Content for TS 23.282 Word version: 19.3.0
1…
5…
6…
6.6…
7…
7.4…
7.4.2.1.10…
7.4.2.2…
7.4.2.5…
7.4.2.8…
7.4.3…
7.5…
7.5.2.1.12…
7.5.2.2…
7.5.2.4…
7.5.2.6…
7.5.2.8…
7.5.2.11…
7.5.2.14…
7.5.3…
7.6
7.7…
7.7.2.1.13…
7.7.2.2…
7.8…
7.9…
7.13…
7.13.3.1.19…
7.13.3.2…
7.13.3.8…
7.13.3.16…
7.13.4…
7.14…
7.14.2.2…
7.17…
7.17.2.13…
7.17.3…
7.17.3.1.4…
7.17.3.2…
7.17.3.2.4…
7.17.3.2.6…
7.17.4…
7.17.6…
7.17.7…
A…
B…
7.14.2.2 IP connectivity point-to-point MCData transport service
7.14.2.3 Remote initiated point-to-point IP connectivity
7.14.2.4 MCData user remote initiated tear down point-to-point IP connectivity
7.14.2.5 Remote initiated point-to-point IP connectivity application priority change
7.14.2.6 Group standalone IP connectivity using media plane
7.15 Location information (on-network)
7.16 Use of ProSe capabilities in off-network MCData communications
...
...
7.14.2.2 IP connectivity point-to-point MCData transport service p. 209
7.14.2.2.1 General p. 209
IP connectivity service capabilities enables MCData unaware data hosts to use usual MCData service capabilities, e.g. data communication between them. This subclause describes the establishment of a point-to-point connection between two IP connectivity clients using the media plane for IP Data transmission. The target MCData user may be addressed using the functional alias that can be shared by multiple MCData users.
In order not to violate the point-to-point principle when a functional alias is shared, only two MCData user can participate to a point-to-point IP connectivity session. If the MCData server detects that the functional alias used as the target of the MCData FD request is simultaneously active for multiple MCData users, then the MCData server can proceed by selecting an appropriate MCData ID based on some selection criteria. The selection of an appropriate MCData ID is left to implementation. These selection criteria can include rejection of the IP connectivity request, if no suitable MCData ID is selected.
7.14.2.2.2 Procedure p. 209
The procedure in Figure 7.14.2.2.2-1 describes the case where an IP connectivity capable MCData client is initiating a point-to-point IP connectivity with another IP connectivity capable MCData client.
Pre-conditions:
- The total data volume limit, e.g. daily time limit or total data volume per day does not restrict the establishment of an IP connectivity IP data exchange.
- MCData clients are linked with individual data hosts.
- MCData clients belong to the same MCData system.
- The data hosts linked with the MCData clients already have an IP address allocated.
- MCData clients have IP connectivity capabilities.
- The linked data hosts are authorized to use the MCData clients to establish an IP connectivity.
- The MCData server has subscribed to the MCData functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
- MCData client 1 understands the correspondence between the IP addresses of target data hosts and MCData client 2. How this relationship is determined is out of scope of the present document.
- Optionally, the MCData clients may have activated a functional alias to be used.
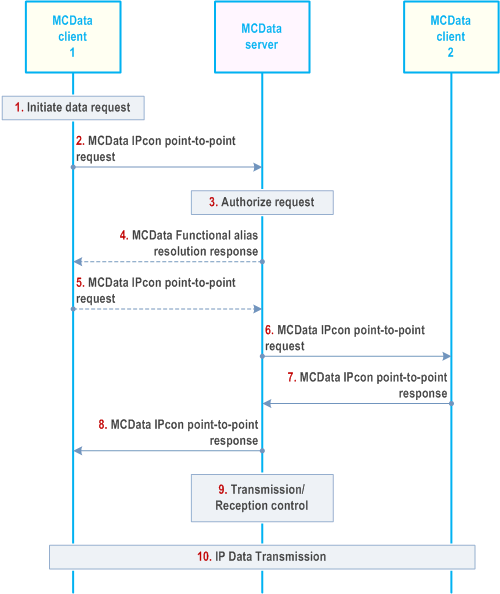
Step 1.
MCData client 1 has IP Data to send to MCData client 2 and initiates an IP connectivity point-to-point request.
