Content for TS 22.261 Word version: 20.1.0
0…
4…
6…
6.4…
6.8…
6.12…
6.15…
6.16…
6.22…
6.26…
6.30…
6.37…
6.41…
6.43…
6.46…
7…
7.4…
7.9
7.10…
7.11…
8…
D…
D.3…
F…
G…
H
I
J…
6.37 Ranging based services
6.37.1 Description
6.37.2 Requirements
6.38 Personal IoT Networks and Customer Premises Networks
6.38.1 Description
6.38.2 Requirements
6.38.2.1 General
6.38.2.2 Gateways
6.38.2.3 Operation without 5G core network connectivity
6.38.2.4 Discovery
6.38.2.5 Relay Selection
6.38.2.6 Security
6.38.2.7 QoS
6.38.2.8 Charging
6.38.2.9 Creation and Management
6.39 5G IMS Multimedia Telephony Service
6.39.1 Description
6.39.2 General
6.39.3 Service Exposure
6.40 AI/ML model transfer in 5GS
6.40.1 Description
6.40.2 Requirements
6.40.2.1 Requirements for direct network connection
6.40.2.2 Requirements for direct device connection
...
...
6.37 Ranging based services |R18| p. 66
6.37.1 Description p. 66
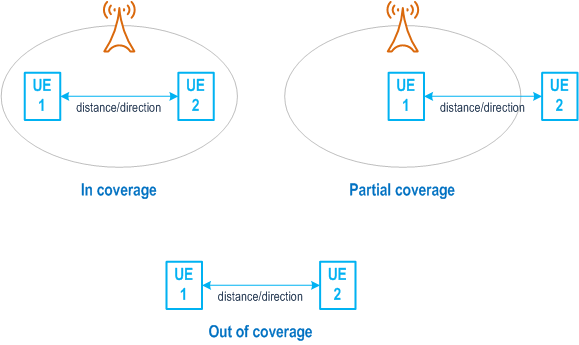
Ranging-based services are the applications utilizing the distance between two UEs and/or the direction of one UE from the other one. In 3D case, direction includes horizontal direction and elevation direction. Ranging-based services can apply to a variety of verticals, such as consumer, smart home, smart city, smart transportation, smart retail, and industry 4.0. Some ranging-based services can only require the distance measurement, some can only require direction measurement, others can require both distance and direction measurement.
Ranging can be supported with or without 5G coverage and Figure 6.37.1-1 is an illustration of ranging between UEs that are in coverage, out of coverage, or with partial coverage. Both licensed and unlicensed spectrum can be used for ranging. If licensed spectrum is used, it shall be fully under operator control.
6.37.2 Requirements p. 66
The 5G system shall be able to support for a UE to discover other UEs supporting ranging.
The 5G system shall be able to authorize ranging for a UE or a group of UE when using licensed spectrum.
The 5G system shall be able to protect privacy of a UE and its user, ensuring that no identifiable information can be tracked by undesired entities during ranging.
The 5G system shall be able to enable or disable ranging.
The 5G system shall support mutual ranging, i.e. two UEs shall be able to initiate ranging to each other.
The 5G system shall be able to ensure that the use of Ranging, if in licensed spectrum, is only permitted in network coverage under the full control of the operator who provides the coverage.
The 5G system shall support energy efficient UE ranging operation.
The 5G system shall be able to start ranging and stop ranging according to the application layer's demand.
The 5G system shall be able to provide mechanisms for a MNO, or authorized 3rd party, to provision and manage ranging operation and configurations.
The 5G system shall be able to support mechanisms for a UE to assist another UE to perform ranging of a third UE (if the requesting UE is LOS with the assisting UE and the assisting UE is LOS with the third UE).
The 5G system shall be able to support ranging enabled UEs to determine the ranging capabilities (e.g. capabilities to perform distance and/or angle measurement) of other ranging enabled UEs.
The 5G system shall be able to allow a ranging enabled UE to determine if another ranging enabled UE is stationary or mobile, before and/or during ranging.
The 5G system shall allow ranging between 2 UEs triggered by and exposed to a third UE.
The 5G system shall allow ranging service between 2 UEs triggered by and exposed to the application server.
The 5G system shall be able to support one UE initiating ranging to the other UE.
The 5G system shall be able to support ranging between UEs which subscribe to different operators.
The 5G system shall be able to allow roaming UEs to perform ranging.
The 5G system shall be able to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of ranging information used by ranging-enabled UEs.
