Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
7 Security for non-3GPP access to the 5G core network
7.1 General
7.1a Determining trust relationship in the UE
7.2 Security procedures
7.2.1 Authentication for Untrusted non-3GPP Access
...
...
7 Security for non-3GPP access to the 5G core network p. 128
7.1 General p. 128
Security for untrusted non-3GPP access to the 5G Core network is achieved by a procedure using IKEv2 as defined in RFC 7296 to set up one or more IPsec ESP [4] security associations. The role of IKE initiator (or client) is taken by the UE, and the role of IKE responder (or server) is taken by the N3IWF.
During this procedure, the AMF delivers a key KN3IWF to the N3IWF. The AMF derives the key KN3IWF from the key KAMF. The key KN3IWF is then used by UE and N3IWF to complete authentication within IKEv2.
Security for trusted non-3GPP access to 5G Core network is defined in clause 7A.
Trusted and untrusted Non-3GPP Access Networks are IP access networks that use access technology whose specification is out of the scope of 3GPP.
Whether a non-3GPP IP access network is trusted or untrusted is not a characteristic of the access network.
In non-roaming scenario it is the HPLMN's operator decision if a non-3GPP IP access network is used as trusted or untrusted non-3GPP access Network. When one or more of the security feature groups provided by the non-3GPP access network are considered not sufficiently secure by the home operator, the non-3GPP access may be identified as an untrusted non-3GPP access for that operator. However, this policy decision may additionally be based on reasons not related to security feature groups.
In roaming scenario, the UDM in HPLMN makes the final decision of whether a non-3GPP IP access network is used as trusted or untrusted non-3GPP access network based on the identities of the access network and the visited network. The UDM may take the VPLMN's policy and capability returned from the AMF or roaming agreement into account
For supporting multiple DNs, the same trust relationship shall apply to all the DNs the UE connects to from a certain non-3GPP access network, i.e. it shall not be possible to access one DN using the non-3GPP access network as trusted, while access to another DN using the same non-3GPP access network as untrusted.
7.1a Determining trust relationship in the UE |R16| p. 128
There are various possibilities to determine the trust relationship in the UE as it is described in TS 23.501. For example, the non-3GPP access networks, which are trusted, can be pre-configured in the UE. If the USIM supports non-3GPP access networks service, the home network operator may configure in the USIM a list of trusted non-3GPP access networks. In case of pre-configured information in the UE, the list of trusted non-3GPP access networks pre-configured by the home network operator in the USIM shall take precedence over information pre-configured in the ME.
7.2 Security procedures p. 129
7.2.1 Authentication for Untrusted non-3GPP Access p. 129
This clause specifies how a UE is authenticated to 5G network via an untrusted non-3GPP access network. It uses a vendor-specific EAP method called "EAP-5G", utilizing the "Expanded" EAP type and the existing 3GPP Vendor-Id, registered with IANA under the SMI Private Enterprise Code registry. The "EAP-5G" method is used between the UE and the N3IWF and is utilized for encapsulating NAS messages. If the UE needs to be authenticated by the 3GPP home network, any of the authentication methods as described in clause 6.1.3 can be used. The method is executed between the UE and AUSF as shown below.
