Content for TS 23.316 Word version: 19.0.0
1…
4…
4.5…
4.7…
4.10…
4.10b…
4.11…
5…
6…
7…
7.2.2…
7.2.3…
7.2.4…
7.3…
7.6…
7.7…
8…
9…
9.5…
10…
A…
C…
C QoS differentiation of traffic of individual non-3GPP devices behind 5G-RG |R19| p. 96
This Annex describes how the traffic of individual non-3GPP devices behind a 5G-RG can be identified and provided with differentiated QoS.
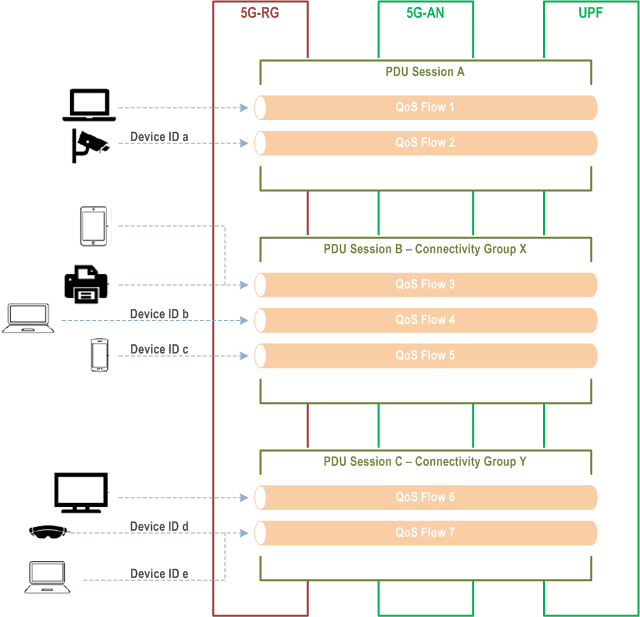
As in this example, two non-3GPP devices mapped to PDU Session A initially used the default QoS Flow (QFI 1); when differentiated QoS is requested for one device, the 5G-RG binds its traffic to a Non-3GPP Device Identifier, and its traffic is mapped to a separate QoS Flow (QFI 2). Four non-3GPP devices mapped to PDU Session B based on their Connectivity Group ID X initially used the default QoS Flow (QFI 3); when differentiated QoS is requested for two of those four devices, the 5G-RG binds their traffic to Non-3GPP Device Identifiers, and their traffic is mapped to separate QoS Flows (QFI 4 and QFI 5). Similarly, three non-3GPP devices mapped to PDU Session C based on their Connectivity Group ID Y initially used the default QoS Flow (QFI 6); when differentiated, but the same, QoS is requested for two of those three devices, the 5G-RG binds their traffic to Non-3GPP Device Identifiers, and their traffic is mapped to a separate QoS Flow (QFI 7).
Figure C-2 illustrates a procedure which enables the 5GS to identify the traffic of individual non-3GPP devices initially using the same PDU Session behind a 5G-RG and provide differentiated QoS.
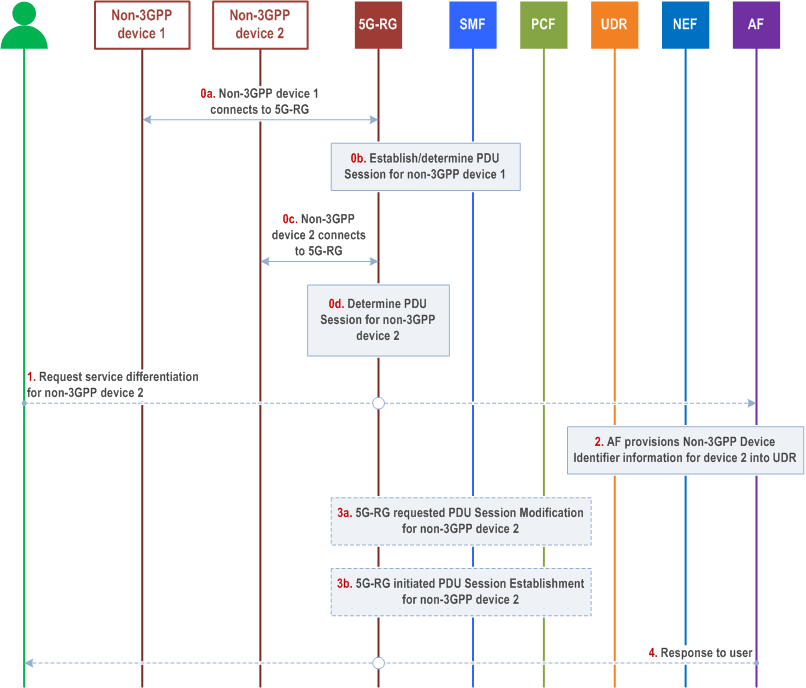
Step 0a.
Non-3GPP device 1 is connected to the 5G-RG.
Step 0b.
To provide connectivity to the non-3GPP device 1, the 5G-RG implements the existing behaviour of either using the URSP rule (optionally containing the Connectivity Group ID as described in clause 4.10b), or using UE Local Configuration, to map the traffic of the non-3GPP device 1 to a PDU Session.
Step 0c.
Non-3GPP device 2 is connected to the 5G-RG.
Step 0d.
To provide connectivity to the non-3GPP device 2, the 5G-RG implements the existing behaviour of either using the URSP rule (optionally containing the Connectivity Group ID as described in clause 4.10b), or using UE Local Configuration, to map the traffic of the non-3GPP device 2 to the same PDU Session as non-3GPP device 1.
Step 1.
The 5G-RG subscription owner or an authorized user, using mechanisms out of scope of 3GPP, requests differentiated QoS for the non-3GPP device 2 through the AF.
Step 2.
AF provisions the Non-3GPP Device Identifier Information for the non-3GPP device 2 into the UDR, as defined in clause 4.15.6.15 of TS 23.502.
Step 3.
Based on the network configuration, either a 5G-RG requested PDU Session Modification, or a 5G-RG requested PDU Session Establishment procedure is triggered.
Step 3a.
(5G-RG requested PDU Session Modification) As defined in clause 7.3.2.
Step 3b.
(5G-RG requested PDU Session Establishment) As defined in clause 7.3.1.
Step 4.
In response to step 1, using mechanisms out of scope of 3GPP, the operator portal returns a response to the 5G-RG subscription owner or the authorized user about the completion of the differentiated QoS request for non-3GPP device 2.