The 5G system shall be able to ensure that user privacy is not violated during ranging, e.g., subject to regional or national regulatory requirements.
The 5G system shall be able to ensure security protection (e.g., interworking security) when the ranging concerns UEs subscribed with different operators.
The level of security provided by the existing 5G system shall not be adversely affected when ranging is enabled.
The 5G system shall support means to securely identify other ranging capable UEs, with which a certain UE can perform ranging.
6.38 Personal IoT Networks and Customer Premises Networks |R18| p. 67
6.38.1 Description p. 67
Personal IoT Networks (PINs) and Customer Premises Networks (CPNs) provide local connectivity between UEs and/or non-3GPP devices. The CPN via an eRG or a legacy residential gateway, or PIN Elements via a PIN Element with Gateway Capability can provide access to 5G network services for the UEs and/or non-3GPP devices on the CPN or PIN. CPNs and PINs have in common that in general they are owned, installed and/or (at least partially) configured by a customer of a public network operator.
A Customer Premises Network (CPN) is a network located within a premises (e.g. a residence, office or shop). Via an evolved Residential Gateway (eRG) or a legacy residential gateway, the CPN provides connectivity to the 5G network. The eRG can be connected to the 5G core network via wireline, wireless, or hybrid access: in case of wireless or hybrid access an eRG with USIM is required; in case of wireline access an eRG can be depoyed without a USIM. A Premises Radio Access Station (PRAS) is a base station that can also be installed in a CPN. Through the PRAS, UEs can get access to the CPN and/or 5G network services. The PRAS can be configured to use licensed, unlicensed, or both frequency bands. Connectivity between the eRG and the UE, non-3GPP Device, or PRAS can use any suitable non-3GPP technology (e.g. Ethernet, optical, WLAN).
A Personal IoT Network (PIN) consists of PIN Elements that communicate using PIN Direct Connection or direct network connection and is managed locally (using a PIN Element with Management Capability). Examples of PINs include networks of wearables and smart home / smart office equipment. Via a PIN Element with Gateway Capability, PIN Elements have access to the 5G network services and can communicate with PIN Elements that are not within range to use PIN Direct Connection. A PIN includes at least one PIN Element with Gateway Capability and at least one PIN Element with Management Capability.
A PIN Element with Management Capability is a PIN Element that provides a means for an authorised administrator to configure and manage a PIN.
The requirements as described in clause 26a of TS 22.101 can also apply to Personal IoT Networks and Customer Premises Networks.
6.38.2 Requirements p. 68
6.38.2.1 General p. 68
The 5G system shall support mechanisms to identify a PIN, a PIN Element, an eRG and a PRAS.
Subject to local regulations, the 5G system shall support regulatory requirements for emergency calls, PWS and eCall for UEs connected via a CPN.
The 5G system shall support applications on an Application Server connected to a CPN or PIN.
The 5G system shall be able to support PINs with PIN Elements subscribed to more than one network operator (e.g., a PIN Element that is a MUSIM UE and subscribes to different operators respectively, one PIN Element subscribed to network operator A and another PIN Element subscribed to network operator B).
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator policy, the 5G system shall support an efficient data path within the CPN for intra-CPN communications.
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator policy, the 5G system shall support a data path not traversing the 5G network for intra-PIN communications via direct connections.
The 5G system shall enable the network operator to provide any 5G services to any UE via a PRAS connected via an eRG.
The 5G system shall minimize service disruption for a UE that is moving between CPN access and operator provided mobile access.
The 5G system shall minimize service disruption when a CPN communication path changes between two PRASes.
The 5G system shall be able to minimize service disruption when a PIN Element changes the communication path from one PIN Element (e.g. PIN Element with Gateway Capability) to another PIN Element or operator provided mobile access. The communication path between PIN Elements may include licensed and unlicensed spectrum as well as 3GPP and non-3GPP access.
The 5G system shall be able to support PRAS sharing between multiple PLMNs.
The 5G system shall support mechanisms to aggregate, switch or split the service between non-3GPP RAT and PIN direct connections using licensed spectrum.
6.38.2.2 Gateways p. 69
Subject to operator policy, the 5G network shall support an authorised eRG without a USIM to access the 5G core network via wireline access only.
The 5G system shall be able to support access to the 5G network and its services via at least one gateway (i.e. PIN Element with Gateway Capability or eRG or legacy residential gateway) for authorised UEs and authorised non-3GPP devices in a PIN or a CPN.
