Content for TS 23.401 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.3.6…
4.3.8…
4.3.12…
4.3.16…
4.3.20…
4.3.25…
4.4…
4.6…
4.7…
4.13…
5…
5.1.2…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.3.3…
5.3.3.2
5.3.3.3…
5.3.4…
5.3.4B…
5.3.5…
5.3.8…
5.3.9…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.5.1.2…
5.5.2…
5.5.2.2…
5.5.2.3…
5.5.2.4…
5.6…
5.7.3…
5.7A…
5.10
5.11…
5.19…
D…
D.3…
D.3.4
D.3.5
D.3.6
D.3.7…
D.3.8…
E
F…
J…
K…
L…
M…
O…
4.13 Introduction of satellite support for Cellular IoT
4.13.1 General
4.13.2 Support of RAT types defined in EPC for satellite access
4.13.3 Network/Access selection for satellite access
4.13.4 Verification of UE location
4.13.5 Use of extended NAS timers
4.13.6 Support of Tracking Area Update
4.13.7 Tracking Area handling
4.13.8 Enhanced support of discontinuous network coverage for satellite access
4.13.8.1 General
4.13.8.2 Mobility Management and UE Power Saving Optimization
4.13.8.3 Coverage availability information provisioning to the UE
4.13.8.4 Coverage availability information provisioning to the MME
4.13.8.5 Paging
4.13.8.6 Overload control
4.13.9 Support of Store and Forward Satellite Operation
4.13.10 UE Coarse Location information for NB-IoT satellite access
...
...
4.13 Introduction of satellite support for Cellular IoT |R17| p. 121
4.13.1 General p. 121
This clause describes the functionality for supporting Cellular IoT over satellite access. Support for WB-E-UTRAN, NB-IoT and LTE-M satellite access is specified in TS 36.300.
4.13.2 Support of RAT types defined in EPC for satellite access p. 121
In the case of satellite access with WB-E-UTRAN, NB-IoT or LTE-M, the RAT Types values "WB-E-UTRAN(LEO)", "WB-E-UTRAN(MEO)", " WB-E-UTRAN(GEO)", " WB-E-UTRAN(OTHERSAT)", "NB-IoT(LEO)", "NB-IoT(MEO)", "NB-IoT(GEO)", "NB-IoT(OTHERSAT)", "LTE-M(LEO)", "LTE-M(MEO)", "LTE-M(GEO)" and "LTE-M(OTHERSAT)" are used in EPC to distinguish the different WB-E-UTRAN, NB-IoT and LTE-M satellite access types.
In order to enable efficient enforcement of mobility restrictions:
-
Cells of each NB-IoT satellite RAT type (NB-IoT(LEO), NB-IoT(MEO), NB-IoT(GEO) or NB-IoT(OTHERSAT)) need to be deployed in TAs that are:
- different from TAs for other NB-IoT satellite RAT types; and
- different from TAs supporting terrestrial NB-IoT RAT type; and
- different from TAs for WB-E-UTRAN satellite RAT types; and
- different from TAs for WB-E-UTRAN terrestrial RAT types.
4.13.3 Network/Access selection for satellite access p. 122
Network/Access selection principles specified in clause 4.3.2.2 also apply for satellite access for Cellular IoT.
In the case of satellite access for Cellular IoT, a UE with location capability (i.e. GNSS capability) should use its awareness of its location to select a PLMN that is allowed to operate the UE location as specified in TS 23.122.
In order to ensure that regulatory requirements are met, the network may be configured to enforce this UE choice by verifying the UE location as specified in clause 4.13.4.
4.13.4 Verification of UE location p. 122
In order to ensure that the regulatory requirements are met, the network may be configured to enforce that the selected PLMN is allowed to operate in the current UE location by verifying the UE location during EMM and ESM procedures. In this case, when the MME receives the User Location Information (ULI) for a UE using satellite access for Cellular IoT, the MME may decide to verify the UE location.
In the case of satellite NB-IoT, the UE and the MME may support reporting of Coarse Location Information (with the format defined in TS 24.301) from the UE to MME in the NAS Security Mode Command procedure. As described for the Attach procedure (clause 5.3.2.1), TAU procedures (clauses 5.3.3.1 and 5.3.3.2) and Service Request procedure (clause 5.3.4.1), in the case of NB-IoT, the MME may, if supported by the UE and if the MME has obtained user consent based on proprietary mechanisms depending on local regulations, request the UE, in a NAS Security Mode Command message, to report its Coarse Location Information. If requested, the UE provides its Coarse Location Information in the NAS Security Mode Complete message. The MME provides the received Coarse Location Information to the E-SMLC as described in clause 9.1.17 of TS 23.271. The UE indicates its support for providing Coarse Location Information in the UE Network Capability IE, as described in clause 5.11.3.
