Content for TR 22.837 Word version: 19.3.0
0…
4
5…
5.2…
5.3…
5.4…
5.5…
5.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.10…
5.11…
5.12…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15…
5.16…
5.17…
5.18…
5.19…
5.20…
5.21…
5.22…
5.23…
5.24…
5.25…
5.26…
5.27…
5.28…
5.29…
5.30…
5.31…
5.32…
6…
7…
5.14 Use case on sensing for tourist spot traffic management
5.14.1 Description
5.14.2 Pre-conditions
5.14.3 Service Flows
5.14.4 Post-conditions
5.14.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality
5.14.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case
...
...
5.14 Use case on sensing for tourist spot traffic management p. 48
5.14.1 Description p. 48
In order to ensure the sustainable development of tourist spots, the traffic flow management of tourist attractions should fully consider the space-carrying capacity, facility-carrying capacity, ecological-carrying capacity and other factors that may induce disasters within the area.
The scenic area controls the traffic flow through real-time monitoring, diversion of traffic and early warning and reporting. The flow control of tourist spots includes two aspects: passenger-flow management and vehicle-flow management.
Traffic data collection is an important part of traffic management. Base stations in tourist area can provide 5G communication service and also can sense the passenger and the vehicle in its coverage at gates or per unit area that are set with a finer granularity. For tourist spots with a large area, it will be convenient to use base station to have the traffic sensing data sources when it's difficult to deploy equipment like camera and other sensors.
5.14.2 Pre-conditions p. 48
Network Operator A provides 5G services for a famous tourist spot.
The management department of the tourist spot has subscribed the sensing service provided by 5G network Operator A, and the base stations in the tourist area can be used to sense the traffic flow and the crowd density (for both including the vehicles and passengers) constantly.
Jim is the worker of the tourist spot and responsible for traffic management.
5.14.3 Service Flows p. 48
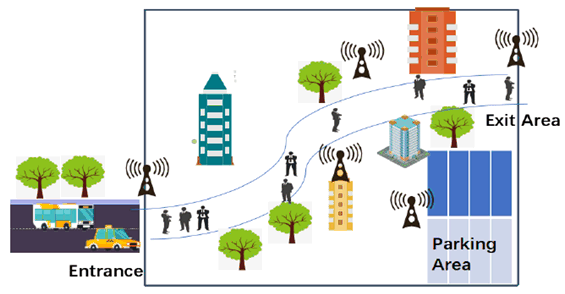
- When the scenic area begins to open, Jim will operate the scenic area traffic monitoring system to start real-time traffic control.
- The traffic management system of the scenic spot will send a service request to the operator network to start sensing the people and vehicles in the scenic spot.
- The base stations at the entrance and exit of the scenic spot can sense the people and vehicles that enter or leave the place, and the base stations in the scenic spot can sense the people and vehicles for certain area (e.g. walkway, parking area).
- Operator A reports the traffic sensing information from the base stations in the scenic spot to the traffic monitoring system. Based on the sensing information, the traffic management system could analyse the traffic status and decide whether the traffic in the area is congested.
- If the congestion exceeds the threshold, the management system would notice Jim about the detail, and Jim would trigger to limit traffic to avoid traffic overload in the scenic spot.
5.14.4 Post-conditions p. 49
With 5GS support to the traffic management system, the vehicles and tourists are controlled within a reasonable range, and the spot can operate normally during business hours.
5.14.5 Existing features partly or fully covering the use case functionality p. 49
None.
5.14.6 Potential New Requirements needed to support the use case p. 49
[PR 5.14.6-1]
The 5G system shall be able to provide means to use base station(s) to perform sensing in certain area.
[PR 5.14.6-2]
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to expose sensing results to a trusted third-party application.
[PR 5.14.6-3]
Subject to regulatory requirements and operator policy, the 5G system shall be able to support the activation and deactivation of the sensing service based on location.
[PR 5.14.6-4]
The 5G system shall be able to provide sensing service with KPIs given in Table 5.14.6-1.
| Scenario | Sensing service area | Confidence level [%] | Accuracy of positioning estimate by sensing (for a target confidence level) | Accuracy of velocity estimate by sensing (for a target confidence level) | Sensing resolution | Max sensing service latency [ms] | Refreshing rate [s] | Missed detection [%] | False alarm [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal
[m] |
Vertical [m] | Horizontal [m/s] | Vertical [m/s] | Range resolution [m] | Velocity resolution (horizontal/ vertical) [m/s x m/s] | |||||||
| Tourist spot traffic management | Outdoor | 95 | [≤2] | N/A | [1] | N/A | [1] | [1] | [≤5000] | [≤0.2] | ≤5
NOTE 2 | ≤5
NOTE 2 |
|
NOTE 1:
The terms in Table 5.14.6-1 are found in clause 3.1.
NOTE 2:
Missed detection or false alarm describes missing to acquire a sensing result or acquiring a wrong sensing result which referring to a target object (a person or a vehicle), in this use case will be missing detect a person or a vehicle, not referring to the number of a crowd of people or vehicles.
|
||||||||||||