When possible, the UE shall be authenticated by reusing the existing UE NAS security context in AMF.
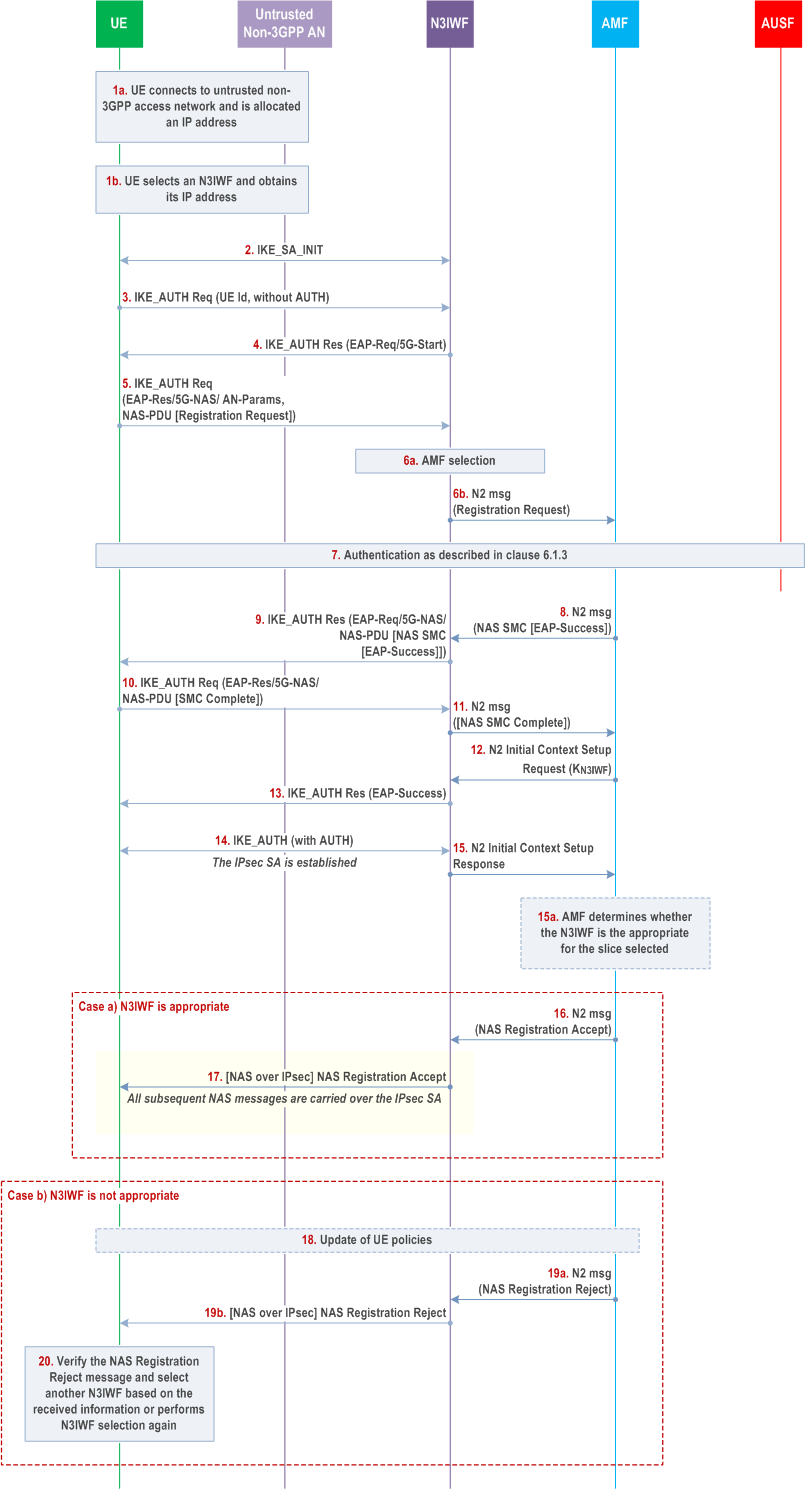
Step 1.
Case a):
The UE connects to an untrusted non-3GPP access network with procedures outside the scope of 3GPP. When the UE decides to attach to 5GC network, the UE selects an N3IWF in a 5G PLMN, as described in clause 6.3.6 of TS 23.501.
Step 2.
The UE proceeds with the establishment of an IPsec Security Association (SA) with the selected N3IWF by initiating an IKE initial exchange according to RFC 7296. After step 2 all subsequent IKE messages are encrypted and integrity protected by using the IKE SA established in this step.
Step 3.
The UE shall initiate an IKE_AUTH exchange by sending an IKE_AUTH request message. The AUTH payload is not included in the IKE_AUTH request message, which indicates that the IKE_AUTH exchange shall use EAP signalling (in this case EAP-5G signalling). As per the RFC 7296, in the IDi the UE shall set the ID type as ID_KEY-ID in this message and set its value equal to any random number. The UE shall not use its GUTI/SUCI/SUPI as the Id in this step. If the UE is provisioned with the N3IWF root certificate, it shall include the CERTREQ payload within the IKE_AUTH request message to request N3IWF's certificate.
Step 4.
The N3IWF responds with an IKE_AUTH response message which includes the N3IWF identity, the AUTH payload to protect the previous message it sent to the UE (in the IKE_SA_INIT exchange) and an EAP-Request/5G-Start packet. The EAP-Request/5G-Start packet informs the UE to initiate an EAP-5G session, i.e. to start sending NAS messages encapsulated within EAP-5G packets. If the UE has sent a CERTREQ payload in step 3, the N3IWF shall also include the CERT payload including N3IWF certificate.
Step 5.
The UE shall validate the N3IWF certificate and shall confirm that the N3IWF identity matches the N3IWF selected by the UE. An absence of the certificate from the N3IWF if the UE had requested the certificate or unsuccessful identity confirmation shall result in a connection failure. The UE shall send an IKE_AUTH request which includes an EAP-Response/5G-NAS packet that contains a Registration Request message containing UE security capabilities and the SUCI. If UE is already with the 5GC over 3GPP access and there is an available security context, the UE shall integrity protect the Registration Request message and shall send the 5G-GUTI instead of SUCI. The N3IWF shall refrain from sending an EAP-Identity request. The UE may ignore an EAP Identity request or respond with the SUCI it sent in the Registration Request. If the UE has registered to the same AMF through 3GPP access, and if this is the first time that the UE connects to the 5GC through non-3GPP access, the value of corresponding UL NAS COUNT used for integrity protection is 0; else it can use the existing non-3GPP specific UL NAS COUNT for integrity protection
Step 6.
The N3IWF shall select an AMF as specified in clause 6.3.5 of TS 23.501. The N3IWF forwards the Registration Request received from the UE to the AMF.
Step 7.