If the MME determines based on the Selected PLMN ID and the identity of the cell serving, or based on the reply from the E-SMLC in case of NB-IoT and Coarse Location Information was provided to E-SMLC, that this UE that it is not allowed to operate at the present UE location the MME should reject any NAS request with a suitable Cause value. If the UE is already registered to the network when the MME determines that the UE is not allowed to operate at the present UE location, the MME may initiate an explicit detach of the UE. The MME should not reject the request or detach the UE unless it has sufficiently accurate UE location information to determine that the UE is located in a geographical area where the PLMN is not allowed to operate.
If the MME is not able to determine the UE location with sufficient accuracy to make a decision or if the received ULI is not sufficiently reliable, the MME proceeds with the Mobility Management or Session Management procedure and may initiate UE location procedure after the Mobility Management or Session Management procedure is complete, as specified in clause 9.1.17 of TS 23.271, to determine the UE location. The MME shall be prepared to detach the UE if the information received from the E SMLC indicates that the UE is registered to a PLMN that is not allowed to operate in the UE location. In case of a NAS procedure, the MME should either reject any NAS request targeted towards a PLMN that is not allowed to operate in the known UE location and indicate a suitable cause value, or accept the NAS procedure and initiate the Detach procedure once the UE location is known. In the Detach Request message to the UE, the MME shall include a suitable cause value.
4.13.5 Use of extended NAS timers p. 123
Whenever the UE is accessing the network using a satellite RAT, the MME and the UE shall set the NAS timers long enough according to this satellite RAT, as specified in TS 24.301.
4.13.6 Support of Tracking Area Update p. 123
A moving cell for NB-IoT, LTE-M or WB-E-UTRAN satellite access may indicate support for one or more Tracking Areas Codes (TACs) for each PLMN (see clause 4.13.7). A UE that is registered with a PLMN may access a cell and does not need to perform a Tracking Area Update procedure for mobility reasons as long as at least one supported TAC for the RPLMN or equivalent to the RPLMN indicated in the cell is part of the UE's Tracking Area List. A UE shall perform a Tracking Area Update procedure when entering a cell where none of the supported TACs for the RPLMN or equivalent to the RPLMN indicated in the cell are part of the UE's Tracking Area List.
When indicating a last visited TAI in an Attach Request or a TAU Request, a UE shall indicate the last selected TAI supported in the last visited cell for that RPLMN or PLMN equivalent to the RPLMN, as specified in TS 24.301.
4.13.7 Tracking Area handling p. 123
For Cellular IoT over satellite access with moving cells, in order to ensure that each TA is Earth-stationary, even if the radio cells are moving across the Earth's surface, the E-UTRAN may change the TAC values that are broadcast in a cell's system information as the cell moves, as described in TS 36.331.
E-UTRAN may broadcast in a cell a single TAC per PLMN and change this TAC value as the cell moves. Alternatively, the E-UTRAN may broadcast in a cell more than one TAC for a PLMN and add or remove TAC values as the cell moves. The eNodeB provides either the single broadcast TAI or all broadcast TAIs corresponding to the Selected PLMN as described in TS 36.413 to the MME as part of the ULI, whenever the TAI is included in the S1-AP message as described in TS 36.413. The eNodeB indicates, if known, also the TAI where the UE is geographically located.
The MME considers the UE to be in a forbidden area if the only TAI or all TAIs received from the eNodeB are forbidden based on subscription data. The UE considers it is in a cell within a forbidden area if the only TAI or all TAIs broadcast in this cell for the selected PLMN are forbidden. In a PLMN, the UE considers it is not in a cell within a forbidden area if at least one broadcast TAI for this PLMN in this cell is not forbidden.
If the MME receives multiple TAIs from E-UTRAN and determines that some, but not all, TAIs in the received list of TAIs are forbidden by subscription or by operator policy, the MME shall send the forbidden TAI(s) to UE as described in clause 5.3.2, 5.3.3 and 5.3.4. The UE stores the TAI(s) in the appropriate Forbidden Area list and removes the TAI(s) from the TAI list.
4.13.8 Enhanced support of discontinuous network coverage for satellite access |R18| p. 124
4.13.8.1 General p. 124
Basic support for discontinuous coverage is specified in clause 4.3.5.2 and clause 4.3.17.7. The present clause 4.13.8 provides additional optional enhancements to discontinuous coverage:
- Mobility management and power saving optimization, see clause 4.13.8.2; and
- Coverage availability information provisioning to the UE, see clause 4.13.8.3; and
- Coverage availability information provisioning to the MME, see clause 4.13.8.4; and
- Paging, see clause 4.13.8.5; and
- Overload control, see clause 4.13.8.6.
4.13.8.2 Mobility Management and UE Power Saving Optimization p. 124
For satellite access that provides discontinuous network coverage, and in case both the UE and the network support Enhanced Discontinuous Coverage, then the Mobility Management and UE Power Saving Optimization functionality may be used.
