Content for TR 22.837 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.12…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
5.22…
5.23…
5.24…
5.25…
5.26…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
6…
7…
5.17 Use case on health monitoring at home
5.17.1 Description
5.17.2 Pre-conditions
5.17.3 Service Flows
5.17.4 Post-conditions
5.17.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality
5.17.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case
...
...
5.17 Use case on health monitoring at home p. 52
5.17.1 Description p. 52
Tom is an elderly person living in his house. Since he has become weaker, he has subscribed to a wireless sensing service of his MNO so that his health state (including e.g. lack of movement, detection of falls, breathing rate) can be monitored 24/7 when he is at his home. Wireless sensing is a promising technology for health monitoring [34] [35] [36] [37] that does not require a person to wear a health monitoring device on his/her body (which people may forget, requires recharging, and can be uncomfortable to wear over long periods of time).
A single base station is not capable of covering Tom's home with good coverage. Thus, multiple base stations capable of acting as wireless transmitters and/or receivers cooperate to ensure excellent coverage. Furthermore, the received reflected radar signal is sometimes weak, and thus, the MNO offers the possibility of using a phone with wireless sensing receiving capabilities. The usage of the phone also allows more accurate measurements of certain vital signs (e.g. breathing rate) since the phone is close to Tom. The usage of the phone also allows the MNO to offload the workload from the base station to the phone. Also other UEs in vicinity of Tom could take part in the sensing.
Figure 5.17.1-1 shows a schematic illustration of how such system could look like, whereby the blue arrow indicates transmitted wireless sensing signals from Base Station A, and the green dashed arrows indicate reflected wireless sensing signals received by Base Station B and Tom's phone.
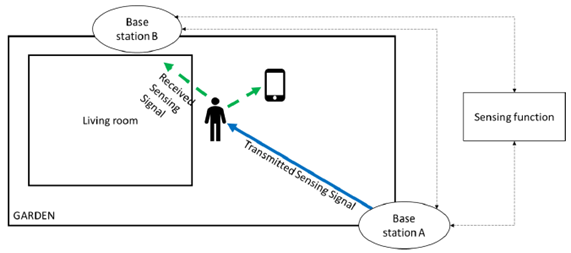
Figure 5.17.1-1: Example of a distributed sensing system (incl. two base stations, a UE and a Sensing function)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
5.17.2 Pre-conditions p. 53
- Tom has subscribed to the sensing service offered by an MNO.
- The MNO has deployed two RAN entities (e.g. base station A and base station B) that are capable of wireless communication and sensing. The base stations can act as wireless sensing transmitters and/or wireless sensing receivers. These two base stations are sufficiently close to Tom's house to provide good coverage in and around Tom's house in the frequency bands used for wireless sensing. Tom's subscription includes a phone with wireless sensing capabilities for more accurate sensing.
- Tom has a mobile phone that is capable of detecting wireless sensing signals. Tom can use it to directly and/or more accurately sense his health state.
- The 3GPP sensing data from the RAN and UEs is collected and processed by a sensing function that can be deployed in the 5G network or provided by an external application or a combination thereof. The exact separation of functionalities between those entities is not explored further in this use case. The sensing function is assumed to be capable of extracting health state information, e.g. lack of movement, detection of falls, breathing rate from this 3GPP sensing data, determine the sensing requirements (e.g. accuracy), and determine the criteria/thresholds (e.g. lack of movement) on when to create an alert.
5.17.3 Service Flows p. 53
- Based on Tom's sensing subscription, information about a user (in this case Tom) is obtained including information about where he lives and sensing requirements that are needed (e.g. sensing of movements which can be used to detect falls or sufficient activity of Tom).
- Base station A starts transmitting the wireless sensing signal.
- Tom is currently located in the living room. If Tom is at this location, base station A can hardly receive the reflection of its transmitted sensing signal. However, base station B can receive a strong reflection of that sensing signal. Base station A and B coordinate with each other so that Base Station B is capable of processing the received reflected wireless sensing signal, generating 3GPP sensing data that is sent to a sensing function for further processing. In this manner, movements of Tom in and around the house can be monitored, and it can be detected if Tom falls.
- Tom feels a bit weak today and decides to measure his health state in more detail. Tom was told that he needs to carry his phone to enable this. Tom picks up his phone and uses it as a wireless sensing receiver capable of picking up and processing the reflected wireless sensing signal transmitted by Base station A. This requires the phone to coordinate wireless sensing with Base station A, which includes for example exchanging of capabilities (since the sensing capabilities can differ per phone) and coordinating of timing/frequencies of sensing signals. Since Tom's phone is very close to Tom, Tom can use his phone for more accurate sensing of certain vital signs, such as breathing rate and heart rate. The phone sends measurements to a sensing function for further processing. When Tom goes to sleep, he puts his phone next to him to monitor his vital signs also during the night.
- When Tom's health state is determined to be in danger, e.g., when Tom falls or stops moving, the family or emergency services gets alerted of such event.
5.17.4 Post-conditions p. 54
The sensing service/application receives accurate 3GPP sensing data about Tom and can generate alerts if an adverse event happens to Tom.
5.17.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality p. 54
None.
5.17.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case p. 54
[PR 5.17.6-1]
The 5G system shall be able to coordinate wireless sensing among a set of RAN entities and UEs.
[PR 5.17.6-2]
The 5G system shall support a mechanism for the 5G network to retrieve the wireless sensing capabilities from UEs and RAN entities, and for the UEs and RAN entities to exchange capabilities amongst each other.
[PR 5.17.6-3]
The 5G system shall support a mechanism for two or more authorized UEs and/or RAN entities to take part in the wireless sensing of a target, whereby the authorization may be provided based on location.
[PR 5.17.6-4]
The 5G system shall support a mechanism to provide wireless sensing capable UEs and RAN entities with information of which network entity to send the 3GPP sensing data to.