Content for TS 33.501 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
5…
5.3…
5.9…
5.10…
6…
6.1.3…
6.1.4…
6.2…
6.2.2…
6.3…
6.4…
6.5…
6.6…
6.7…
6.8…
6.9…
6.10…
6.11
6.12…
6.13
6.14…
6.15…
6.16…
7…
7A…
7A.2.3…
7B…
8…
9…
10…
11…
12…
13…
13.2.2…
13.2.4…
13.3…
13.4…
14…
15…
16…
A…
B…
C…
D…
E…
F…
G…
I…
I.9…
J…
K…
M…
N…
O…
P…
R
S…
T…
U…
V…
W…
X…
Y…
Z…
7A Security for trusted non-3GPP access to the 5G core network
7A.1 General
7A.2 Security procedures
7A.2.1 Authentication for trusted non-3GPP access
...
...
7A Security for trusted non-3GPP access to the 5G core network |R16| p. 133
7A.1 General p. 133
Security for trusted non-3GPP access to the 5G Core network is achieved when the UE registers to the 5GC via the TNAN. The UE registers to 5GC and, at the same time, it authenticates with the TNAN by using the EAP-5G procedure, similar to the one used with the registration procedure for untrusted non-3GPP access.
The link between the UE and the TNAN can be any data link (L2) that supports EAP encapsulation. The requirement on the Ta interface between the TNAP and TNGF can be found in clause 4.2.8.3.2 of TS 23.501. The TNGF terminates the EAP-5G signalling andfowards the NAS message to the 5GC when the UE attempts to register to 5GC via the TNAN. The security relies on Layer-2 security between UE and TNAP, which is a trusted entity so that no IPSec encryption would be necessary between UE and TNGF, i.e. NULL encryption is sufficient for the user plane and signalling. However, integrity protection would be provided.
During IPSec IKE negotiations the UE and TNGF may negotiate MOBIKE support as specified in RFC 4555, this would facilitate quick re-establishment IPSec connection and any associated SAs later if needed. Separate IPSec SAs may be used for NAS transport and PDU Sessions. At the end of the UE's registration to 5GC, an IPSec SA (NWt) is established between the UE and TNGF. This is used to protect NAS messages between the UE and TNGF. Later when the UE initiates a PDU session establishment, the TNGF initiates establishment of one or more IPSec child SAs per PDU session. This results in additional IPSec SA's (NWt) to be setup between the UE and TNGF-UP which are then for user plane transport between the two.
Clause 7A.2.1.2 describes when UE reconnects from one TNAP to another TNAP connecting to the same TNGF, authentication of UE from the previous context without performing the full primary authentication.
Clause 7A.2.4 describes how WLAN UEs that do not support 5GC NAS (N5CW) register via trusted non-3GPP access. Those N5CW devices are able to authenticate to the network with 3GPP credentials and register with the help of an interworking function (TWIF) that provides the 5GC NAS protocol stack towards the AMF.
Clause 7A.2.4.2 describes how WLAN UEs that do not support 5GC NAS (N5CW) moves from one TNAP to another TNAP connecting to the same TWIF without performing the full primary authentication.
As defined in clause 7.1, it is the home operator policy decision if a non-3GPP access network is treated as trusted non-3GPP access network. When all of the security domains in clause 4.1 of the present specification related to the non-3GPP access network are considered sufficiently secure by the home operator, the non-3GPP access may be identified as a trusted non-3GPP access for that operator. However, this policy decision may additionally be based on reasons not related to security feature groups.
7A.2 Security procedures p. 133
7A.2.1 Authentication for trusted non-3GPP access p. 133
7A.2.1.1 General |R19| p. 133
This clause specifies how a UE is authenticated to 5G network via a trusted non-3GPP access network.
