Content for TS 23.401 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4…
4.2.2…
4.3…
4.3.6…
4.3.8…
4.3.12…
4.3.16…
4.3.20…
4.3.25…
4.4…
4.6…
4.7…
4.13…
5…
5.1.2…
5.3…
5.3.2…
5.3.3…
5.3.3.2
5.3.3.3…
5.3.4…
5.3.4B…
5.3.5…
5.3.8…
5.3.9…
5.4…
5.4.4…
5.5…
5.5.1.2…
5.5.2…
5.5.2.2…
5.5.2.3…
5.5.2.4…
5.6…
5.7.3…
5.7A…
5.10
5.11…
5.19…
D…
D.3…
D.3.4
D.3.5
D.3.6
D.3.7…
D.3.8…
E
F…
J…
K…
L…
M…
O…
5.3.3.3 Routing Area Update with MME interaction and without S-GW change
5.3.3.6 Routing Area Update with MME interaction and with S-GW change
...
...
5.3.3.3 Routing Area Update with MME interaction and without S-GW change p. 192
The Routing Area Update without S-GW change procedure takes place when a UE that is registered with an MME selects a UTRAN or GERAN cell and the S-GW is not changed by the procedure. In this case, the UE changes to a Routing Area that the UE has not yet registered with the network. This procedure is initiated by an ECM-IDLE state UE and may also be initiated if the UE is in ECM-CONNECTED state. The RA update case is illustrated in Figure 5.3.3.3-1.
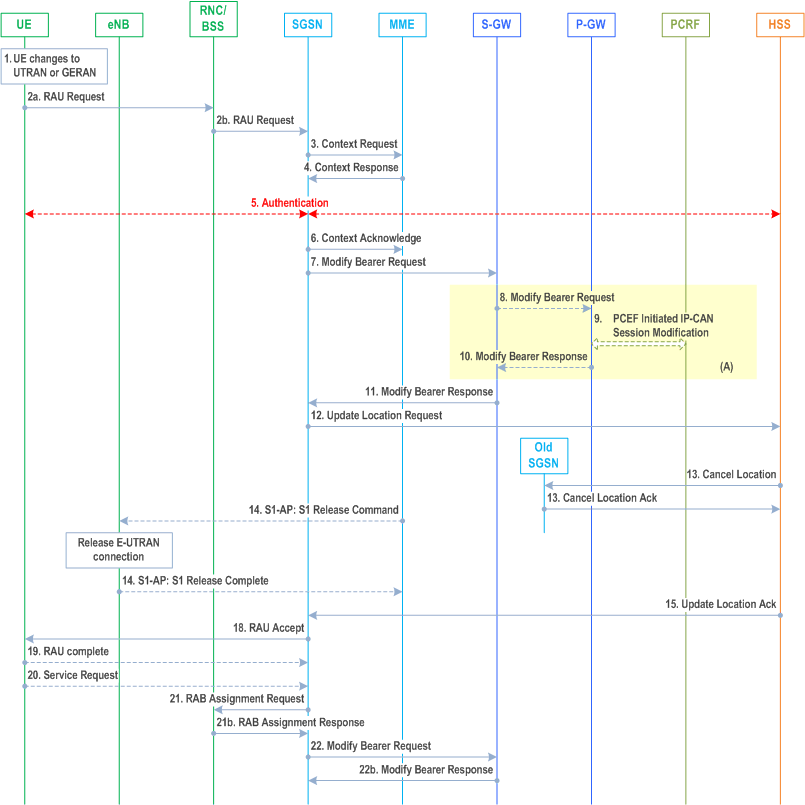
Step 1.
Step 2a.
Step 2b.
Step 3.
Step 4.
Step 5.
Step 6.
Step 7.
Step 8.
Step 9.
Step 10.
Step 11.
Step 12.
Step 13.
Step 14.
Step 15.
Step 16.
Step 17.
Step 18.
Step 19.
Step 20.
Step 21.
Step 22.
In the case of a rejected routing area update operation, due to regional subscription, roaming restrictions or access restrictions (see TS 23.221 and TS 23.008) the new SGSN should not construct an MM context. In the case of receiving the subscriber data from HSS, the new SGSN may construct an MM context and store the subscriber data for the UE to optimise signalling between the SGSN and the HSS. A reject shall be returned to the UE with an appropriate cause and the PS signalling connection shall be released. Upon return to idle, the UE shall act according to TS 23.122.
If the network supports the MOCN configuration for network sharing, the SGSN may, if the UE is not a 'Network Sharing Supporting MS', in this case decide to initiate redirection by sending a Reroute Command to the RNS, as described in TS 23.251 instead of rejecting the routing area update.
If the new SGSN is unable to update the bearer context in one or more P-GWs, the new SGSN shall deactivate the corresponding bearer contexts as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure" of TS 23.060. This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routing area update.
The new SGSN shall determine the Maximum APN restriction based on the received APN Restriction of each bearer context in the Context Response message and then store the new Maximum APN restriction value.
The PDP contexts shall be prioritized by the new SGSN. If the new SGSN is unable to support the same number of active PDP contexts as received from the old MME, the prioritisation is used to decide which PDP contexts to maintain active and which ones to delete. In any case, the new SGSN shall first update all PDP contexts in one or more P-GWs and then deactivate the PDP context(s) that it cannot maintain as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure" of TS 23.060. This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routing area update.
If the routing area update procedure fails a maximum allowable number of times, or if the SGSN returns a Routing Area Update Reject (Cause) message, the UE shall enter PMM DETACHED state.
The UE selects a UTRAN or GERAN cell. This cell is in a Routing Area that the UE not yet registered with the network, or the UE reselects a UTRAN or GERAN cell and the TIN indicates "GUTI". The UE in ECM-CONNECTED state may change to the GERAN cell through Network Assisted Cell Change (NACC).