If the AMF receives a 5G-GUTI and the Registration is integrity protected, it may use the security context to verify the integrity protection as describe in clause 6.4.6. If the UE has registered to the same AMF through 3GPP access, and if this is the first time that the AMF receives UE's NAS signalling through non-3GPP access, the value of corresponding UL NAS COUNT used for integrity verification is 0; else it can use the existing non-3GPP specific UL NAS COUNT for integrity verification. If integrity is verified successfully, this means that UE is authenticated by AMF.If integrity is verified successfully and no newer security context has been activated over the 3GPP access, then s the primary authentication and tep 8 to step 11 may be skipped. If integrity is verified successfully and a newer security context has been activated over the 3GPP access then authentication may be skipped but the AMF shall activate the newer context with a NAS SMC procedure as described in step 8 and onwards. Otherwise, the AMF shall authenticate the UE.
If the AMF decides to authenticate the UE, it shall use one of the methods from clause 6.1.3. In this case, the AMF shall send a key request to the AUSF. The AUSF may initiate an authentication procedure as specified in clause 6.1.3. Between AMF and UE, the authentication packets are encapsulated within NAS authentication messages and the NAS authentication messages are carried in N2 signalling between the AMF and N3IWF, and then are encapsulated within EAP-5G/5G-NAS packets between the N3IWF and the UE.
In the final authentication message from the home network, the AUSF shall send the anchor key KSEAF derived from KAUSF to the SEAF. The SEAF shall derive the KAMF from KSEAF and send it to the AMF which is used by the AMF to derive NAS security keys. If EAP-AKA' is used for authentication as described in clause 6.1.3.1, then the AUSF shall include the EAP-Success. The UE also derives the anchor key KSEAF and from that key it derives the KAMF followed by NAS security keys. The NAS COUNTs associated with NAS connection identifier "0x02" are set at the UE and AMF.
Step 8.
The AMF shall send a Security Mode Command (SMC) to the UE in order to activate NAS security associated with NAS connection identifier "0x02". This message is first sent to N3IWF (within an N2 message). If EAP-AKA' is used for authentication, the AMF shall encapsulate the EAP-Success received from AUSF within the SMC message.
Step 9.
The N3IWF shall forward the NAS SMC to UE within an EAP-Request/5G-NAS packet.
Step 10.
The UE completes the authentication (if initiated in step 7) and creates a NAS security context or activates another one based on the received ngKSI in the NAS SMC. UE shall respond to the NAS SMC it received from the AMF based on the selected algorithms and parameters as described in clause 6.7.2. The UE shall encapsulate the NAS SMC Complete in the EAP-5G Response.
Step 11.
The N3IWF shall forward the NAS packet containing NAS SMC Complete to the AMF over the N2 interface.
Step 12.
The AMF upon reception of the NAS SMC Complete from the UE or upon success of integrity protection verification, initiates the NGAP procedure to set up the AN context. AMF shall compute the N3IWF key, KN3IWF, using the uplink NAS COUNT associated with NAS connection identifier "0x02" as defined in Annex A.9 for the establishment of the IPsec SA between the UE and the N3IWF and shall include it in the NGAP Initial Context Setup Request sent to the N3IWF.
Step 13.
N3IWF sends an EAP-Success/EAP-5G to the UE upon reception of the NGAP Initial Context Setup Request containing the N3IWF key, KN3IWF. This completes the EAP-5G session and no further EAP-5G packets are exchanged. If the N3IWF does not receive the KN3IWF from AMF, the N3IWF shall respond with an EAP-Failure
Step 14.
The IPsec SA is established between the UE and N3IWF by using the N3IWF key KN3IWF that was created in the UE using the uplink NAS COUNT associated with NAS connection identifier "0x02" as defined in Annex A.9 and was received by N3IWF from the AMF in step 12.
Step 15.
Upon successful establishment of the IPsec SA between the UE and the N3IWF, the N3IWF shall send the NGAP Initial Context Setup Response message to the AMF.
Step 15a.
The AMF may determine whether the N3IWF is appropriate for the slice selected as defined in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502. If it is compatible with the selected N3IWF, then proceed with step 16 and step 17. Otherwise, the AMF shall proceed with step 18 to step 20, and step 16 to 17 are skipped.
Step 16.
Case b):
When NGAP Initial Context Setup Response for the UE is received by the AMF, AMF shall send the NAS Registration Accept message for the UE over the N2 towards the N3IWF.
Step 17.
Upon receiving the NAS Registration Accept message from the AMF, the N3IWF shall forward it to the UE over the established IPsec SA. All further NAS messages between the UE and the N3IWF shall be sent over the established IPsec SA.
Step 18.
The AMF may trigger the UE policy update procedure and update the UE policy as defined in step 15 and step 16 in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502.
Step 19.
The AMF shall send a Registration Reject message via N3IWF to the UE as defined in step 17 in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502. The Registration Reject message is ciphered and integrity protected.
Step 20.
The UE shall decipher and verify the integrity of the Registration Reject message. If verification is successful, then the UE proceeds with step 18 in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502, and sends a Registration request message to the AMF via a new selected N3IWF.