The 5G system shall be able to support IP traffic offload to data network for a CPN.
Under operator control, an eRG, shall be able to efficiently deliver 5G multicast/broadcast services to authorized UEs and non-3GPP devices in the CPN.
6.38.2.3 Operation without 5G core network connectivity p. 69
The 5G system shall allow PIN Elements to communicate when there is no connectivity between a PIN Element with Gateway Capability and a 5G network. For a Public Safety PIN licensed spectrum may be used for PIN direct communications otherwise unlicensed spectrum shall be used.
When a CPN has lost connectivity with the 5G network, the 5G system shall provide an operator-controlled mechanism to enable:
- in the default configuration, or under certain conditions configured by the operator, the PRAS radio interface shall be deactivated; and
- under certain other conditions configured by the operator, the CPN shall continue existing intra-CPN communication, as long as no interaction with the 5G network is needed (e.g. refreshing security keys).
6.38.2.4 Discovery p. 69
The 5G system shall enable a UE or non-3GPP device in a CPN or PIN to discover other UEs or non-3GPP devices within the same CPN or PIN subject to acess rights.
The 5G system shall efficiently support service discovery mechanisms where a UE or non-3GPP device in a CPN or PIN can discover, subject to access rights:
- availability and reachability of other entities (e.g. other UEs or non-3GPP devices) on the CPN or PIN;
- capabilities of other entities on the CPN (e.g. PRAS, eRG) or PIN (e.g. relay UE, connection types) and/or;
- services provided by other entities on the CPN or PIN (e.g. the entity is a printer).
6.38.2.5 Relay Selection p. 70
In addition to the relay selection requirements in clause 6.9.2.4, relay selection within a PIN is enabled for both UEs and non-3GPP device and supports the additional selection criteria:
- The 5G system shall support a mechanism for a PIN Element to select a relay for PIN direct connection that enables access to the target PIN Element.
6.38.2.6 Security p. 70
The 5G system shall provide user privacy; location privacy, identity protection and communication confidentiallity for non-3GPP devices and UEs that are using the PIN Element with Gateway Capability, eRG or PRAS.
The 5G system shall support a mechanism to minimize the security risk of communications using an eRG.
The 5G system shall enable the network operator associated with an eRG to control the security policy of an eRG.
Subject to operator policy, the 5G network shall provide support to authenticate an eRG without a USIM to access the 5G core network via wireline access only.
The 5G system shall support a mechanism to minimize the security risk of communications via a PRAS.
The PRAS (and its associated backhaul connectivity) shall provide a level of security equivalent to regular 5G base stations.
The 5G system shall enable the network operator associated with the Premises Radio Access Station (PRAS) to control the security policy of the PRAS.
The 5G system shall support authentication of a UE with 3GPP credentials for communication with entities (UEs, non-3GPP devices) in a CPN.
The 5G system shall provide support for a network operator to authenticate a PRAS.
The 5G system shall provide support for a network operator to authorize a PRAS for its use in a CPN.
The 5G system shall support a PIN Element using non operator managed credentials (e.g. provided by a third party) for performing communications within the PIN when those communications use PIN direct connections.
The 5G system shall support a mechanism to mitigate repeated and unauthorized attempts to access PIN Elements (e.g. mitigate a malicious flood of messages).
6.38.2.7 QoS p. 70
The 5G system shall support real time E2E QoS monitoring and control for any intra-CPN data traffic to or from a UE (i.e. via eRG or via PRAS and eRG).
The 5G system shall support real time E2E QoS monitoring and control for any data traffic between a UE within a CPN and the 5G network (i.e. via eRG or via PRAS and eRG).
6.38.2.8 Charging p. 70
The 5G system shall support charging data collection for data traffic to/from individual UEs in a CPN or PIN (i.e., UEs behind the PIN Element with Gateway Capability or eRG and/or PRAS).
The 5G system shall be able to generate charging data that can differentiate between backhaul for the PRAS and other data traffic over the same access.
6.38.2.9 Creation and Management p. 71
The 5G system shall support a mechanism for the network operator to provision an eRG with:
- policies on which transport (e.g. wireless, cable, etc.) is best suited for different negotiated QoS levels,
- authentication credentials,
- identification,
- initial OA&M information, and
-
associated subscription.
The 5G system shall enable the network operator to configure a PRAS with:
- radio settings pertaining to licensed spectrum,
- authentication credentials,
- identification,
- initial OA&M information, and
- associated subscription.
