Content for TS 23.542 Word version: 18.4.0
0…
5…
8…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.5.3…
8.5.4…
8.5.7…
8.5.8…
8.5.9…
8.5.10…
8.5.11…
8.5.12…
8.5.13…
8.5.14…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
A…
8.10 PIN Authorization
8.10.1 General
8.10.2 Procedure
8.10.2.1 General
8.10.2.2 PIN authorization with PIN server
8.10.3 Information flows
8.10.3.1 General
8.10.3.2 PIN authorization request
8.10.3.3 PIN authorization response
8.10 PIN Authorization p. 125
8.10.1 General p. 125
The PIN authorization procedure is used by a PINE, PEGC or PEMC to acquire security information needed to perform procedures with other functional entities (e.g., PIN Server, PEMC, PEGC) of the PIN. The security information is used by a PINE, PEGC or PEMC (e.g., a requestor) when performing procedures of clause 8 that require security credentials for request authorization. A PINE, PEGC or PEMC performs the PIN authorization procedure with the PIN server.
For deployments where a PIN server has CAPIF core function capabilities, and a PINE, PEGC, PEMC or AS have CAPIF API invoker capabilities, as defined in TS 23.222, security information may be obtained via CAPIF mechanisms as specified in TS 33.122.
8.10.2 Procedure p. 125
8.10.2.1 General p. 125
PIN authorization procedure is either performed directly with the PIN server or indirectly via the PEGC for PINE(s) that require support of the PEGC to access the PIN server; the PEGC can deliver the PIN authorization request of the PINE to the PIN server when needed.
8.10.2.2 PIN authorization with PIN server p. 125
Figure 8.10.2.2-1 illustrates PIN authorization procedure based on request/response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE/PEGC/PEMC has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g., IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The PINE/PEGC/PEMC has been pre-configured with the PIN identifier;
- The PIN server has been configured with the PIN profile;
- The requestor has been authenticated.
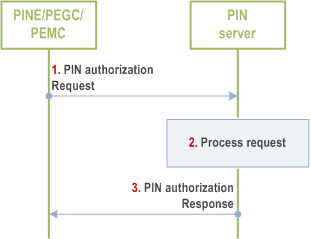
Step 1.
The PINE sends a PIN authorization request to the PIN server. The request includes the PIN identifier, and the requestor identifiers, name, description, and address.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the PIN server validates if the requestor is allowed to access the requested PIN using the information provided in the request and the PIN configuration information from the PIN profile.
Step 3.
The PIN server sends a PIN authorization response to the requestor. If the PIN server successfully determines that the requestor is allowed to access the PIN, the PIN server includes security information for the requestor to use within the PIN. If the PIN server fails to authorize the requestor, the PIN server indicates failure in the response and includes a failure reason.
8.10.3 Information flows p. 126
8.10.3.1 General p. 126
The following information flows are specified for PIN authorization:
- PIN authorization request and response.
8.10.3.2 PIN authorization request p. 126
Table 8.10.3.2-1 describes information elements in the PIN authorization request sent from the PINE or AS to the PIN server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifiers | M | The identifiers of the requestor (i.e., GPSI of the PINE, and PINE identifier or AS identifier).
See NOTE. |
| PIN identifier | M | Identifier of the PIN. |
| Requestor IP Address | O | The IP address of PINE or AS. |
|
NOTE:
If the PINE registration is accepted by PIN server, the PIN Server may use the PIN client ID provided in the PINE registration for authorization.
|
||
8.10.3.3 PIN authorization response p. 126
Table 8.10.3.3-1 describes information elements in the PIN authorization response sent to the PINE.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PIN authorization request was successful. |
| > Security information | M | The security information to be used by the requestor in PIN procedures. |
| Failure response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PIN authorization request failed. |
| > Cause | M | Provides the cause for PIN authorization request failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the IE shall be present.
|
||