Step 2a.
The UE sends a Routing Area Update Request (old P-TMSI, P-TMSI Type, old RAI, UE Core Network Capability, MS Network Capability, P-TMSI Signature, additional P-TMSI/RAI, KSI, Voice domain preference and UE's usage setting) message to the new SGSN. The UE shall set the P-TMSI Type to indicate whether the P-TMSI is a native P-TMSI or is mapped from a GUTI.
If the UE's internal TIN indicates "GUTI" and the UE holds a valid GUTI then the UE indicates the GUTI as the old P-TMSI and old RAI. If the UE's TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT-related TMSI" and the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then these two elements are indicated as old P-TMSI and old RAI. Mapping a GUTI to a P-TMSI and an RAI is specified in TS 23.003.
If the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI and the old P-TMSI and old RAI indicate a P-TMSI/RAI mapped from a GUTI, then the UE indicates these parameters as additional P-TMSI/RAI.
The old P-TMSI is indicated in the RAU Request message for Iu-mode only. For Gb mode the TLLI is derived from the value that is determined as the old P-TMSI according to the rules above. The routing parameter that is signalled in the RRC signalling to the RNC for routing to the SGSN is derived from the identifier that is signalled as the old P-TMSI according to the rules above. For a combined MME/SGSN the RAN is configured to route the NRI(s) of this combined node to the same combined node. The RAN is also configured to route NRI(s) of P-TMSIs that are generated by the UE's mapping of the GUTIs allocated by the combined node. Such a RAN configuration may also be used for separate nodes to avoid changing nodes in the pool caused by inter RAT mobility.
If the UE has a follow-on request, i.e. if there is pending uplink traffic (signalling or data), the 3G SGSN may use, as an implementation option, the follow-on request indication to release or keep the Iu connection after the completion of the RA update procedure.
KSI is mapped from an eKSI identifying a KASME if the UE indicates a P-TMSI mapped from GUTI in the information element "old P-TMSI". KSI identifies a (CK, IK) pair if the UE indicates a P-TMSI in the information element "old P-TMSI".
The UE sets the voice domain preference and UE's usage setting according to its configuration, as described in clause 4.3.5.9.
Step 2b.
The RNC shall add the Routing Area Identity, CSG access mode, CSG ID before forwarding the message to the SGSN. This RA identity corresponds to the RAI in the MM system information sent by the RNC to the UE. The BSS shall add the Cell Global Identity (CGI) of the cell where the UE is located before passing the message to the new SGSN. CSG ID is provided by RAN if the UE sends the RAU Request message via a CSG cell or a hybrid cell. CSG access mode is provided if the UE sends the RAU Request message via a hybrid cell. If the CSG access mode is not provided but the CSG ID is provided, the SGSN shall consider the cell as a CSG cell. For SIPTO at the Local Network the with stand-alone GW architecture the RNC includes the Local Home Network ID in the Initial UE Message and in Direct Transfer message if the target cell is in a Local Home Network.
Step 3.
The new S4 SGSN determines the type of the old node, i.e. MME or SGSN, as specified in clause 4.3.19, uses the old RAI received from the UE to derive the old MME address, and sends a Context Request (P-TMSI, old RAI, New SGSN Address, P-TMSI Signature) message to the old MME to get the context for the UE. To validate the Context Request the old MME uses a NAS token mapped from the P-TMSI Signature. If the UE is not known in the old MME, the old MME responds with an appropriate error cause. If integrity check fails in the old MME, the old MME responds with an appropriate error cause which shall initiate the security functions in the new S4 SGSN. If the security functions authenticate the UE correctly, the new S4 SGSN shall send a Context Request (IMSI, old RAI, New SGSN Address, UE Validated) message to the old MME.UE Validated indicates that the new S4 SGSN has authenticated the UE. If the new S4 SGSN indicates that it has authenticated the UE or if the old MME authenticates the UE, the old MME starts a timer.
If the UE with emergency bearers is not authenticated in the old MME (in a network supporting unauthenticated UEs) the old MME continues the procedure with sending a Context Response and starting the timer also when it cannot validate the Context Request.
Step 4.
The old MME responds with one Context Response (IMSI, ME Identity (if available), KSI, CK, IK, unused Authentication Quintets, EPS Bearer Contexts, Serving-GW signalling Address and TEID(s), ISR Supported, MS Info Change Reporting Action (if available), CSG Information Reporting Action (if available), UE Time Zone, UE Core Network Capability, UE Specific DRX Parameters, Change to Report (if present)) message. The PDN-GW Address and TEID(s) (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE Keys (PMIP-based S5/S8) for uplink traffic and control plane, and the TI(s) is part of the EPS Bearer context(s). The unused Authentication Quintets in the MM Context may be sent if stored by the MME and the MME received the unused Authentication Quintets from the same SGSN previously. ISR Supported is indicated if the old MME and associated Serving-GW are capable to activate ISR for the UE.
If the UE receives emergency bearer services from the old MME and the UE is UICCless, IMSI can not be included in the Context Response. For emergency attached UEs, if the IMSI cannot be authenticated, then the IMSI shall be marked as unauthenticated. Also, in this case, security parameters are included only if available.
The new S4 SGSN shall ignore the UE Core Network Capability contained in the Context Response only when it has previously received an UE Core Network Capability in the Routing Area Update Request. If UE is not known in the old MME, the old MME responds with an appropriate error cause.
Change to Report flag is included by the old MME if reporting of change of UE Time Zone, or Serving Network, or both towards Serving-GW / PDN-GW was deferred by the old MME.
