Content for TS 23.401 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.3.6…
4.3.8…
4.3.12…
4.3.16…
4.3.20…
4.3.25…
4.4…
4.6…
4.7…
4.13…
5…
5.1.2…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.3.3…
5.3.3.2
5.3.3.3…
5.3.4…
5.3.4B…
5.3.5…
5.3.8…
5.3.9…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.5.1.2…
5.5.2…
5.5.2.2…
5.5.2.3…
5.5.2.4…
5.6…
5.7.3…
5.7A…
5.10
5.11…
5.19…
D…
D.3…
D.3.4
D.3.5
D.3.6
D.3.7…
D.3.8…
E
F…
J…
K…
L…
M…
O…
D.3.7 E-UTRAN to GERAN A/Gb mode Inter RAT handover
D.3.7.1 General
D.3.7.2 Preparation phase
D.3.7.3 Execution phase
...
...
D.3.7 E-UTRAN to GERAN A/Gb mode Inter RAT handover p. 418
D.3.7.1 General p. 418
The interoperation procedures describe information flows for Gn/Gp SGSNs and other EPS network elements. All messages between SGSN and MME, between SGSN and BSS, between SGSN and HSS and between SGSN and P-GW (GGSN in TS 43.129) as well as the therein contained information elements are the same as specified for the adequate TS 43.129 procedures. These messages and procedure step descriptions are taken from TS 43.129 for explanatory purposes only. These descriptions are in italic text and shall not be modified by the interoperation procedures. It cannot be assumed that the messages and procedure step descriptions that are taken from TS 43.129 will be updated when modifications or corrections are performed for TS 43.129. If there are any discrepancies for these messages and procedure step descriptions TS 43.129 takes precedence.
The messages between the MME and any other node than the Gn/Gp SGSN as well as the therein contained information elements are the same as specified in the main body of this technical specification for the IRAT handover E-UTRAN to/from GERAN A/Gb mode procedure (clauses 5.5.2.3 and 5.5.2.4). These descriptions are in bold italic text and should be modified simultaneously when clauses 5.5.2.3 or 5.5.2.4 are updated. If there are any discrepancies, the procedure step descriptions in clauses 5.5.2.3 or 5.5.2.4 take precedence.
D.3.7.2 Preparation phase p. 419
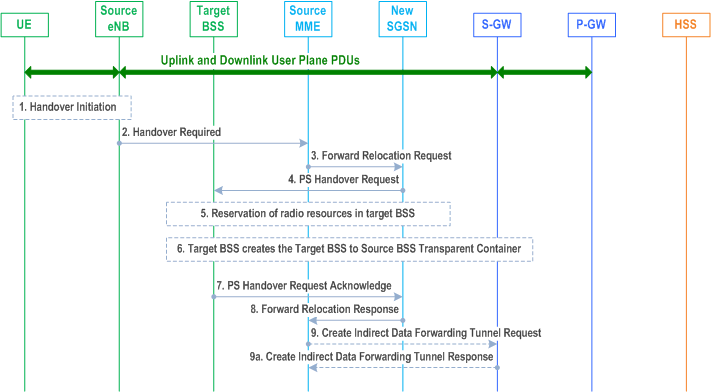
Step 1.
The source eNodeB decides to initiate an Inter RAT Handover to the target GERAN A/Gb mode (2G) system. At this point both uplink and downlink user data is transmitted via the following: Bearer(s) between UE and Source eNodeB, GTP tunnel(s) between Source eNodeB, Serving-GW and PDN-GW.
If the UE has an ongoing emergency bearer service the source eNodeB shall not initiate PS handover to GERAN.
Step 2.
The source eNodeB sends a Handover Required (Cause, Target System Identifier, Source BSS to Target BSS Transparent Container) message to the Source MME to request the CN to establish resources in the Target BSS, Target SGSN and the Serving-GW. The bearers that will be subject to data forwarding (if any) are identified by the new SGSN in a later step (see step 8 below).