Step 2.
MCData client 1 sends a MCData IPcon point-to-point request towards the MCData server. The MCData IPcon point-to-point request contains either the MCData ID of MCData client 2 or its associated functional alias. MCData user at MCData client 1 may include its associated functional alias
Step 3.
MCData server checks whether MCData user at MCData client 1 is authorized to send an MCData IPcon point-to-point request and checks if MCData client 2 is authorised to receive the IP connectivity service. If a functional alias is used to address the target MCData user, the MCData server resolves the functional alias to the corresponding MCData ID(s) for which the functional alias is active and proceed with step 4 otherwise proceed with step 6.
Step 4.
The MCData server responds back to MCData client 1 with a functional alias resolution response message that contains the resolved MCData ID.
Step 5.
If the MCData server replies with a MCData functional alias resolution response message, the MCData client 1 assumes the MCData IPcon point-to-point request in step 2 is rejected and sends a new MCData IPcon point-to-point request towards the resolved MCData ID.
Step 6.
MCData server initiates the MCData IPcon point-to-point request towards the determined MCData client 2.
Step 7.
MCData client 2 sends a MCData IPcon point-to-point response to the MCData server that contains the information if the request is accepted or the reason of rejection. If accepted, the MCData client 2 may include the data transmission time limit.
Step 8.
MCData server forwards the MCData IPcon point-to-point response of MCData client 2 to MCData client 1.
Step 9.
The MCData server applies transmission and reception control and the necessary policy to ensure that appropriate data is transmitted between the MCData clients.
Step 10.
MCData client 1 and MCData Client 2 have successfully established media plane for data communication and MCData client 1 and MCData client 2 exchange IP Data.
7.14.2.3 Remote initiated point-to-point IP connectivity |R17| p. 211
7.14.2.3.1 General p. 211
The MCData service shall support mechanisms that allow an authorized MCData user to trigger remotely the establishment of a point-to-point IP connectivity service. This encompasses the procedure of a remote MCData user that addresses the establishment of an IP connectivity between the requested MCData client and the destination MCData client.
7.14.2.3.2 Procedure p. 211
The procedure in Figure 7.14.2.3.2-1 describes the case where an authorised MCData user triggers remotely the establishment of a point-to-point IP connectivity connection between two other MCData users, required MCData user that establish IP connectivity session to the targeted MCData user.
Pre-conditions:
- The MCData clients are linked with individual data hosts.
- MCData clients belong to the same MCData system.
- The data hosts linked with the MCData clients already have an IP address allocated.
- MCData clients have IP connectivity capabilities.
- The linked data hosts are authorized to use the MCData clients to establish an IP connectivity.
- The MCData server has subscribed to the MCData functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
- MCData clients understands the correspondence between the IP addresses of target data hosts and MCData client 3. How this relationship is determined is out of scope of the present document.
- Optionally, the MCData clients may have activated a functional alias to be used.
- MCData client 1 is authorized to establish remote initiated point-to-point IP connectivity sessions.
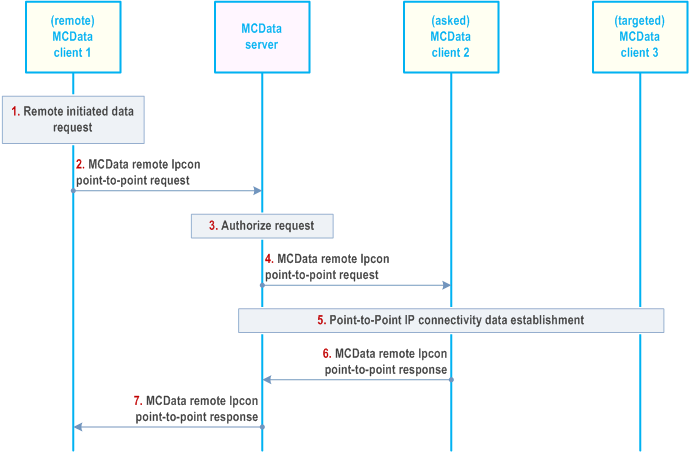
Step 1.
MCData client 1 would like to establish a remote point-to-point IP connectivity to allow IP Data exchange between two other MCData clients, the asked MCData client 2 and the targeted MCData client 3.