If both the UE and the network indicate support for "Enhanced Discontinuous Coverage Support" and if the UE determines it will lose coverage and will become unavailable, and decides to remain in no service during that time, then:
- The UE may be able to determine, including considering current and expected future locations of the UE, a Start of Unavailability Period and/or Unavailability Period Duration for when it expects to be out of coverage.
- The UE triggers a TAU procedure and includes an indication of upcoming loss of coverage in the TAU Request message to the MME. If the UE is able to determine a Start of Unavailability Period and/or Unavailability Period Duration it also includes them in the TAU Request message.
- The UE should trigger the TAU procedure early enough such that the procedure, under normal conditions, is able to complete before the start of the unavailability period.
- The UE and the MME re-negotiate unavailability at every TAU procedure, if it is required. If Start of Unavailability Period and/or Unavailability Period Duration is not included in a TAU Request message any pending loss of coverage configuration stored in the UE context at MME is discarded.
- If the UE determines an upcoming loss of coverage to the network no longer applies or determines a new Start of Unavailability Period or Unavailability Period Duration related to the upcoming loss of coverage, the UE sends a new TAU Request to the MME to update the Start of Unavailabililty Period and/or Unavailability Period Duration.
- If the UE did not include a Start of Unavailability Period in the TAU Request message, the MME considers implicitly the Start of Unavailability Period to be the time at which it has received the TAU Request message from the UE. If the UE included a Start of Unavailability Period, the Start of Unavailability Period indicates the time at which the UE determines it expects to lose coverage, i.e. time until which the UE determines it is available.
- The MME may determine, if not provided by the UE, or update the Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period. If the MME knows an Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period (e.g. based on information available to the MME as described in clause 4.13.8.4) for the UE, and the UE not include an Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period or included an Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period different to the Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period known to the MME, the MME should include the Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period known to the MME in the TAU Accept or Attach Accept message and use those values in subsequent steps of this procedure. How the UE treats the MME provided Unavailability Period Duration and/or the Start of Unavailability Period is up to UE implementation e.g. to help to determine when to return to coverage after a discontinuous coverage period, whether to listen to paging in eDRX, not to initiate any NAS signalling (including Service Request for MO data) within the discontinuous coverage period in case of any UL signalling/data request or the UE may deactivate its Access Stratum functions for satellite access in order to optimise power consumption until coverage returns, etc.
- The MME indicates to the UE in the Attach Accept or TAU Accept whether the UE is not required to perform a TAU procedure when the unavailability period has ended. The MME indicates to the UE in the Attach Accept or TAU Accept whether the UE is not required to perform a TAU procedure when the unavailability period has ended.
- The MME stores the information that the UE is unavailable at the Start of Unavailability Period in the UE context, and considers the UE is unreachable from then until the UE enters ECM_CONNECTED state.
4.13.8.3 Coverage availability information provisioning to the UE p. 125
A UE may use satellite coverage availability information for satellite access to support discontinuous coverage operations. Satellite coverage availability information can be provided to a UE by an external server via a PDN Connection or SMS. The protocol and format of satellite coverage availability information via PDU Connection or SMS is not defined in this release of the specification, but some examples on the information that constitutes the satellite coverage availability information is defined in Annex N.
4.13.8.4 Coverage availability information provisioning to the MME p. 126
The MME may use satellite coverage availability information to support satellite access by UEs with discontinuous coverage operation. Satellite coverage availability information may be provisioned to the MME by O&M.
The satellite coverage availability information is not UE specific and can be applied by the MME for any UE in the affected area.
4.13.8.5 Paging p. 126
In the case of satellite access that provides discontinuous network coverage, the MME may utilize sub-area paging (e.g. first page in the last known ECGI or TA and retransmission in all registered TAs). The MME may utilize the location information as received at or before the S1 release due to the discontinuous coverage for paging optimisation.
The MME may e.g. receive UE location from eNodeB during the Attach or TAU procedure e.g. triggered for Mobility Management and Power Saving Optimization for discontinuous network coverage as described in clause 4.13.8.2, or the MME may request the Location Reporting Procedure when the UE is in ECM_CONNECTED state as described in clause 5.9.1.
4.13.8.6 Overload control p. 126
The MME and UE may only use the procedure defined in this clause if both the UE and MME indicate "Enhanced Discontinuous Coverage Support", see clause 4.13.8.1.
In order to avoid a large number of UEs causing excessive signalling load on the network when leaving coverage or re-gaining coverage after being out of coverage, the MME may determine a Maximum Time Offset controlling when UEs are allowed to initiate NAS signalling with the network, as described in this clause.
In this case, the MME determines this Maximum Time Offset based on network configuration, high priority access and priority services. The MME sends this Maximum Time Offset to individual UEs during the Attach or TAU procedures.