The new SGSN maps the EPS bearers to PDP contexts 1-to-1 and maps the EPS Bearer QoS parameter values of an EPS bearer to the Release 99 QoS parameter values of a PDP context as defined in Annex E. The PDP context(s) are established in the indicated order. The SGSN deactivates the PDP contexts which cannot be established.
If SIPTO at the Local Network is active for a PDN connection in the architecture with stand-alone GW, the old MME shall include the Local Home Network ID of the old cell in the EPS Bearer context corresponding to the SIPTO at the Local Network PDN connection.
For UE using CIoT EPS Optimisation without any activated PDN connection, there is no EPS Bearer Context(s) included in the Context Response message.
The old MME only transfers the EPS Bearer Context(s) that the new SGSN supports. If not supported, EPS Bearer Context(s) of non-IP PDN connection are not transferred to the new SGSN. EPS Bearer Context(s) of Ethernet PDN connection type are not transferred to the new SGSN. If the EPS Bearer Context(s) of a PDN connection has not been transferred, the old MME shall consider all bearers of that PDN connection as failed and release that PDN connection by triggering the MME requested PDN disconnection procedure specified in clause 5.10.3.
Step 5.
Security functions may be executed. Procedures are defined in clause 5.3.10 on "Security Function".
If the new SGSN is configured to allow emergency bearer services for unauthenticated UE the new SGSN behave as follows:
- where a UE has only emergency bearer services, the SGSN either skip the authentication and security procedure or accepts that the authentication may fail and continues the Routing Area Update procedure; or
- where a UE has both emergency and non-emergency bearer services and authentication fails, the SGSN continues the Routing Area Update procedure and deactivates all the non-emergency PDP contexts as specified in TS 23.060.
Step 6.
The new S4 SGSN sends a Context Acknowledge (ISR Activated) message to the old MME. Unless ISR is indicated by the new S4 SGSN, the old MME marks in its context that the information in the GWs is invalid. This ensures that the old MME updates the GW if the UE initiates a TAU procedure back to the old MME before completing the ongoing RAU procedure.
ISR Activated indicates to the old MME that it shall maintain the UE's contexts and the MME stops the timer started in step 3. In this case, if the Implicit Detach timer is running, the old MME shall re-start it with a slightly larger value than the UE's E-UTRAN Deactivate ISR timer. When ISR Activated is not indicated and this timer expires the old MME deletes all bearer resources of that UE. As the Context Acknowledge from the new S4 SGSN does not include any S-GW change the old MME does not send any Delete Session Request message to the S-GW. The SGSN shall not activate ISR if the associated Serving-GW does not support ISR.
If the security functions do not authenticate the UE correctly, then the RAU is rejected, and the new S4 SGSN sends a reject indication to the old MME. The old MME shall continue as if the Identification and Context Request was never received.
For UE using CIoT EPS Optimisation without any activated PDN connection, the steps 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 are skipped.
If the new SGSN identifies that the RAT type has changed, the SGSN checks the subscription information to identify for each APN whether to maintain the PDN connection, disconnect the PDN connection with a reactivation request or disconnect PDN connection without reactivation request. If the SGSN decides to deactive a PDN connection it performs SGSN-initiated PDN Connection Deactivation procedure after tracking area procedure is completed. Existing SM cause values as specified in TS 24.008 (e.g. #39, "reactivation requested"; #66 "Requested APN not supported in current RAT and PLMN combination"; and for a dedicated bearer, possibly #37 "QoS not accepted") are used to cause predictable UE behaviour.
Step 7.
In this procedure flow the Serving-GW is not relocated. The SGSN sends a Modify Bearer Request (new SGSN Address and TEID, RAT type, ISR Activated) message per PDN connection to the Serving-GW. If indicated, the information ISR Activated indicates that ISR is activated. As it is a mobility from E-UTRAN, if the target SGSN supports location information change reporting, the target SGSN shall include the User Location Information (according to the supported granularity) in the Modify Bearer Request, regardless of whether location information change reporting had been requested in the previous RAT by the PDN-GW. If the PDN-GW requested User CSG information, the SGSN also includes the User CSG information IE in this message. If either the UE Time Zone has changed, or Context Response message from old MME indicated pending UE Time Zone change reporting (via Change to Report flag), the SGSN includes the UE Time Zone IE in this message. If either the Serving Network has changed, or Context Response message from old MME indicated pending Serving Network change reporting (via Change to Report flag) the SGSN includes the new Serving Network IE in this message. In network sharing scenarios Serving Network denotes the serving core network.
When the Modify Bearer Request does not indicate ISR Activated the S-GW deletes any ISR resources by sending a Delete Bearer Request to the other CN node that has bearer resources on the S-GW reserved. RAT type indicates a change in radio access.
If ISR Activated is indicated or SGSN and SGW are configured to release S4 U-Plane when EPS Bearer Contexts associated with the released RABs are to be preserved, the SGSN does not send SGSN address and TEID for U-Plane in Modify Bearer Request.
Step 8.
If the RAT type has changed or the Serving-GW has received the User Location Information IE and/or the UE Time Zone IE and/or User CSG information IE and/or the Serving Network IE from the MME in step 7 the Serving-GW informs the PDN-GW(s) about the change of this information that e.g. can be used for charging, by sending the message Modify Bearer Request (RAT type) per PDN connection to the PDN-GW(s) concerned. User Location Information IE and/or UE Time Zone IE and/or User CSG information IE and/or Serving Network IE are also included if they are present in step 7.
Step 9.
If dynamic PCC is deployed, and RAT type information or UE location information needs to be conveyed from the PDN-GW to the PCRF, then the PDN-GW shall send this information to the PCRF by means of an IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203.
Step 10.
The PDN-GW updates its context field and returns a Modify Bearer Response (MSISDN) message to the Serving-GW. MSISDN is included if the PDN-GW has it stored in its UE context. If location information change reporting is required and supported in the target SGSN, the PDN-GW shall provide MS Info Change Reporting Action in the Modify Bearer Response.