Step 2.
The MCData client 1 sends an MCData remote IPcon point-to-point request towards the MCData server. The MCData IPcon point-to-point request contains the MCData ID and optionally the corresponding functional aliases of MCData client 2 and either the MCData ID or the functional alias of MCData client 3. MCData user at MCData client 1 may include its associated functional alias.
Step 3.
MCData server checks whether MCData user at MCData client 1 is authorized to send a remote MCData IPcon point-to-point request and if MCData client 2 and 3 are authorized to receive the IP connectivity service.
Step 4.
MCData server sends the MCData remote IPcon point-to-point request towards the MCData client 2.
Step 5.
MCData client 2 considers the provided targeted MCData ID or targeted functional alias to establish the point-to-point IP connectivity to MCData client 3 according to clause 7.14.2.2. The IP connectivity status shall be forwarded by MCData client 2 to MCData client 1.
Step 6.
MCData client 2 send an MCData remote IPcon point-to-point response to the MCData server encompassing the IP connectivity status of the point-to-point IP connectivity session between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
Step 7.
The MCData server forwards the MCData remote IPcon point-to-point response to the remote MCData client 1.
7.14.2.4 MCData user remote initiated tear down point-to-point IP connectivity |R17| p. 212
7.14.2.4.1 General p. 212
The MCData service shall support mechanisms that allow an authorized MCData user to tear down remotely an established point-to-point IP connectivity. This encompasses the procedure of a remote MCData user that addresses the tear down of an IP connectivity between the requested MCData client and the destination MCData client.
7.14.2.4.2 Procedure p. 212
The procedure in Figure 7.14.2.4.2-1 describes the case where an authorised MCData user triggers remotely the tear down of a point-to-point IP connectivity connection between two other MCData users, the asked MCData user that tear down IP connectivity session to the targeted MCData user.
Pre-conditions:
- The point-to-point IP connectivity has been established between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
- Optionally, the MCData client 1 may have activated a functional alias to be used.
- MCData client 1 is authorized to tear down point-to-point IP connectivity sessions.
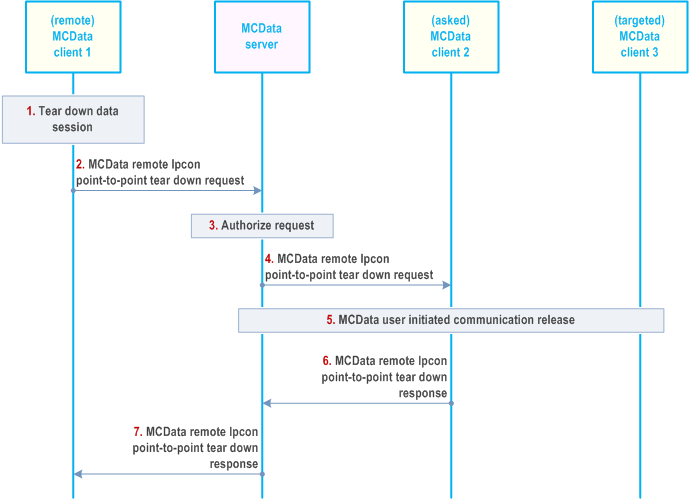
Step 1.
MCData client 1 would like to tear down a point-to-point IP connectivity between two other MCData clients, the asked MCData client 2 and the targeted MCData client 3.
Step 2.
The MCData client 1 sends an MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down request towards the MCData server. The MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down request contains the MCData IDs of MCData client 2 and MCData client 3. MCData user at MCData client 1 may include its associated functional alias.
Step 3.
MCData server checks whether MCData user at MCData client 1 is authorized to send MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down request and checks if the asked MCData client 2 is allowed to tear down an IP connectivity point-to-point session.
Step 4.
MCData server sends the MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down request towards the MCData client 2.
Step 5.
MCData client 2 considers the provided targeted MCData ID to tear down the point-to-point IP connectivity to MCData client 3. The status of the IP connectivity tear down request shall be forwarded by MCData client 2 to remote MCData client 1.
Step 6.
MCData client 2 sends MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down response to the MCData server encompassing the tear down IP connectivity status between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
Step 7.
The MCData server forwards the MCData remote IPcon point-to-point tear down response to the remote MCData client 1.
