Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
J SRVCC from 5G to UTRAN
J.1 SRVCC from NR to UTRAN
J.2 Emergency call in SRVCC from NR to UTRAN
...
...
J (Normative) SRVCC from 5G to UTRAN |R16| p. 276
J.1 SRVCC from NR to UTRAN p. 276
J.1.1 General p. 276
5G Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) is specified in TS 23.216, TS 23.501 and TS 23.502. This clause specifies the security aspect to support SRVCC from 5G to UTRAN. SRVCC from UTRAN to 5G shall not be allowed. After a 5G to UTRAN SRVCC session has terminated, a UE shall run a successfully (re)authentication in 5GS before allowed to access 5G.
During SRVCC from 5G to UTRAN CS, the MSC server should never know the KAMF nor should the KAMF be revealed to an entity other than an AMF.
The AMF derives new key(s) to create a mapped SRVCC security context for the MSC server instead of sending KAMF to the MSC server.
J.1.2 Procedure p. 276
As described in TS 23.216, there is no direct interface between the AMF in 5G and the MSC in UTRAN to support SRVCC, so the keys used to protect the SRVCC session once the UE is handed over to UTRAN are derived by MME based on security context mapping from 5G to E-UTRAN and then forwarded to the MSC during the HO procedure.
The procedure is initiated when the gNB wants to trigger a 5G SRVCC handover to UTRAN.
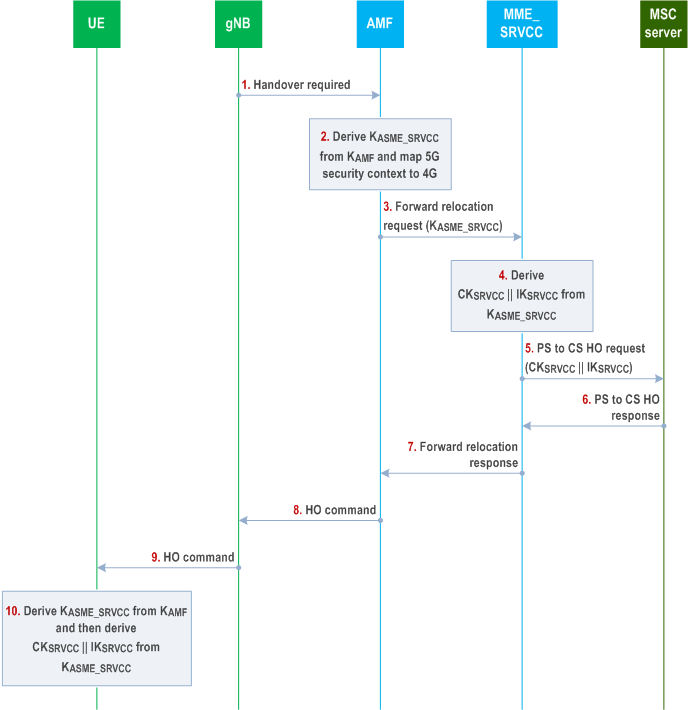
Step 1.
If the SRVCC handover is not completed successfully, the new mapped CKSRVCC, IKSRVCC and KSISRVCC cannot be used. In this case, the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC shall delete the newly mapped SRVCC security context for the UE, including CKSRVCC, IKSRVCC and KSISRVCC.
The gNB sends Handover required message to the AMF.
Step 2.
The AMF shall derive a new KASME_SRVCC key using the KAMF key and the current downlink 5G NAS COUNT of the current 5G security context as described in clause A.21. The AMF increases the downlink 5G NAS COUNT by one.
Step 3.
The AMF shall assign the value of ngKSI to the eKSI (maps ngKSI to eKSI) and shall transfer the new KASME_SRVCC key and the UE security capability to the MME_SRVCC via Forward relocation request message.
Step 4.
The MME_SRVCC shall derive the CKSRVCC, IKSRVCC based on the new KASME_SRVCC key as in clause A.12 of TS 33.401 using a downlink NAS COUNT of zero.
Step 5.
The MME_SRVCC assigns the value of eKSI to KSISRVCC (maps eKSI to KSISRVCC) and transfers CKSRVCC, IKSRVCC with KSISRVCC and the UE security capability to the MSC server in PS to CS HO request message.
Step 6.
The MSC server sends the PS to CS HO response message to the MME_SRVCC.
Step 7.
The MME_SRVCC sends the Forward relocation response message to the AMF.
Step 8.
The AMF sends the HO command to the gNB, in which the AMF shall include the 4 LSBs of the downlink NAS COUNT used to calculate KASME_SRVCC.
Step 9.
The gNB sends the HO command to the UE, in which the gNB shall include the 4 LSB of the downlink NAS COUNT received from the AMF.
Step 10.
When the UE receives the message, the UE shall derive the new KASME_SRVCC key as described in Annex A.21 using the KAMF key and the downlink 5G NAS COUNT estimated from the 4 LSB received form the AMF. The UE shall further derive CKSRVCC, IKSRVCC based on the new KASME_SRVCC key as described in the clause A.12 of TS 33.401 using a downlink NAS COUNT of zero. The UE shall identify the CKSRVCC and IKSRVCC from eKSI (= ngKSI) as the MME_SRVCC does.
J.2 Emergency call in SRVCC from NR to UTRAN p. 277
J.2.1 General p. 277
IMS Emergency Sessions can be authenticated or unauthenticated depending on the serving network policy (or regulatory requirements) if unauthenticated IMS Emergency Sessions are allowed. Any behaviour not explicitly specified as being special to IMS Emergency Sessions is handled in accordance to normal procedures.
J.2.2 Procedure p. 277
When the SVRCC is for an emergency session, the security procedure in clause J.1.2 is applied.
However, in the case when the SRVCC is for an unauthenticated emergency session, since the derived keys have no ability to affect the output of the NULL algorithms, call set up needs to continue even though the network and the UE derive different keys.