Step 11.
The Serving-GW updates its context fields. If ISR Activated is indicated in step 7 and RAT Type received in step 7 indicates UTRAN or GERAN, then the Serving-GW only updates the SGSN Control Plane Address and keeps the MME related information unchanged. Otherwise the Serving-GW shall update all of the information stored locally for this UE with the related information received from the SGSN. Then the Serving-GW returns a Modify Bearer Response (Serving-GW address and TEID for uplink traffic, MS Info Change Reporting Action) message.
When the SGSN receives the Modify Bearer Response message, the SGSN checks if there is a "Availability after DDN Failure" monitoring event or a "UE Reachability" monitoring event configured for the UE in the SGSN and in such a case sends an event notification (see TS 23.682 for further information).
Step 12.
The new SGSN verifies whether it holds subscription data for the UE identified by the P-TMSI, the additional PTMSI/RAI or by the IMSI received with the context data from the old CN node.
The additional P-TMSI/RAI allows the new SGSN to find any already existing UE context stored in the new SGSN. If there are no subscription data in the new SGSN for this UE, or for some network sharing scenario (e.g. GWCN) if the PLMN-ID of the RAI supplied by the RNC is different from that of the RAI in the UE's context, then the new SGSN informs the HSS of the change of the SGSN by sending an Update Location (SGSN Number, SGSN Address, IMSI, Homogenous Support of IMS Voice over PS Sessions, UE SRVCC capability, equivalent PLMN list) message to the HSS. For "Homogenous Support of IMS Voice over PS Sessions", see clause 5.3.8A of TS 23.060. The inclusion of the equivalent PLMN list indicates that the SGSN supports the inter-PLMN handover to a CSG cell in an equivalent PLMN using the subscription information of the target PLMN.
If the UE initiates the RAU procedure in a VPLMN supporting Autonomous CSG Roaming and the HPLMN has enabled Autonomous CSG Roaming in the VPLMN (via Service Level Agreement) and the SGSN needs to retrieve the CSG subscription information of the UE from the CSS, the SGSN initiates the Update CSG Location Procedure with CSS as described in clause 5.3.12.
Step 13.
The HSS sends a Cancel Location (IMSI, Cancellation Type) message to the old SGSN with the Cancellation Type set to Update Procedure.
When receiving the Cancel Location message the old SGSN removes all the UE contexts. The old SGSN acknowledges with a Cancel Location Ack (IMSI) message.
Step 14.
When receiving the Context Acknowledge message from the new SGSN and if the old MME has an S1-MME association for the UE, the source MME sends a S1-U Release Command to the source eNodeB after the timer started in step 3 has expired. The RRC connection is released by the source eNodeB. The source eNodeB confirms the release of the RRC connection and of the S1-U connection by sending a S1-U Release Complete message to the source MME.
Step 15.
The HSS acknowledges the Update Location message by sending an Update Location Ack (IMSI, Subscription Data) to the new SGSN. The Subscription Data may contain the CSG subscription data for the registered PLMN and for the equivalent PLMN list requested by SGSN in step 12.
If the UE initiates the RAU procedure at a CSG cell, the new S4 SGSN shall check whether the CSG ID and associated PLMN is contained in the CSG subscription and is not expired. If the CSG ID and associated PLMN is not present or expired, the S4 SGSN shall send a RAU reject message to the UE with an appropriate cause value. The UE shall remove the CSG ID and associated PLMN from its Allowed CSG list if present.
If the Update Location is rejected by the HSS, the new SGSN rejects the RAU Request from the UE with an appropriate cause sent in the RAU Reject message to the UE. In such cases, the new SGSN releases any local SGSN EPS Bearer contexts for this particular UE.
Step 16.
Void.
Step 17.
Void.
Step 18.
If due to regional subscription restrictions or access restrictions (e.g. CSG restrictions) the UE is not allowed to access the RA:
- For UEs with ongoing emergency bearer services, the new SGSN accept the Routing Area Update Request and deactivates the non-emergency PDP contexts as specified in clause 9.2.4.2 in TS 23.060. If the Routing Area Update procedure is initiated in PMM-IDLE/STANDBY state, all non-emergency PDP Contexts are deactivated by the Routing Area without PDP Context deactivation signalling between the UE and the SGSN
- For all other cases, the new SGSN rejects Routing Area Update Request with an appropriate cause to the UE and notifies the HSS of rejection (details of this notification is covered in stage 3).
Step 19.
If P-TMSI was included in the Routing Area Update Accept message, the UE acknowledges the new P-TMSI by returning a Routing Area Update Complete message to the SGSN.
Step 20.
For Iu-mode, if the UE has uplink data or signalling pending it shall send a Service Request (P-TMSI, CKSN, Service Type) message to the new SGSN. If a P-TMSI was allocated in step 18, that P-TMSI is the one included in this message. Service Type specifies the requested service. Service Type shall indicate one of the following: Data or Signalling.
Step 21.
If the UE has sent the Service Request, the new 3G SGSN requests the RNC to establish a radio access bearer by sending a RAB Assignment Request (RAB ID(s), QoS Profile(s), GTP SNDs, GTP SNUs, PDCP SNUs) message to the RNC. If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN provides to the RNC the Serving-GW's Address for User Plane and TEID for uplink data.
Step 22.
If the SGSN established Direct Tunnel in step 21) it shall send Modify Bearer Request per PDN connection to the Serving-GW and include the RNC's Address for User Plane and downlink TEID for data. The Serving-GW updates the Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and return a Modify Bearer Response.