The 'Target System Identifier' IE contains the identity of the target global cell Id.
Step 3.
The old SGSN determines from the Target Cell Identifier that the type of handover is inter-RAT/mode handover. In the case of Inter-RAT/ mode Inter-SGSN PS handover, the old SGSN initiates the PS Handover resource allocation procedure by sending a Forward Relocation Request (IMSI, Tunnel Endpoint Identifier Control Plane, RANAP Cause, Target Cell Identifier, MM Context, PDP Contexts, Packet Flow ID, SNDCP XID parameters, LLC XID parameters, PDP Context Prioritisation, Source BSS To Target BSS Transparent Container [RN part] in the BSS Container, Source RNC Id, SGSN Address for control plane) message to the new SGSN. If the old SGSN supports PS handover procedures then it has to allocate a valid PFI according to clause 4.4.1 during the PDP Context activation procedure. Each PDP context contains the GGSN Address for User Plane and the Uplink TEID for Data (to this GGSN Address and Uplink TEID for Data the old SGSN and the new SGSN send uplink packets).
The MM context includes information on the EPS Bearer context(s). If none of the UE's EPS Bearers can be supported by the selected target SGSN, the old SGSN rejects the handover attempt by sending a Handover Preparation Failure (Cause) message to the Source eNodeB.
The MM context contains security related information, e.g. supported ciphering algorithms as described in TS 29.060. The relation between GSM and UMTS security parameters is defined in TS 33.102,
The new SGSN selects the ciphering algorithm to use. This algorithm will be sent transparently from the new SGSN to the MS. The IOV-UI parameter generated in the new SGSN and used, as input to the ciphering procedure will also be transferred transparently from the new SGSN to the MS.
When the new SGSN receives the Forward Relocation Request message the required PDP, MM, SNDCP and LLC contexts are established and a new P-TMSI is allocated for the MS. When this message is received by the new SGSN it begins the process of establishing PFCs for all PDP contexts.
When the new SGSN receives the Forward Relocation Request message it extracts from the PDP Contexts the NSAPIs and SAPIs and PFIs to be used in the new SGSN. If for a given PDP Context the new SGSN does not receive a PFI from the old SGSN, it shall not request the target BSS to allocate TBF resources corresponding to that PDP Context. If none of the PDP Contexts forwarded from the old SGSN has a valid PFI allocated the new SGSN shall consider this as a failure case and the request for PS handover shall be rejected.
In the case when an SAPI and PFI was available at the old SGSN but the new SGSN does not support the same SAPI and PFI for a certain NSAPI as the old SGSN, the new SGSN shall continue the PS handover procedure only for those NSAPIs for which it can support the same PFI and SAPI as the old SGSN. All PDP contexts for which no resources are allocated by the new SGSN or for which it cannot support the same SAPI and PFI (i.e. the corresponding NSAPIs are not addressed in the response message of the target SGSN), are maintained and the related SAPIs and PFIs are kept. These PDP contexts may be modified or deactivated by the new SGSN via explicit SM procedures upon RAU procedure.
The old SGSN shall indicate the current XID parameter settings if available (i.e. those negotiated at the old SGSN when the MS was in A/Gb mode or received during a previous inter-SGSN PS handover) to the new SGSN. If the new SGSN can accept all XID parameters as indicated by the old SGSN, the new SGSN shall create a NAS container for PS HO indicating 'Reset to the old XID parameters'. Otherwise, if the new SGSN cannot accept all XID parameters indicated by the old SGSN or if no XID parameters were indicated by the old SGSN, the new SGSN shall create a NAS container for PS HO indicating Reset (i.e. reset to default parameters).
Step 4.