7.14.2.5 Remote initiated point-to-point IP connectivity application priority change |R17| p. 213
7.14.2.5.1 General p. 213
The MCData service shall support mechanisms that allow an authorized MCData user to trigger remotely the adaptation of a point-to-point IP connectivity data bearer service priority. This encompasses the procedure of a remote MCData user that addresses the priority change of a point-to-point IP connectivity between the requested MCData clients.
7.14.2.5.2 Procedure p. 213
The procedure in Figure 7.14.2.5.2-1 describes the case where an authorised MCData user triggers remotely the priority change of a point-to-point IP connectivity connection between two other MCData users.
Pre-conditions:
- Optionally, the MCData client 1 may have activated a functional alias to be used.
- A point-to-point IP connectivity is established between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
- MCData client 1 is authorized to change remotely communication priority of a point-to-point IP connectivity session.
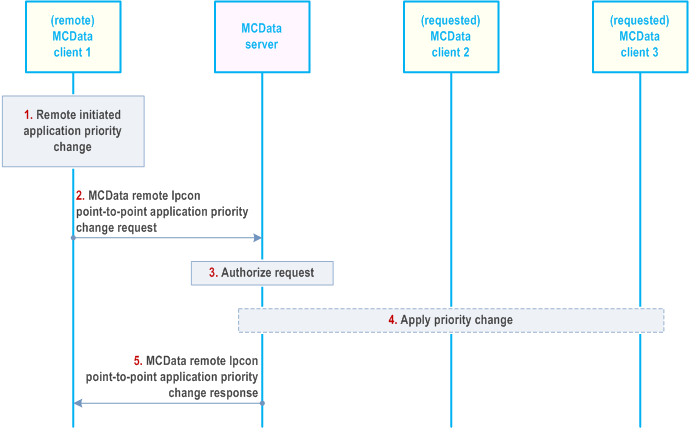
Step 1.
MCData client 1 would like to change the priority that corresponds to an established point-to-point IP connectivity between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
Step 2.
The MCData client 1 sends a remote MCData IPcon point-to-point application priority change request towards the MCData server. The MCData IPcon point-to-point application priority change request contains the MCData IDs of MCData client 2 and MCData client 3. MCData user at MCData client 1 may include its associated functional alias.
Step 3.
MCData server checks whether MCData user at MCData client 1 is authorized to send a remote MCData IPcon point-to-point application priority change request.
Step 4.
MCData server applies the requested priority to the point-to-point IP connectivity between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
Step 5.
MCData server sends the remote MCData IPcon point-to-point application priority change response to MCData client 1 encompassing the priority status of the point-to-point IP connectivity between MCData client 2 and MCData client 3.
7.14.2.6 Group standalone IP connectivity using media plane |R17| p. 214
7.14.2.6.1 General p. 214
IP connectivity service capabilities enables authorized MCData unaware data host to use usual MCData service capabilities, e.g. data communication among them. This subclause describes the establishment of a group standalone IP connectivity to a selected MCData group results in affiliated group members exchanging IP data.
7.14.2.6.2 Procedure p. 215
The procedure in Figure 7.14.2.6.2-1 describes the case where an IP connectivity capable MCData client is initiating group standalone MCData IP connectivity communication session with an MCData group for exchanging IP Data between group participants using MCData IPcon-2 reference point.
Pre-conditions:
- MCData client 1 to MCData client n belong to the same MCData group, are registered for receiving MCData service and are affiliated to the corresponding MCData group.
- The total data volume limit, e.g. daily time limit or total data volume per day, does not restrict the establishment of an IP connectivity MCData transmission.
- MCData client 1 to MCData client n are linked with individual data hosts.
- MCData client 1 to MCData client n belong to the same MCData system.
- The data hosts linked with the MCData clients already have an IP address allocated.
- MCData clients have IP connectivity capabilities.
- The linked data hosts are authorized to use the MCData clients to establish an IP connectivity.
- The MCData server has subscribed to the MCData functional alias controlling server within the MC system for functional alias activation/de-activation updates.
- MCData clients understand the correspondence between the IP addresses of target data hosts and MCData clients. How this relationship is determined is out of scope of the present document.
- MCData clients understand the relationship between the addressing of IP packets which are intended to be sent to the group and the MCData group address.