5.3.3.4 Void
5.3.3.5 Void
5.3.3.6 Routing Area Update with MME interaction and with S-GW change p. 199
The Routing Area Update with S-GW change procedure takes place when a UE that is registered with an MME selects a UTRAN or GERAN cell and the S-GW is changed by the procedure. In this case, the UE changes to a Routing Area that the UE has not yet registered with the network. This procedure is initiated by an ECM-IDLE state UE and may also be initiated if the UE is in ECM-CONNECTED state. This RA update case is illustrated in Figure 5.3.3.6-1.
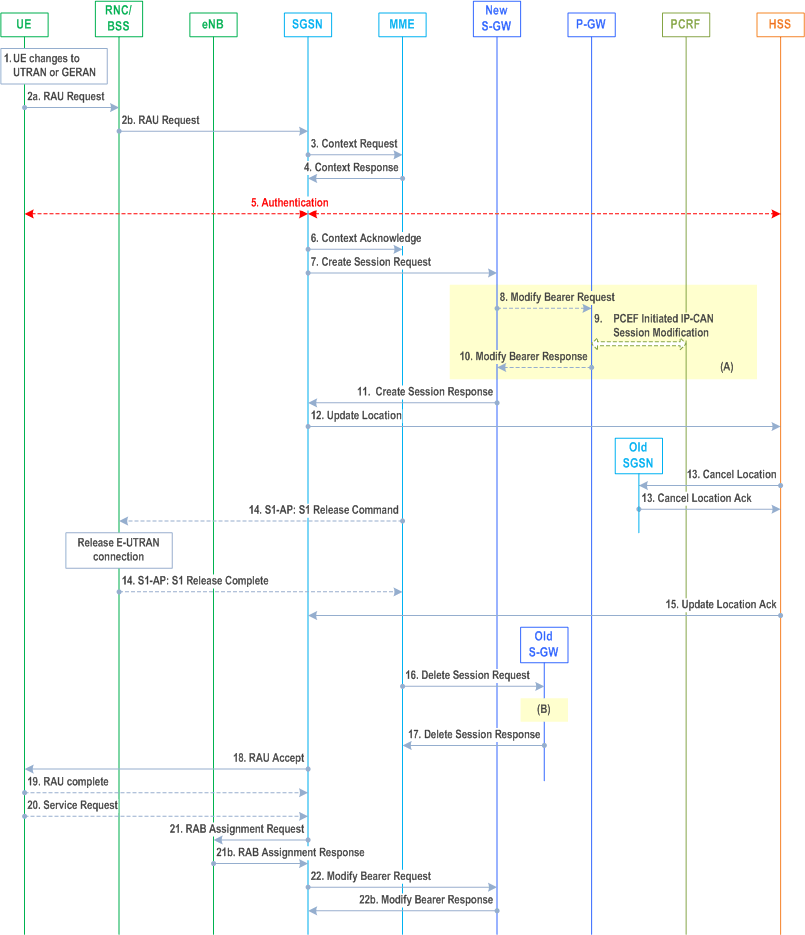
Step 1.
Step 2a.
Step 2b.
Step 3.
Step 4.
Step 5.
Step 6.
Step 7.
Step 8.
Step 9.
Step 10.
Step 11.
Step 12.
Step 13.
Step 14.
Step 15.
Step 16.
Step 17.
Step 18.
Step 19.
Step 20.
Step 21.
Step 22.
In the case of a rejected routing area update operation, due to regional subscription, roaming restrictions, access restrictions (see TS 23.221 and TS 23.008) or because the SGSN cannot determine the HLR address to establish the locating updating dialogue, the new SGSN should not construct an MM context. In the case of receiving the subscriber data from HLR, the new SGSN may construct an MM context and store the subscriber data for the UE to optimise signalling between the SGSN and the HSS. A reject shall be returned to the UE with an appropriate cause and the PS signalling connection shall be released. Upon return to idle, the UE shall act according to TS 23.122.
If the new SGSN is unable to update the bearer context in one or more P-GWs, the new SGSN shall deactivate the corresponding bearer contexts as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure" of TS 23.060. This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routing area update.
The new SGSN shall determine the Maximum APN restriction based on the received APN Restriction of each bearer context in the Context Response message and then store the new Maximum APN restriction value.
The PDP contexts shall be prioritized by the new SGSN. If the new SGSN is unable to support the same number of active PDP contexts as received from old MME, the prioritisation is used to decide which PDP contexts to maintain active and which ones to delete. In any case, the new SGSN shall first update all PDP contexts in one or more P-GWs and then deactivate the PDP context(s) that it cannot maintain as described in clause "SGSN-initiated PDP Context Deactivation Procedure" of TS 23.060. This shall not cause the SGSN to reject the routing area update.
If the routing area update procedure fails a maximum allowable number of times, or if the SGSN returns a Routing Area Update Reject (Cause) message, the MS shall enter IDLE state.
The UE selects a UTRAN or GERAN cell. This cell is in a Routing Area that the UE not yet registered with the network or the UE reselects a UTRAN or GERAN cell and the TIN indicates "GUTI". The UE in ECM-CONNECTED state may change to the GERAN cell through Network Assisted Cell Change (NACC).
Step 2a.
The UE sends a Routing Area Update Request (old RAI, old P-TMSI, P-TMSI Type, UE Core Network Capability, MS Network Capability, P-TMSI Signature, additional P-TMSI/RAI, KSI, Voice domain preference and UE's usage setting) message to the new SGSN. The UE shall set the P-TMSI Type to indicate whether the P-TMSI is a native P-TMSI or is mapped from a GUTI.
If the UE's TIN indicates "GUTI" and the UE holds a valid GUTI then the UE indicates the GUTI as the old P-TMSI and old RAI. If the UE's TIN indicates "P-TMSI" or "RAT-related TMSI" and the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI then these two elements are indicated as old P-TMSI and old RAI. Mapping a GUTI to a P-TMSI and an RAI is specified in TS 23.003.
