Content for TR 26.928 Word version: 18.0.0
0…
4…
4.1.2…
4.2…
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.6…
4.6.7
4.7…
4.9…
5…
6…
7…
8
A…
A.4…
A.7…
A.10…
A.13
A.14
A.15
A.16
A.17
A.18…
A.16 Use Case 15: XR Meeting p. 110
| Use Case Name |
|---|
| XR Meeting |
| Description |
This use case is a mix of a physical and a virtual meeting. It is an XR extension of the virtual meeting place use case described in TR 26.918. The use case is exemplified as follows:
Company X organizes a workshop with discussions in a couple of smaller subgroups in a conference room, as for instance shown in the Figure below. Each subgroup gathers around dedicated spots or tables and discusses a certain topic and participants are free to move to the subgroup of their interest. Remote participation is enabled.
The main idea for the remote participants is to create a virtual, 3D-rendered space where they can meet and interact through their avatars with other people. This 3D-rendered virtual space is a simplified representation of the real conference room, with tables at the same positions as in the real world. Remote participants are equipped with HMD supporting binaural playback. A remote participant can move freely in the virtual conference room and interact with the different subgroups of people depending, for example, on the discussion they are having. A remote participant can speak to other participants in their immediate proximity and obtain a spatial audio rendering of what the other participants are saying. They can hear the real participants from their relative positions in the virtual world, and they can freely walk from one subgroup to another to seamlessly join different conversations that may happen concurrently in the meeting space. Consistent with the auditory scene, the remote participant will be able to see on the HMD a rendered "Scene view" of the complete virtual meeting space from their viewpoint, i.e. relative to position and viewing direction. As options, the remote participant may also select to see a "Top view" of the complete meeting space with all participants (or their avatars) or a "Table view". The latter is generated from a 360-degree video capture at the relevant table. The audio experience remains in any case as during "Scene view".
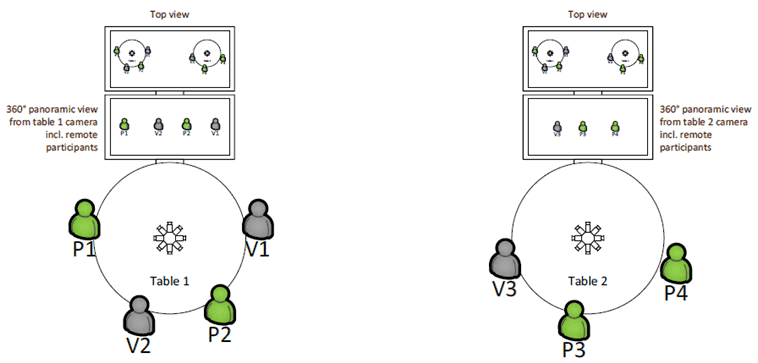
The physical participants see and hear avatars representing the remote participants through AR Glasses supporting binaural playback. They interact with the avatars in the discussions as if these were physically present participants. For physical participants, the interactions with other physical and virtual participants happen in an augmented reality. In addition, at each subgroup meeting spot, a video screen displays a 360-degree panoramic "Table view" taken from the middle of the respective table, including the overlaid avatars of the remote participants taking part in the subgroup discussion. Also displayed is the complete meeting space with all participants (or their avatars) in a top view.
A schematic of the configuration at the physical meeting space is shown in the following Figure. In that Figure, P1 through P4 represent the physical participants while V1 through V3 are the remote participants. Also shown are two subgroup meeting spots (tables), each with a 360-degree camera mounted on its center. Further, at each table the two video screens are shown for the 360-degree panoramic "Table view" and for the "Top view".
|
| Categorization |
|
Type:
AR, VR, XR
Degrees of Freedom:
6DoF
Delivery:
Interactive, Conversational
Device:
Phone, HMD with binaural playback support, AR Glasses with binaural playback support
|
| Preconditions |
On a general level the assumption is that all physical attendees (inside the meeting facilities) wear a device capable of binaural playback and, preferably, AR glasses. Remote participants are equipped with HMDs supporting binaural playback. The meeting facility is a large conference room with a number of spatially separated spots (tables) for subgroup discussions. Each of these spots is equipped with at least one video screen. At each of the spots a 360-degree camera system is installed.
Specific minimum preconditions
|
| Requirements and QoS/QoE Considerations |
QoS: conversational requirements as for MTSI, using RTP for Audio and Video transport.
|
| Feasibility |
Under "Preconditions" the minimum preconditions are detailed and broken down by all involved nodes of the service, such as remote participants, physical participants, meeting facilities and conference call server. In summary, the following capabilities and technologies are required:
|
| Potential Standardization Status and Needs |
|