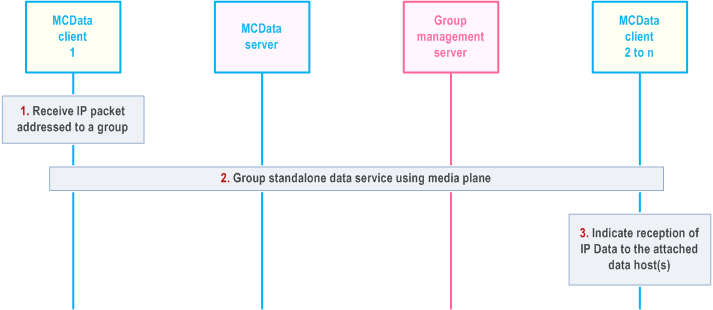
Step 1.
MCData client 1 receives an IP packet from the IP data host which is addressed to an IP address that signifies an MCData group destination.
Step 2.
MCData client 1 uses the MCData group standalone short data service using media plane procedure in accordance with clause 7.4.2.6 to establish IPcon group standalone communication session to the MCData user that are members of the corresponding MCData group with the following scope:
Step 3.
- IP Data exchange
- The application identifier is used to indicate about the use of a group communication in the IP connectivity context
- Payload destination indicates the consumption by the linked data host
- The use of disposition shall be discarded for the use of IP connectivity
MCData clients 2-n recognize that the payload is for IP connectivity service and forward the received IP data to the linked data hosts.
7.15 Location information (on-network) |R16| p. 216
The MCData system makes use of all of the procedures for location management as specified in TS 23.280, utilising the CSC-14 reference point between the location management client and location management server and the CSC-15 reference point between the MCData server and location management server.
- The MC service client is the MCData client;
- The MC service server is the MCData server;
- The MC service group is the MCData group;
- The MC service ID is the MCData ID; and
- The MC service group ID is the MCData group ID.
7.16 Use of ProSe capabilities in off-network MCData communications |R17| p. 216
7.16.1 General p. 216
When an MCData user using a ProSe-enabled UE wants to communicate with a specific MCData group or MCData user using ProSe capabilities, the MCData client enables the use of the ProSe layer procedures for public safety, as specified in TS 23.303.
For an off-network MCData group communication, the MCData client obtains configuration data such as the user info ID of the MCData user sending data and the ProSe Group IP multicast address and ProSe Layer-2 Group ID associated to the target MCData group (as described in clause 8.1.3.2 of TS 23.280), and provides it to the ProSe layer. The ProSe Layer-2 Group ID of the target MCData group may be used by the ProSe layer as the target group info and the discovery group ID (defined in TS 23.303).
Prior to initiating an off-network MCData group communication, a group member discovery procedure may be initiated to identify whether other members of the target MCData group are in the proximity of the MCData user sending data, as described in the ProSe direct discovery for public safety use procedure in TS 23.303. The off-network MCData group communication using the ProSe capability is based on the one-to-many ProSe direct communication procedure for public safety use described in TS 23.303.
For an off-network one-to-one MCData communication, the MCData client obtains configuration data such as the ProSe discovery group ID and user info ID of the target MCData user from the "List of MCData users this MCData user is authorized to initiate a one to-one communication" in the MCData user profile and requests the IP address of the MCData UE associated with the target MCData user from the ProSe layer.
The MCData client enables the ProSe layer to determine the IP address for the communication with the target MCData UE by providing the ProSe discovery group ID and user info ID (as defined in TS 23.303) associated to the target MCData user. This may trigger the ProSe direct discovery for public safety use procedure to identify whether the target MCData user is in the proximity of the MCData user sending data. The user info ID of the target MCData user is used by the ProSe layer as the target info (as defined in TS 23.303).
The ProSe layer can then provide the IP address related to the target MCData user to the MCData client to initiate the off-network one-to-one MCData communication based on the one-to-one ProSe direct communication procedure described in TS 23.303.
7.16.2 Procedures p. 217
The off-network MCData communication procedures using the ProSe capabilities are described within the corresponding clauses of each MCData capability, e.g. SDS procedures for off-network are described in clause 7.4.3 and file distribution procedures for off-network are described in clause 7.5.3.