If the UE holds a valid P-TMSI and related RAI and the old P-TMSI and old RAI indicate a P-TMSI/RAI mapped from a GUTI, then the UE indicates these parameters as additional P-TMSI/RAI.
The old P-TMSI is indicated in the RAU Request message for Iu-mode only. For Gb mode the TLLI is derived from the value that is determined as the old P-TMSI according to the rules above. The routing parameter that is signalled in the RRC signalling to the RNC for routing to the SGSN is derived from the identifier that is signalled as the old P-TMSI according to the rules above. For a combined MME/SGSN the RAN is configured to route the NRI(s) of this combined node to the same combined node. The RAN is also configured to route NRI(s) of P-TMSIs that are generated by the UE's mapping of the GUTIs allocated by the combined node. Such a RAN configuration may also be used for separate nodes to avoid changing nodes in the pool caused by inter RAT mobility.
If the UE has a follow-on request, i.e. if there is pending uplink traffic (signalling or data), the 3G-SGSN may use, as an implementation option, the follow-on request indication to release or keep the Iu connection after the completion of the RA update procedure.
KSI is mapped from an eKSI identifying a KASME if the UE indicates a P-TMSI mapped from GUTI in the information element "old P-TMSI". KSI identifies a (CK, IK) pair if the UE indicates a P-TMSI in the information element "old P-TMSI".
The UE sets the voice domain preference and UE's usage setting according to its configuration, as described in clause 4.3.5.9.
Step 2b.
The RNC shall add the Routing Area Identity, CSG access mode, CSG ID before forwarding the message to the SGSN. This RA identity corresponds to the RAI in the MM system information sent by the RNC to the UE. The BSS shall add the Cell Global Identity (CGI) of the cell where the UE is located before passing the message to the new SGSN. CSG ID is provided by RAN if the UE sends the RAU Request message via a CSG cell or a hybrid cell. CSG access mode is provided if the UE sends the RAU Request message via a hybrid cell. If the CSG access mode is not provided but the CSG ID is provided, the SGSN shall consider the cell as a CSG cell. For SIPTO at the Local Network the with stand-alone GW architecture the RNC includes the Local Home Network ID in the Initial UE Message and in Direct Transfer message if the target cell is in a Local Home Network.
Step 3.
The new S4 SGSN determines the type of the old node, i.e. MME or SGSN, as specified in clause 4.3.19, uses the old RAI received from the UE to derive the old MME address, and the new S4 SGSN sends a Context Request (P-TMSI, old RAI, New SGSN Address, P-TMSI Signature) message to the old MME to get the context for the UE. To validate the Context Request the old MME uses a NAS token mapped from the P-TMSI Signature. If the UE is not known in the old MME, the old MME responds with an appropriate error cause. If integrity check fails in the old MME, the old MME responds with an appropriate error cause which should initiate the security functions in the new S4 SGSN. If the security functions authenticate the UE correctly, the new S4 SGSN shall send a Context Request (IMSI, old RAI, New SGSN Address, UE Validated) message to the old MME. UE Validated indicates that the new S4 SGSN has authenticated the UE. If the new S4 SGSN indicates that it has authenticated the UE or if the old MME authenticates the UE, the old MME starts a timer.
If the UE with emergency bearers is not authenticated in the old MME (in a network supporting unauthenticated UEs) the old MME continues the procedure with sending a Context Response and starting the timer also when it cannot validate the Context Request.
Step 4.
The old MME responds with a Context Response (MM Context, EPS Bearer Contexts, Serving-GW signalling Address and TEID(s), MS Info Change Reporting Action (if available), CSG Information Reporting Action (if available), UE Time Zone and ISR Supported) message. The MM context contains security related information as well as other parameters (including IMSI) as described in clause 5.7.2 (Information Storage for MME). The PDN-GW Address and TEID(s) (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE Keys (PMIP-based S5/S8) for uplink traffic and control plane, and the TI(s) is part of the EPS Bearer context(s). The unused Authentication Quintets in the MM Context may be sent if stored by the MME and if the MME received the unused Authentication Quintets from the same SGSN previously.
If the UE receives only emergency bearer services from the old MME and the UE is UICCless, IMSI can not be included in the Context Response. For emergency attached UEs, if the IMSI cannot be authenticated, then the IMSI shall be marked as unauthenticated. Also, in this case, security parameters are included only if available. ISR Supported is indicated if the old MME and associated Serving-GW are capable to activate ISR for the UE.
The new SGSN shall ignore the UE Core Network Capability in the MM Context of the Context Response only when it has previously received an UE Core Network Capability in the Routing Area Request. If UE is not known in the old MME, the old MME responds with a appropriate error cause.
The new SGSN maps the EPS bearers to PDP contexts 1-to-1 and maps the EPS Bearer QoS parameter values of an EPS bearer to the Release 99 QoS parameter values of a bearer context as defined in Annex E. The PDP context(s) are established in the indicated order. The SGSN deactivates the PDP contexts which cannot be established.
If SIPTO at the Local Network is active for a PDN connection in the architecture with stand-alone GW, the old MME shall include the Local Home Network ID of the old cell in the EPS Bearer context corresponding to the SIPTO at the Local Network PDN connection.
If the UE uses power saving functions and the DL Data Buffer Expiration Time for the UE has not expired (see High latency communication in clause 4.3.17.7), the old MME indicates Buffered DL Data Waiting in the Context Response. When this is indicated, the new SGSN shall invoke data forwarding (corresponding to clause 5.3.3.1A) and setup the user plane in conjunction to the RAU procedure for delivery of the buffered DL data to the UE.
For UE using CIoT EPS Optimisation without any activated PDN connection, there is no EPS Bearer Context(s) included in the Context Response message.
