Content for TR 22.837 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.12…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
5.22…
5.23…
5.24…
5.25…
5.26…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
6…
7…
5.11 Use case on sensing at crossroads with/without obstacle
5.11.1 Description
5.11.2 Pre-conditions
5.11.3 Service Flows
5.11.4 Post Conditions
5.11.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality
5.11.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case
...
...
5.11 Use case on sensing at crossroads with/without obstacle p. 38
5.11.1 Description p. 38
The various ways of transportation (e.g. vehicles, walking people, motor vehicle, non-motor vehicle) and the dense buildings make the traffic condition complicated. Typically, traffic accidents often happen at the crossroads for example the pedestrians suddenly rush to the road from the invisible place (e.g., behind the high buildings, behind the tall trees), which cause an urgent need to monitor the real-time road status for all days, thus with the collaboration of trusted third-party e.g. map service provider or ITS management platform, driving warning or assistant driving information can be provide timely to vehicles.
The road status includes vehicle moving information, VRU (Vulnerable Road User) information (e.g. VRU location, VRU moving direction, VRU moving speed, etc.), abnormal vehicle behaviour, road obstacles and road condition.
The road status information can be sensed by the cameras and radars on RSU (Road Side Unit). But considering the crossroad condition is very complicated, there are always some blind points. 5G based sensing can provide sensing information to fill these gaps.
For example, it is expected that the base station can sense the surrounding environment e.g. the road, and send the 3GPP sensing data to the core network. The core network can carry out systematic calculation and analysis of the 3GPP sensing data for outputting the sensing result. Such sensing result can be sent to a trusted third-party e.g. map service provider for combination with navigation map data, so as to make the driver aware of the congestion and traffic accidents in advance, and effectively increase the comfort and safety of driving. The base station sensing operations could improve the real-time map service with high reliability and quality.
But in some cases of above, the obstacles (e.g., high buildings or trees) block the transmission of radio signals. The availability and accuracy of the sensing service for the target objects which are located in the area will be greatly impacted.
To guarantee sensing service in this area, multiple 5G system sensing entities can work together.
5.11.2 Pre-conditions p. 38
Network operator "VV" has released a sensing service for road status sensing and has deployed base stations especially at multiple crossroads to continuously sense the road status.
Due to the high buildings (e.g. Building A) near the crossroads, there are some areas with obstacles for 5G base stations. Some 5G system sensing entities are further deployed by the network operator 'VV' to help radio signal transmission and collect 3GPP sensing data.
Network operator "VV" has a collaboration with the ITS management department that the user who has registered the Network operator "VV"'s "road status sensing service" can receive real-time road status information, driving warning or assistant driving information from ITS management platform.
Bob has registered the road status sensing service from Network operator "VV".
Network operator "VV" can also deliver the real-time road information and the real time location/ trajectory of vehicles to a map service provider. The map service provider can provide "assisted driving service" based on this information.
Bob has a vehicle with the "assisted driving service" provided by the map service provider.
Bob drives the vehicle from home to the company in the morning of a working day.
5.11.3 Service Flows p. 39
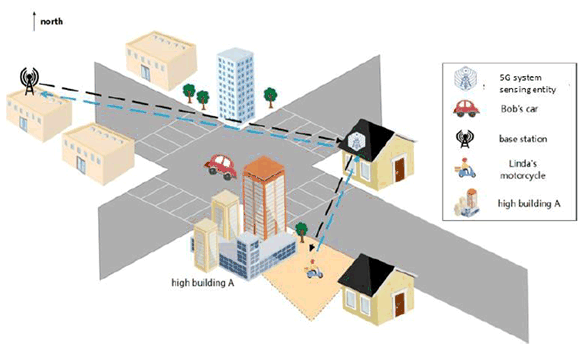
- The 5G base station continuously collects 3GPP sensing data of the road status and the sensing result is continuously reported to the trusted third-party (e.g. the map service provider or ITS management platform) by 5G network according to the preconfigured refresh rate (e.g. in the midnight, it uses slow refresh rate with 0.2Hz, and in the working day morning, it uses fast refresh rate with 10Hz). The refresh rate can be adjusted according to the trusted third-party demand and network operator's policy.