If the UE receives this Maximum Time Offset from the network in an Attach or TAU Accept, the UE shall replace any previously received Maximum Time Offset on the same RAT type and PLMN with this one.
When the UE knows a later time at which coverage will be lost and when the UE does not send a TAU Request to the MME in advance (see clause 4.13.8.2), the UE determines a random value up to the minimum of the latest Maximum Time Offset for this PLMN and RAT type and the time until coverage will be lost. The UE shall send the TAU Request at the time when coverage will be lost less the random value to the MME indicating the loss of coverage.
Upon returning to coverage after being out of coverage due to discontinuous coverage, the UE sets the discontinuous coverage wait timer value to a random value up to and including the latest Maximum Time Offset for this PLMN and RAT type, and starts this timer. The UE shall not initiate any NAS signalling on that RAT Type and PLMN while the discontinuous coverage wait timer is running.
The UE shall stop the discontinuous coverage wait timer and initiate NAS signalling if the UE receives paging message, has pending emergency services or when UE enters a Tracking Area outside the current Tracking Area List.
4.13.9 Support of Store and Forward Satellite Operation |R18| p. 126
4.13.9.1 General |R19| p. 126
The Store and Forward Satellite Operation applies in E-UTRAN with satellite access and is suitable for delay-tolerant communication services (e.g. CIoT/MTC, SMS, etc.). If the satellite does not support Store and Forward Satellite operation and there is no feeder link connection to the ground network, then the satellite cannot provide any service to any UEs. When both the service link and feeder link are available, all services can be provided. To support Store and Forward Satellite operation, some network functionality needs to be deployed on the satellite payload.
Example deployments are described in Annex O.
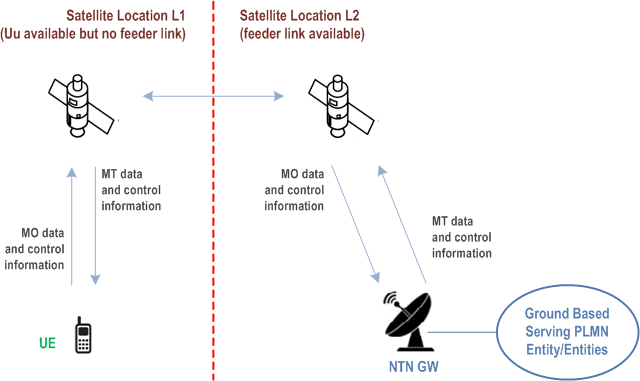
In Store and Forward Satellite operation, the end-to-end exchange of signalling/data traffic is handled in a sequence of steps reflecting the intermittent availability of the service link when the satellite can exchange data with the UE and of the intermittent availability of the ground link when the satellite can exchange data with the core network. This is depicted in Figure 4.13.9.1-1.
For example, a simple sequence of events for the transmission of data from the UE to a server on the ground may involve two steps: firstly, when service link is available (e.g. location L1 in Figure 4.13.9.1-1) the UE sends the data to the satellite. Subsequently (e.g. location L2 in Figure 4.13.9.1-1), the satellite carrying the payload connects to the ground network and delivers the UE data to the network.
Downlink data can be stored onto the same or a different satellite and provided to the UE later using the first step and the process is repeated.
When a satellite supports Store and Forward Satellite operation and is operating in S&F Mode, the on-board eNodeB broadcasts an indication of operating in S&F Mode as described in TS 36.300, which the UE uses to determine the current operation mode of the satellite. If a satellite is operating in S&F Mode and if a UE is enabled for Store and Forward Satellite operation, then the UE indicates the S&F capability during Attach and Tracking Area Update.
The MME may adapt periodic update timer, mobile reachable timer and Implicit Detach timer to the fact that the UE is served in S&F mode.
When an MME is operating in S&F Mode:
- If the MME cannot complete a NAS procedure with the information currently available on the satellite e.g. when the MME does not have UE security context or, if the MME needs to retrieve UE-specific authentication vectors or subscription information from the ground network, it shall reject the NAS procedure. In this case, if the UE supports Store and Forward Satellite operation, the MME shall include a reject cause indicating the NAS rejection is due to S&F operation.
- If a UE indicates Store and Forward capability, the MME may provide to the UE a S&F Wait Timer when accepting or rejecting a NAS procedure.
4.13.10 UE Coarse Location information for NB-IoT satellite access |R19| p. 128
As described in clause 4.13.4, in the case of NB-IoT, the MME may request the UE to report its Coarse Location Information for location verification purposes. In addition, as described in TS 36.300 and TS 36.413, the eNB may request, in a S1-AP Initial UE message, the MME to provide the Coarse Location Information to eNB. In that case, the MME provides, if available, the Coarse Location Information to the eNB as described in TS 36.413.