The old MME only transfers the EPS Bearer Context(s) that the new SGSN supports. If not supported, EPS Bearer Context(s) of non-IP PDN connection are not transferred to the new SGSN. EPS Bearer Context(s) of Ethernet PDN connection type are not transferred to the new SGSN. If the EPS Bearer Context(s) of a PDN connection has not been transferred, the old MME shall consider all bearers of that PDN connection as failed and release that PDN connection by triggering the MME requested PDN disconnection procedure specified in clause 5.10.3.
Step 5.
Security functions may be executed. Procedures are defined in clause 5.3.10 on "Security Function".
For ongoing emergency services only, if the new SGSN is configured to support emergency bearer services in limited service state, it may skip the authentication procedure or proceed even if authentication fails. If the new SGSN does not support emergency bearer services in limited service state, then it rejects the RAU request with an appropriate reject cause.
Step 6.
If the new SGSN identifies that the RAT type has changed, the SGSN checks the subscription information to identify for each APN whether to maintain the PDN connection, disconnect the PDN connection with a reactivation request or disconnect PDN connection without reactivation request. If the SGSN decides to deactive a PDN connection it performs SGSN-initiated PDN Connection Deactivation procedure after tracking area procedure is completed. Existing SM cause values as specified in TS 24.008 (e.g. #39, "reactivation requested"; #66 "Requested APN not supported in current RAT and PLMN combination"; and for a dedicated bearer, possibly #37 "QoS not accepted") are used to cause predictable UE behaviour.
The new SGSN determines to relocate the Serving-GW. The Serving-GW is relocated when the old Serving-GW cannot continue to serve the UE. The new SGSN may also decide to relocate the Serving-GW if a new Serving-GW is expected to serve the UE longer and/or with a more optimal UE to PDN-GW path, or if a new Serving-GW can be co-located with the PDN-GW. Selection of a new Serving-GW is performed according to clause 4.3.8.2 on "Serving-GW selection function".
The new SGSN sends a Context Acknowledge (Serving-GW change indication) message to the old MME. Serving-GW change indication indicates a new Serving-GW has been selected. The old MME marks in its context that the information in the GWs is invalid. This ensures that the old MME updates the GWs if the UE initiates a TAU procedure back to the old MME before completing the ongoing RAU procedure.
The old MME deletes all bearer resources of the UE when the timer started in step 3 expires.
If the security functions do not authenticate the UE correctly, then the RAU is rejected, and the new S4 SGSN sends a reject indication to the old MME. The MME shall continue as if the Identification and Context Request was never received.
For UE using CIoT EPS Optimisation without any activated PDN connection, the steps 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 16 and 17 are skipped.
Step 7.
In this procedure flow the Serving-GW is relocated. The SGSN sends a Create Session Request (IMSI, bearer contexts, SGSN Address and TEID for the control plane, RAT Type, Type, the Protocol Type over S5/S8, Serving Network, UE Time Zone, etc) message per PDN connection to the selected new Serving-GW. The PDN-GW address is indicated in the bearer contexts. Type indicates to the Serving-GW to send the Modify Bearer Request to the PDN-GW. The Protocol Type over S5/S8 is provided to Serving-GW which protocol should be used over S5/S8 interface. RAT type indicates a change in radio access. As it is a mobility from E-UTRAN, if the target SGSN supports location information change reporting, the target SGSN shall include the User Location Information (according to the supported granularity) in the Modify Bearer Request, regardless of whether location information change reporting had been requested in the previous RAT by the PDN-GW. If the PDN-GW requested User CSG information, the SGSN also includes the User CSG Information IE in this message.
Step 8.
The new Serving-GW sends the message Modify Bearer Request (Serving-GW Address, Serving-GW TEID, RAT type, Serving Network) per PDN connection to the PDN-GW concerned. User Location Information IE and/or UE Time Zone IE and/or User CSG Information IE are also included if they are present in step 7.
Step 9.
If dynamic PCC is deployed, and RAT type information or UE location information or UE Time Zone needs to be conveyed from the PDN-GW to the PCRF, then the PDN-GW shall send this information to the PCRF by means of an IP-CAN Session Modification procedure as defined in TS 23.203.
Step 10.
The PDN-GW updates its context field and returns a Modify Bearer Response (Charging Id, MSISDN) message to the Serving-GW. The MSISDN is included if the PDN-GW has it stored in its UE context. If location information change reporting is required and supported in the target SGSN, the PDN-GW shall provide MS Info Change Reporting Action in the Modify Bearer Response.
If the Serving-GW is relocated, the PDN-GW shall send one or more "end marker" packets on the old path immediately after switching the path. If the source Serving-GW has no downlink user plane established, the Serving-GW shall discard the "end marker" received from the PDN-GW and shall not send Downlink Data Notification. Otherwise the Serving-GW shall forward the "end marker" packets to the source eNodeB.
Step 11.
The new Serving-GW updates its bearer context. This allows the Serving-GW to route Bearer PDUs to the PDN-GW when received from RNC. The new Serving-GW returns a Create Session Response (Serving-GW address and TEID, PDN-GW Address and TEIDs (for GTP-based S5/S8) or GRE keys (for PMIP-based S5/S8, MS Info Change Reporting Action) at the PDN-GW(s) for uplink traffic) message to the SGSN.
When the SGSN receives the Create Session Response message, the SGSN checks if there is a "Availability after DDN Failure" monitoring event or a "UE Reachability" monitoring event configured for the UE in the SGSN and in such a case sends an event notification (see TS 23.682 for further information).
Step 12.
The new SGSN verifies whether it holds subscription data for the UE identified by the P-TMSI, the additional P-TMSI/RAI or by the IMSI received with the context data from the old CN node.