The new SGSN sends a PS Handover Request (Local TLLI, IMSI, Cause, Target Cell Identifier, Source BSS to Target BSS Transparent Container (RN part), PFCs To Be Set Up List, NAS container for PS HO) message to the target BSS. The new SGSN shall not request resources for PFCs associated with PDP contexts with maximum bit rate for uplink and downlink of 0 kbit/s or for which the Activity Status Indicator within the PDP Context indicates that no active RAB exists on the source side.
Step 5.
Based upon the ABQP for each PFC the target BSS makes a decision about which PFCs to assign radio resources. The algorithm by which the BSS decides which PFCs that need resources is implementation specific. Due to resource limitations not all downloaded PFCs will necessarily receive resource allocation. The target BSS allocates TBFs for each PFC that it can accommodate.
Step 6.
The target BSS shall prepare the Target BSS to Source BSS Transparent Container which contains a PS Handover Command including the CN part (NAS container for PS HO) and the RN part (PS Handover Radio Resources).
Step 7.
Target BSS shall send the PS Handover Request Acknowledge message (Local TLLI, List of Set Up PFCs, Target BSS to Source BSS Transparent Container) message to the new SGSN. Upon sending the PS Handover Request Acknowledge message the target BSS shall be prepared to receive downlink LLC PDUs from the new SGSN for the accepted PFCs.
Any PDP contexts for which a PFC was not established are maintained in the new SGSN and the related SAPIs and PFIs are kept. These PDP contexts may be modified or deactivated by the new SGSN via explicit SM procedures upon the completion of the routing area update (RAU) procedure.
Step 8.
The new SGSN passes the assigned list of TEIDs for each PDP context for which a PFC was assigned in the RAB setup information IE in the Forward Relocation Response (Cause, List of Set Up PFCs, Target BSS to Source BSS Transparent Container) in the BSS Container, Tunnel Endpoint Identifier Control Plane, SGSN Address for User Traffic, Tunnel Endpoint Identifier Data II) message to the old SGSN. The NSAPIs of the active PDP Contexts received in the Forward Relocation Request message for which the PS handover continues, i.e. for which resources are allocated for the PFCs in the target BSS, are indicated in this message.
The Tunnel Endpoint Identifier Data II, one information for each PDP context, is the tunnel endpoint of the new SGSN and is used for data forwarding from the Source eNodeB, via the new SGSN, to the target BSS.
The new SGSN activates the allocated LLC/SNDCP engines as specified in TS 44.064 for an SGSN originated Reset or 'Reset to the old XID parameters'.
When the old SGSN receives the Forward Relocation Response message and it decides to proceed with the handover, the preparation phase is finished and the execution phase will follow.
Step 9.
If 'Indirect Forwarding' applies, the source MME sends a Create Indirect Data Forwarding Tunnel Request message (Cause, SGSN Address(es) and TEID(s) for Data Forwarding) to the Serving-GW. Cause indicates that the bearer(s) are subject to data forwarding.
Indirect forwarding may be performed via a Serving-GW which is different from the Serving-GW used as the anchor point for the UE.
Step 9a.
The Serving-GW returns a Create Indirect Data Forwarding Tunnel Response (Cause, Serving-GW Address(es) and TEID(s) for Data Forwarding) message to the target MME. If the Serving-GW doesn't support data forwarding, an appropriate cause value shall be returned and the Serving-GW Address(es) and TEID(s) will not be included in the message.