This is based on the specified procedure in clause 4.12a.2.2 of TS 23.502 "Registration procedure for trusted non-3GPP access". The authentication procedure is similar to the authentication procedure for Untrusted non-3GPP access defined in clause 7.2.1 with few differences, which are mentioned below:
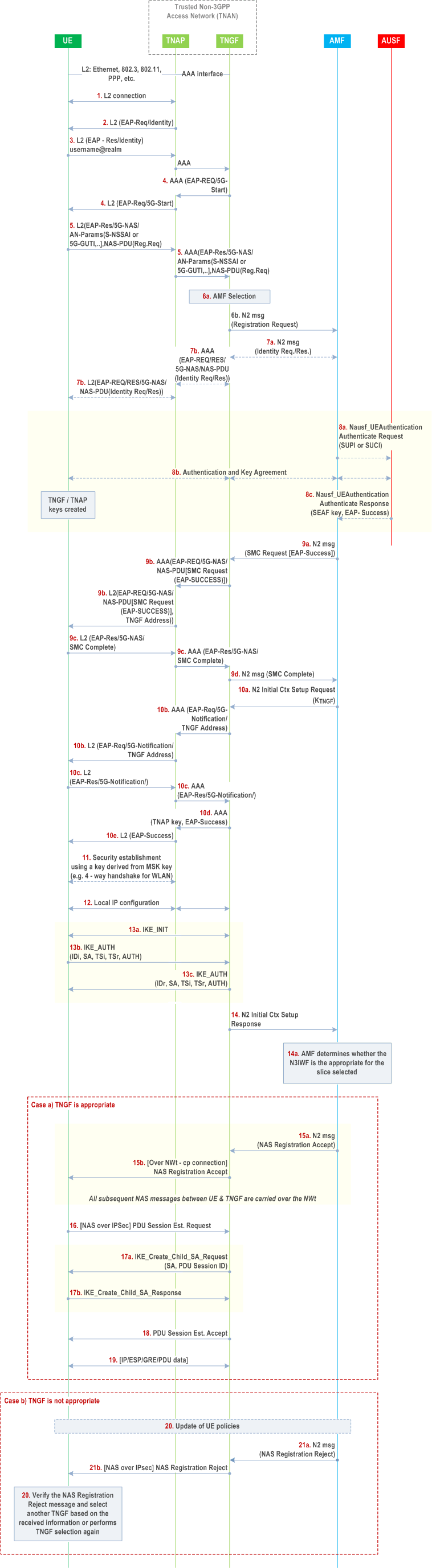
Step 0.
Case a):
The UE selects a PLMN and a TNAN for connecting to this PLMN by using the Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network selection procedure specified in clause 6.3.12 of TS 23.501. During this procedure, the UE discovers the PLMNs with which the TNAN supports trusted connectivity (e.g. "5G connectivity").
Step 1.
A layer-2 connection is established between the UE and the TNAP. In case of IEEE 802.11 [80], this step corresponds to an 802.11 [80] Association. In case of PPP, this step corresponds to a PPP LCP negotiation. In other types of non-3GPP access (e.g. Ethernet), this step may not be required.
Step 2-3.
An EAP authentication procedure is initiated. EAP messages shall be encapsulated into layer-2 packets, e.g. into IEEE 802.3/802.1x packets, into IEEE 802.11/802.1x packets, into PPP packets, etc. The UE provides a NAI that triggers the TNAP to send a AAA request to a TNGF. Between the TNAP and TNGF the EAP packets are encapsulated into AAA messages.
Step 4-10.
An EAP-5G procedure is executed as specified in clause 7.2.1 with the following modifications:
Step 11.
- The EAP-5G packets shall not be encapsulated into IKEv2 packets. The UE shall also include a UE Identity Id in the AN parameter, i.e. a 5G-GUTI or a SUCI. The value in the UE identity shall be stored at TNGF to as key identifier as described in step 13.
- A KTNGF as specified in Annex A.9 (equivalent to KN3IWF) is created in the UE and in the AMF after the successful authentication. The KTNGF is transferred from the AMF to TNGF in step 10a (within the N2 Initial Context Setup Request).
- The TNAP is a trusted entity. The TNGF shall generate the KTNAP as specified in Annex A.22 and transfers it from TNGF to TNAP in step 10b (within a AAA message).
- After receiving the TNGF key from AMF in step 10a, the TNGF shall send to UE an EAP-Request/5G-Notification packet containing the "TNGF Contact Info", which includes the IP address of TNGF. After receiving an EAP-Response/5G-Notification packet from the UE, the TNGF shall send message 10d containing the EAP-Success packet.