- In the working day morning, Bob has started his road status sensing service when he begins driving his vehicle to his office.
- Bob drives his vehicle from home to his office and started assisted driving service. The map service provider sends the road sensing request to the 3GPP core network.
- In the crossroad, there are some higher buildings. It is difficult for Bob to timely detect other vehicles and VRUs in the area. As example in Figure 5.11.3-1, Bob is driving his vehicle and crossing the crossroad toward the southeast of the crossroad. Linda is driving her motorcycle on a side road toward the main road which is also the southeast of the crossroad. The line of sight between Bob and Linda is blocked by the high building A which is at a corner of the intersection.
- Linda's motorcycle activity is continuously sensed by the base station under the help of other 5G system sensing entities.
- The 5G system collects and associates the multiple 3GPP sensing data from multiple base stations with the crossroad location. Considering the obstacles (e.g., high buildings or trees) in this area, it impacts the sensing quality and availability of the 3GPP sensing data from the blocked base stations. So, the 5G system needs to select suitable 3GPP sensing data to derive the sensing result to guarantee the availability of the sensing service.
- The motorcycle sensing result which includes the motorcycles moving speed, moving direction, position etc. is periodically reported to the the map service provider and ITS management platform.
- The other vehicles in the crossroad have been sensed and related sensing result are also reported to the map service provider and ITS management platform.
- The map service provider fuses the sensing result with the map and then sends to the Tom's vehicle.
- According to the continuously received motorcycle sensing results, the ITS management platform can analyze and identify that there will be a potential collision risk between Bob and Linda. The collision warning then is sent to Bob.
5.11.4 Post Conditions p. 40
Bob's vehicle receives the real-time map information which warns Bob that there is another cross-direction motorcycle driving towards his vehicle. Bob stops his vehicle before the crossroad to avoid a potential collision. With the assistance of RAN sensing, Bob arrives in the company safely and easily. Bob starts the daily work in the office.
Bob receives the warning and drives safely through the crossroads.
Linda can also ride safely to the crossroad. The potential risk of collision is avoided.
5.11.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality p. 40
None.
5.11.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case p. 40
[PR 5.11.6-1]
The 5G system shall be able to support a mechanism to provide available sensing service in a target sensing service area.
[PR 5.11.6-2]
The 5G RAN shall be able to collect 3GPP sensing data from requested target sensing service area according to the operator's policy.
[PR 5.11.6-3]
The 5G system shall be able to report the sensing result to the trusted third-party with refresh rate which is requested by the trusted third-party e.g. a map service provider, and controllable by the operator, according to a business agreement.
[PR 5.11.6-4]
The 5G system shall support means for a trusted third-party application, e.g. a map service provider to configure sensing per location.
[PR 5.11.6-5]
The 5G system shall be able to support the sensing service with given KPIs in Table 5.11.6-1.
| Scenario | Sensing service area | Confidence level [%] | Accuracy of positioning estimate by sensing (for a target confidence level) | Accuracy of velocity estimate by sensing (for a target confidence level) | Sensing resolution | Max sensing service latency[ms] | Refreshing rate [s] | Missed detection [%] | False alarm [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal
[m] |
Vertical [m] | Horizontal [m/s] | Vertical [m/s] | Range resolution [m] | Velocity resolution (horizontal/ vertical) [m/s x m/s] | |||||||
| Sensing at crossroads with/without obstacle | Outdoor | 95 | ≤1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ≤100
NOTE 2 | ≤ 0.1 | ≤5 | ≤5 |
|
NOTE 1:
The terms in Table 5.11.6-1 are found in clause 3.1.
NOTE 2:
The value is sourced from [28].
|
||||||||||||