D.3.7.3 Execution phase p. 422
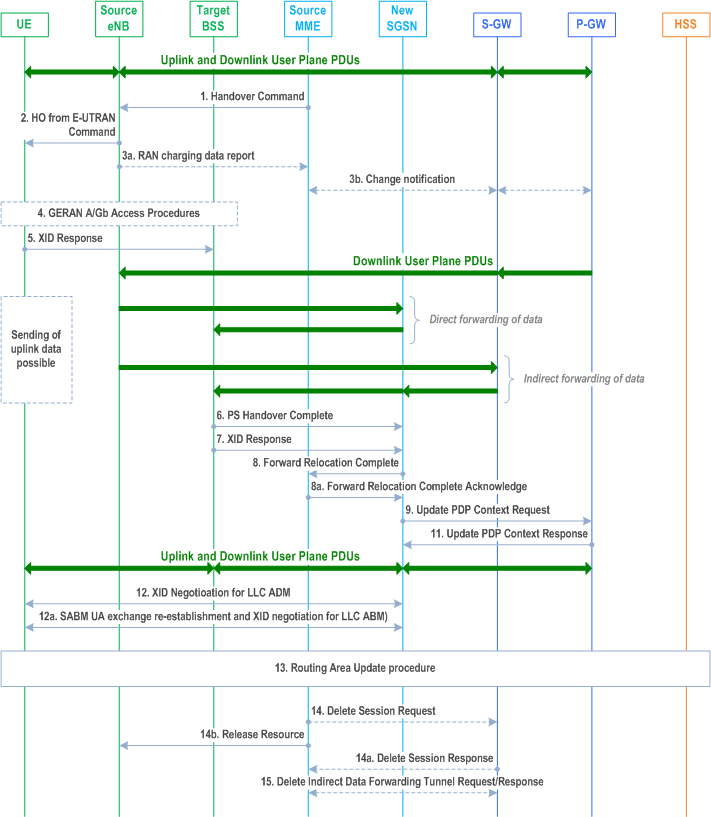
The source eNodeB continues to receive downlink and uplink user plane PDUs.
Step 1.
The Source MME completes the preparation phase towards Source eNodeB by sending the message Handover Command (Target BSS to Source BSS Transparent Container (PS Handover Command with RN part and EPC part), Bearers Subject to Data Forwarding List). The "Bearers Subject to Data forwarding list" may be included in the message and it shall be a list of 'Address(es) and TEID(s) for user traffic data forwarding' received from target side in the preparation phase (Forward Relocation Response message (Step 8)).
Source eNodeB initiate data forwarding for the bearers specified in the "Bearers Subject to Data Forwarding List". The data forwarding goes directly to target SGSN decided in the preparation phase.
Step 2.
The Source eNodeB will give a command to the UE to handover to the Target Access System via the message HO from E-UTRAN Command. This message includes a transparent container including radio aspect parameters that the Target BSS has set-up in the preparation phase (RN part). This message also includes the XID and IOV-UI parameters received from the Target SGSN (EPC part).
Upon the reception of the HO from E-UTRAN Command message containing the Handover Command message, the UE shall associate its bearer IDs to the respective PFIs based on the relation with the NSAPI and shall suspend the uplink transmission of the user plane data.
Step 3.
If the PLMN has configured Secondary RAT usage data reporting and the source eNodeB has Secondary RAT usage data to report, the eNodeB sends the RAN Usage data report message (Secondary RAT usage data) to the MME. Since the handover is an inter-RAT handover, the MME continues with the Secondary RAT usage data reporting procedure as in clause 5.7A.3. The reporting procedure in clause 5.7A.3 is only performed if PGW secondary RAT usage reporting is active.
Step 4.
The MS executes the handover according to the parameters provided in the message delivered in step 2. The procedure is the same as in step 6 in clause 5.1.4.2 of TS 43.129 with the additional function of association of the received PFI and existing RAB Id related to the particular NSAPI as described in clause 4.4.1 in TS 43.129.
The UE locally deactivates ISR by setting its TIN from "RAT-related TMSI" to "GUTI", if any EPS bearer context activated after the ISR was activated in the UE exists.
Step 5/7.
After accessing the cell using access bursts and receiving timing advance information from the BSS in step 2, the MS processes the NAS container and then sends one XID Response message to the new SGSN. The MS sends this message immediately after receiving the Packet Physical Information message containing the timing advance or, in the synchronised network case, immediately if the PS Handover Access message is not required to be sent (see clause 6.2 in TS 43.129).