The common TNAP key is used by the UE and TNAP to derive security keys according to the applied non-3GPP technology and to establish a security association to protect all subsequent traffic. In case of IEEE 802.11 [80], the KTNAP is the Pairwise Master Key (PMK) and a 4-way handshake is executed (see IEEE 802.11 [80]) which establishes a security context between the WLAN AP and the UE that is used to protect unicast and multicast traffic over the air. All messages between UE and TNAP are encrypted and integrity protected from this step onwards.
Step 12.
The UE receives IP configuration from the TNAN, e.g. with DHCP.
Step 13.
The UE shall initiate an IKE_INIT exchange with the TNGF. The UE has received the IP address of TNGF during the EAP-5G signalling in step 9b, subsequently, the UE shall initiate an IKE_AUTH exchange and shall include the same UE Id (i.e. SUCI or 5G-GUTI) as in the UE Id provided in step 5. The common KTIPSe is used for mutual authentication. The key KTIPSec is derived as specified in Annex A.22. NULL encryption is negotiated as specified in RFC 2410. After step 13c, an IPsec SA is established between the UE and TNGF (i.e. a NWt connection) and it is used to transfer all subsequent NAS messages. This IPsec SA does not apply encryption but only apply integrity protection.
Step 14.
After the NWtp connection is successfully established, the TNGF responds to AMF with an N2 Initial Context Setup Response message.
Step 14a.
The AMF may determine whether the TNGF is appropriate for the slice selected as defined in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502. If it is compatible with the selected TNGF, then proceed with steps 15 to step 19. Otherwise, the AMF shall proceed with step 20 to step 22, and step 15 to step 19 are skipped.
Step 15.
Case b:)
Finally, the NAS Registration Accept message is sent by the AMF and is forwarded to UE via the established NWt connection.
Step 16-18.
The UE initiates a PDU session establishment. This is carried out exactly as specified in clause 4.12a.5 of TS 23.502. The TNGF may establish one or more IPSec child SA's per PDU session.
Step 19.
User plane data for the established PDU session is transported between the UE and TNGF inside the established IPSec child SA.
Step 20.
The AMF may trigger the UE policy update procedure and update the UE policy as defined in step 17 and step 18 in clause 4.12a.2.2 of TS 23.502.
Step 21.
The AMF shall send a Registration Reject message via TNGF to the UE as defined in step 19 to step 21 in clause 4.12a.2.2 of TS 23.502. The Registration Reject message is ciphered and integrity protected.
Step 22.
The UE shall decipher and verify the integrity of the Registration Reject message. If verification is successful, then the UE proceeds with step 21 in clause 4.12.2.2 of TS 23.502, and sends a Registration request message to the AMF via a new selected TNGF.
7A.2.1.2 Re-authentication for UE moving from one TNAP to another TNAP connecting to the same TNGF |R19| p. 136
When a UE associates with a TNAP in a TNAN connected to a TNGF, if the TNAP and TNGF in TNAN support FT, the TNAP in the TNAN advertises the FT capability as in IEEE 802.11 [80]. During the IKE process, the UE also indicates MOBIKE indication if it supports MOBIKE and TNGF acknowledges it if supported.
The UE and TNGF perform the following in addition to the procedures specified in clause 7A.2.1.1 of the present document. If the TNAP supports FT, the TNGF shall derive a fresh key to enable re-authentication based on FT procedure, i.e. KFT, from KTNGF as specified in clause A.22 of the present document and either keep KFT if the TNGF acts as the R0KH or send the KFT to the R0KH otherwise. If the UE supports FT and connects to the TNAN supporting the FT, the UE shall determine to enable re-authentication based on FT procedure and derive a FT key, KFT, from KTNGF as specified in clause A.22 of the present document.
The UE and R0KH use KFT as Master PMK (MPMK) to construct the FT key hierarchy as specified in IEEE 802.11 [80] to perform re-authentication and security (re-)establishment while the UE switches between different TNAPs within the same mobility domain (i.e., identified by the MDID specified by IEEE 802.11 [80]) connected to the same TNGF. To perform such a switch the UE performs the FT procedure as specified in IEEE 802.11 [80]. The R0KH derives a key PMK-R1 from PMK-R0 and provides the key PMK-R1 to the new TNAP in TNAN during the FT procedure.
After the UE switch between TNAPs is complete, if MOBIKE is supported, the UE may send the request to restore the IPSec connectivity, and all IPSec SAs as defined in RFC 4555.