The additional P-TMSI/RAI allows the new SGSN to find any already existing UE context stored in the new SGSN. If there are no subscription data in the new SGSN for this UE, or for some network sharing scenario (e.g. GWCN) if the PLMN-ID of the RAI supplied by the RNC is different from that of the RAI in the UE's context, then the new SGSN informs the HSS of the change of SGSN by sending an Update Location (SGSN Number, SGSN Address, IMSI, Homogenous Support of IMS Voice over PS Session, UE SRVCC capability, equivalent PLMN list) message to the HSS. For "Homogenous Support of IMS Voice over PS Sessions", see clause 5.3.8A of TS 23.060. The inclusion of the equivalent PLMN list indicates that the SGSN supports the inter-PLMN handover to a CSG cell in an equivalent PLMN using the subscription information of the target PLMN.
If the UE initiates the RAU procedure in a VPLMN supporting Autonomous CSG Roaming and the HPLMN has enabled Autonomous CSG Roaming in the VPLMN (via Service Level Agreement) and the SGSN needs to retrieve the CSG subscription information of the UE from the CSS, the SGSN initiates the Update CSG Location Procedure with CSS as described in clause 5.3.12.
Step 13.
The HSS sends a Cancel Location (IMSI, Cancellation Type) message to the old SGSN with the Cancellation Type set to Update Procedure.
When receiving the Cancel Location message the old SGSN removes all the UE contexts. The old SGSN acknowledges with a Cancel Location Ack (IMSI) message.
Step 14.
When receiving the Context Acknowledge message from the new S4 SGSN and if the old MME has an S1-MME association for the UE, the source MME sends a S1-U Release Command to the source eNodeB after the timer started in step3 has expired. The RRC connection is released by the source eNodeB. The source eNodeB confirms the release of the RRC connection and of the S1-U connection by sending a S1-U Release Complete message to the source MME.
Step 15.
The HSS acknowledges the Update Location message by sending an Update Location Ack (IMSI, Subscription Data) to the new SGSN. If the Update Location is rejected by the HSS, the new SGSN rejects the RAU Request from the UE with an appropriate cause. In such cases, the SGSN releases any local SGSN EPS Bearer contexts for this particular UE, and additionally deletes the EPS bearer resources in the new Serving-GW by sending the Delete Session Request (Cause, Operation Indication) messages to the new Serving-GW. The Operation Indication flag shall not be set. Therefore, the new Serving-GW receiving this request shall not initiate a delete procedure towards the PDN-GW.
The new SGSN validates the UE's presence in the (new) RA. If due to regional subscription restrictions or access restrictions (e.g. CSG restrictions) the UE is not allowed to be attached in the RA, the SGSN rejects the Routing Area Update Request with an appropriate cause to the UE and notifies the HSS of the rejection. The Subscription Data may contain the CSG subscription data for the registered PLMN and for the equivalent PLMN list requested by SGSN in step 12.
If the UE initiates the RAU procedure at a CSG cell, the new S4 SGSN shall check whether the CSG ID and associated PLMN is contained in the CSG subscription and is not expired. If the CSG ID and associated PLMN is not present or expired, the S4 SGSN shall send a RAU reject message to the UE with an appropriate cause value. The UE shall remove the CSG ID and associated PLMN from its Allowed CSG list if present.
Step 16.
When the timer started in step 3 expires and the old MME received the Serving-GW change indication in the Context Acknowledge message, the old MME deletes the EPS bearer resources by sending Delete Session Request (Cause, Operation Indication) messages to the old Serving-GW. The operation Indication flag is not set, that indicates to the old Serving-GW that the old Serving-GW shall not initiate a delete procedure towards the PDN-GW. If ISR is activated the cause indicates to the old S-GW that the old S-GW shall delete the bearer resources on the other old CN node by sending Delete Bearer Request message(s) to that CN node.
Step 17.
The old Serving-GW acknowledges with Delete Session Response (Cause) messages. The old Serving-GW discards any packets buffered for the UE.
Step 18.
If due to regional subscription restrictions or access restrictions the UE is not allowed to access the RA:
- For UEs with ongoing emergency bearer services, the new SGSN accept the Routing Area Update Request and deactivates the non-emergency PDP contexts as specified in clause 9.2.4.2 of TS 23.060. If the Routing Area Update procedure is initiated in PMM-IDLE/STANDBY state, all non-emergency PDP Contexts are deactivated by the Routing Area Update procedure without PDP Context deactivation signalling between the UE and the SGSN.
- For all other cases, the new SGSN rejects Routing Area Update Request with an appropriate cause to the UE and notifies the HSS of rejection (details of this notification is specified in stage 3).
Step 19.
If the P-TMSI was included in the RAU Accept message, the UE acknowledges the new P-TMSI by returning a Routing Area Update Complete message to the SGSN.
Step 20.
For Iu-mode, if the UE has uplink data or signalling pending it shall send a Service Request (P-TMSI, CKSN, Service Type) message to the new SGSN. If a P-TMSI was allocated in step 18, that P-TMSI is the one included in this message. Service Type specifies the requested service. Service Type shall indicate one of the following: Data or Signalling.
Step 21.
If the UE has sent the Service Request, the new 3G SGSN requests the RNC to establish a radio access bearer by sending a RAB Assignment Request (RAB ID(s), QoS Profile(s), GTP SNDs, GTP SNUs, PDCP SNUs) message to the RNC. If Direct Tunnel is established the SGSN provides to the RNC the Serving-GW's Address for User Plane and TEID for uplink data.
Step 22.
If the SGSN established Direct Tunnel in step 21) it shall send Modify Bearer Request to the Serving-GW and include the RNC's Address for User Plane and downlink TEID for data. The Serving-GW updates the Address for User Plane and TEID for downlink data and return a Modify Bearer Response.