Upon sending the XID Response message, the MS shall resume the user data transfer only for those NSAPIs for which there are radio resources allocated in the target cell. For NSAPIs using LLC ADM for which radio resources were not allocated in the target cell the MS may request for radio resources using the legacy procedures.
Step 6.
Upon reception of the first correct RLC/MAC block (sent in normal burst format) from the MS the target BSS sends a PS Handover Complete (Local TLLI, Handover Complete Status) message to inform the new SGSN that the MS has arrived in the target cell. Each uplink N-PDU received by the new SGSN via the target BSS is then forwarded directly to the GGSN.
A timer in source MME is started to supervise when resources in Source eNodeB and Source Serving-GW shall be released.
Step 8.
Upon receiving the PS Handover Complete message, the new SGSN send a Forward Relocation Complete message to the old SGSN to indicate completion of the PS handover procedures. The old SGSN responds with a Forward Relocation Complete Acknowledge message.
For all bearers that were not included in the Forward Relocation Request message sent in step 3, the old SGSN now releases them by sending a Delete Bearer Command to the SGW, or, the appropriate message to the SCEF.
Step 9/11.
The new SGSN sends an Update PDP Context Request (new SGSN Address, TEID, QoS Negotiated) message to the GGSN concerned. The GGSN updates the PDP context fields and returns an Update PDP Context Response (TEID) message. From now on the GGSN sends new incoming downlink IP packets to the new SGSN instead of to the old SGSN.
The PDN-GW shall include a Charging Id to be used at the SGSN as the Charging ID for reporting usage for this PDP context. The PDN-GW shall include the Charging Id in the offline charging data.
Step 12.
If the new SGSN indicated Reset (i.e. reset to default parameters) in the NAS container for PS HO included in the Handover from UTRAN Command message (UTRAN) or the Handover from GERAN Iu Command message, then on receipt of the PS Handover Complete the new SGSN initiates an LLC/SNDCP XID negotiation for each LLC SAPI used in LLC ADM. In this case if the SGSN wants to use the default parameters, it shall send an empty XID Command. If the new SGSN indicated 'Reset to the old XID parameters' in the NAS container for PS HO, no further XID negotiation is required for LLC SAPIs used in LLC ADM only.
Step 12a.
The new SGSN (re-)establishes LLC ABM for the PDP contexts which use acknowledged information transfer. During the exchange of SABM and UA the SGSN shall perform LLC/SNDCP XID negotiation.
Step 13.
The MS sends a Routing Area Update Request (Old P-TMSI, Old RAI, Old P-TMSI signature, Update Type) message to the new SGSN informing it that the source cell belongs to a new routing area. The MS shall send this message immediately after message 5, see TS 23.060.
The new SGSN knows that a handover has been performed for this MS and can therefore exclude the SGSN context procedures which normally are used within the RA Update procedure.
For a MS supporting CIoT EPS Optimisations, the MS uses the PDP context status information in the RAU Accept to identify any non-transferred bearers that it shall locally release.
xbind#5.5.2.3:43.129
For further descriptions of the Routing Area Update procedure see clauses 5.5.2.3 and 5.6.1.1.1 of TS 43.129.
Step 14.
When the timer started at step 8 expires, the source MME sends a Release Resources message to the source eNodeB. The Source eNodeB releases its resources related to the UE.
Additionally, the source MME deletes the EPS bearer resources by sending Delete Session Request (Cause, Operation Indication, Secondary RAT usage data) messages to the Serving-GW. The operation Indication flag is not set, that indicates to the Serving-GW that it shall not initiate a delete procedure towards the PDN-GW. Secondary RAT usage data was included if it was received in step 3a. The Serving-GW acknowledges with Delete Session Response (Cause) messages. If ISR is activated then the cause indicates to the old Serving-GW that the old Serving-GW shall delete the bearer resources on the other old CN node by sending Delete Bearer Request message(s) to that CN node.
Step 15.
When the timer started in step 8 expires and if resources for indirect forwarding have been allocated then they are released.