1.
SLPP Assistance Data Delivery procedure is used for unsolicited assistance data transfer.
Endpoint A may send a request to endpoint B for assistance data and may indicate the particular assistance data needed.
Step 2.
Endpoint B transfers assistance data to endpoint A. The transferred assistance data should match any assistance data requested in step 1.
Step 3.
Optionally, endpoint B may transfer additional assistance data to endpoint A in one or more additional SLPP messages.

7.11.2.3 SLPP location information transfer p. 68
The term "location information" applies both to an actual position estimate and to values used in computing position (e.g., SL-PRS measurements). It can be delivered either in response to a request or unsolicited.

Step 1.
SLPP Location Information Delivery procedure is used for unsolicited location information transfer.
Endpoint A may send a request for location information to endpoint B and may indicate the type of location information needed and associated QoS.
Step 2.
In response to step 1, the endpoint B transfers location information to endpoint A. The location information transferred should match the location information requested in step 1.
Step 3.
Optionally (e.g., if requested in step 1), endpoint B in step 2 may transfer additional location information to endpoint A in one or more additional SLPP messages.

7.11.2.4 Error handling p. 68
The procedure is used to notify the sending endpoint by the receiving endpoint that the receiving SLPP message is erroneous or unexpected.

7.11.2.5 Abort p. 69
The procedure is used to notify the other endpoint by one endpoint to abort an ongoing SLPP procedure between the two endpoints.

7.11.2.6 Sequence of Procedures p. 69
SLPP procedures are not required to occur in any fixed order, in order to provide greater flexibility in positioning. Despite the flexibility allowed by SLPP, it is expected that procedures will normally occur in the following order:
- Capability Transfer;
- Assistance Data Transfer;
- Location Information Transfer (measurements and/or location estimate).