- Authorizing/deauthorizing PIN Elements;
- Authorizing/deauthorizing PIN Elements with Management Capability;
- Authorizing/deauthorizing PIN Elements with Gateway Capability;
- Establishing duration of the PIN;
- Configure PIN Elements to enable service discovery of other PIN Elements;
- Authorize/deauthorise if a PIN Element can use a PIN Element with Gateway Capability to communicate with the 5GS;
- Authorize/deauthorise for a PIN Element(s):
- which other PIN Element it can communicate with,
- which applications/service or service in that PIN it can access,
- which PIN Element it can use as a relay.
- Authorize/deauthorise a UE to perform service discovery of PIN Elements over the 5G network;
- Configure a PIN Element for external connectivity e.g.via 5G system;
- Configure the connectivity type (e.g. licensed, unlicensed PIN direct connection) a PIN Element can use.
6.39 5G IMS Multimedia Telephony Service |R18| p. 72
6.39.1 Description p. 72
The 5G system is expected to support advanced capabilities and performance of enhanced IMS multimedia telephony service to meet new demands from consumers, business customers and vertical markets. Nowadays 3GPP has introduced new network capabilities and new types of devices (e.g. AR/VR/XR devices, robot, etc.), which can bring promising improvements to IMS multimedia telephony service. While more and more individual consumers enjoy multimedia telephony services across the globe, multimedia telephony services become popular also among business customers. There are several primary business functions that organizations use multimedia telephony services for, including internal communication, talking with prospects (sales call), contacting current customers and clients, customer support, and contact centre (or call centre) activities. While business customers consider the multimedia telephony services offer attractive features to their business, they also experience some practical issues that expect support from the 5G system.
6.39.2 General p. 72
The following set of requirements complement the requirements listed in TS 22.173.
The IMS multimedia telephony service shall support AR media processing.
6.39.3 Service Exposure p. 72
Requirements in this clause are subject to regulatory requirements and operator policy.
The 5G system shall provide means to allow a trusted third-party to update the multimedia telephony service subscription and allocate a third-party specific identity to an authorized user.
The following requirements apply to the originating side:
- The 5G network shall provide a means for third parties (e.g. enterprises) to be authorized to verify the use of calling identity information by its authorized users.
- The 5G network shall provide a means for authorized third parties to verify that an authenticated user is authorized to include or reference the pre-established calling identity information included in the call setup or retrieved by the called party.
- The 5G network shall provide a means to verify the authenticity of the pre-established stored identity information that is referenced by the call setup and retrieved by the called party.
- The 5G network shall provide a means for third parties (e.g. enterprises) to be able to verify the caller's authorization to use the identity information either in addition to or instead of verification performed by the terminating PLMN.
- The 5G network shall provide a means to verify the authenticity of any stored identity information referenced by the call setup to be presented to the called party.
6.40 AI/ML model transfer in 5GS |R18| p. 73
6.40.1 Description p. 73
Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML) is being used in a range of application domains across industry sectors. In mobile communications systems, mobile devices (e.g. smartphones, automotive, robots) are increasingly replacing conventional algorithms (e.g. speech recognition, image recognition, video processing) with AI/ML models to enable applications. The 5G system can at least support three types of AI/ML operations:
- AI/ML operation splitting between AI/ML endpoints The AI/ML operation/model is split into multiple parts according to the current task and environment. The intention is to offload the computation-intensive, energy-intensive parts to network endpoints, whereas leave the privacy-sensitive and delay-sensitive parts at the end device. The device executes the operation/model up to a specific part/layer and then sends the intermediate data to the network endpoint. The network endpoint executes the remaining parts/layers and feeds the inference results back to the device.
- AI/ML model/data distribution and sharing over 5G system Multi-functional mobile terminals might need to switch the AI/ML model in response to task and environment variations. The condition of adaptive model selection is that the models to be selected are available for the mobile device. However, given the fact that the AI/ML models are becoming increasingly diverse, and with the limited storage resource in a UE, it can be determined to not pre-load all candidate AI/ML models on-board. Online model distribution (i.e. new model downloading) is needed, in which an AI/ML model can be distributed from a NW endpoint to the devices when they need it to adapt to the changed AI/ML tasks and environments. For this purpose, the model performance at the UE needs to be monitored constantly.
- Distributed/Federated Learning over 5G system The cloud server trains a global model by aggregating local models partially-trained by each end devices. Within each training iteration, a UE performs the training based on the model downloaded from the AI server using the local training data. Then the UE reports the interim training results to the cloud server via 5G UL channels. The server aggregates the interim training results from the UEs and updates the global model. The updated global model is then distributed back to the UEs and the UEs can perform the training for the next iteration.
6.40.2 Requirements p. 73
6.40.2.1 Requirements for direct network connection |R19| p. 73
Based on operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to provide means to allow an authorized third-party to monitor the resource utilisation of the network service that is associated with the third-party.
Based on operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to provide an indication about a planned change of bitrate, latency, or reliability for a QoS flow to an authorized 3rd party so that the 3rd party AI/ML application is able to adjust the application layer behaviour if time allows. The indication shall provide the anticipated time and location of the change, as well as the target QoS parameters.
Based on operator policy, 5G system shall be able to provide means to predict and expose predicted network condition changes (i.e. bitrate, latency, reliability) per UE, to an authorized third party.
Subject to user consent, operator policy and regulatory constraints, the 5G system shall be able to support a mechanism to expose monitoring and status information of an AI-ML session to a 3rd party AI/ML application.
5G system shall be able to provide event alerting to an authorized 3rd party, together with a predicted time of the event (e.g., alerting about traffic congestion or UE moving into/out of a different geographical area).
The 5G system shall be able to expose aggregated QoS parameter values for a group of UEs to an authorized service provider.
The 5G system shall be able to support an authorised 3rd party to change aggregated QoS parameter values associated with a group of UEs, e.g. UEs of a FL group.
Subject to user consent, operator policy and regulatory requirements, the 5G system shall be able to expose information (e.g. candidate UEs) to an authorized 3rd party to assist the 3rd party to determine member(s) of a group of UEs (e.g. UEs of a FL group).
6.40.2.2 Requirements for direct device connection |R19| p. 74
Based on user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party request, the 5G system shall support a means to authorize specific UEs to transmit data (e.g. AI-ML model data for a specific application,) via direct device connection in a certain location and time.
Based on user consent, operator policy, and trusted 3rd party's request, the 5G system shall be able to provide means for an operator to authorize specific UEs who participate in the same service (e.g. for the same AI-ML FL task) to exchange data with each other via direct device connection, e.g. when direct network connection cannot fulfil the required QoS.
Based on user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party request, the 5G system shall be able to dynamically add or remove specific UEs to/from the same service (e.g. a AI-ML federated learning task) when communicating via direct device connection.
Based on user consent and operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to provide means for the network to configure and modify remote UEs' communication QoS, when a relay UE is involved, e.g., to satisfy end to end latency for proximity-based work task offloading.
Subject to user consent and operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to support configuration of the QoS (e.g., latency, reliability, data rate) of a communication path using direct device connection, e.g., for AI-ML data transfer.
Based on user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party request, the 5G system shall be able to support means to monitor the QoS characteristics (e.g. data rate, latency) of traffic transmitted via direct device connection or relayed by a UE, and 5G network expose the monitored information to the 3rd party.
Subject to user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party request, the 5G system shall be able to provide means the network to predict and expose QoS information changes for UEs' traffic using direct or indirect network connection (e.g., bitrate, latency, reliability).The 5G system shall be able to support a mechanism for a trusted third-party to negotiate with the 5G system for a suitable QoS for direct device connections of multiple UEs exchanging data with each other (e.g. a group of UEs using the same AI-ML service).
Based on user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party's request, the 5G system shall be able to support and provision an aggregated QoS for multiple remote UEs served by a relay UE.
Based on user consent, operator policy and trusted 3rd party's request, the 5G system shall be able to support configuring specific QoS limitations applied to multiple UEs communicating via direct device connection (e.g. part of a joint AI-ML inference task).
Subject to user consent, regulation, trusted 3rd party's request and operator policy, the 5G network shall be able to expose information to assist the 3rd party to determine candidate UEs for data transmission via direct device connection (e.g. for AIML model transfer for a specific application).
Subject to user consent, operator policy, regulation and trusted 3rd party's request, the 5G network shall be able to expose information of certain UEs using the same service to the 3rd party (e.g. to assist a joint AIML task of UEs in a specific area using direct device communication)
The 5G system shall be able to support charging mechanisms for multiple UEs exchanging data for the same service using the direct device connection (e.g. for AI-ML applications).