Content for TS 23.542 Word version: 18.4.0
0…
5…
8…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.5.3…
8.5.4…
8.5.7…
8.5.8…
8.5.9…
8.5.10…
8.5.11…
8.5.12…
8.5.13…
8.5.14…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
A…
8.3 PIN server discovery
8.3.1 General
8.3.2 Procedure
8.3.2.1 Static PIN server discovery
8.3.2.2 Procedures of PIN server discovery via PEGC
8.3.3 Information flows
8.3.3.1 General
8.3.3.2 PIN server discovery request
8.3.3.3 PIN server discovery response
...
...
8.3 PIN server discovery p. 28
8.3.1 General p. 28
Some of the PIN management procedures involves the PIN server and hence the PINE requires the PIN server endpoint address before triggering the PIN management procedures, for example, the PIN creation procedure. Also there could be multiple PIN servers deployed within a PLMN and it is important to PIN elements to discover the appropriate PIN server to connect.
8.3.2 Procedure p. 28
8.3.2.1 Static PIN server discovery p. 28
The aim of PIN server discovery procedure is to receive one or more endpoint information (e.g. URI(s), FQDN(s), IP address(es)) of PIN server. And the PEMC, PEGC, PIN elements are all able to receive the PIN server endpoint information.
The PIN server can be discovered by the following method:
- pre-configured in the PIN elements or PIN clients;
- configured by the user;
- derived from HPLMN identifier for non-roaming scenario or from VPLMN identifier for roaming scenario.
- DNS query for PIN server.
8.3.2.2 Procedures of PIN server discovery via PEGC p. 29
Some of the PIN elements can have the application interaction towards the PEGC, for example, via WiFi or Bluetooth, and in these case the PEGC can provide the PIN server end point information to PIN elements.
For some of the PEGC, it has the open access capability to accept the application layer connection from the PIN elements.
Pre-conditions:
- The PIN elements or PIN client has application layer connection with PEGC;
- The UE Identifier or PIN client Identifier is available;
- The PEGC supports the open access and can reroute the request from PINE to PEMC behind the PEGC;
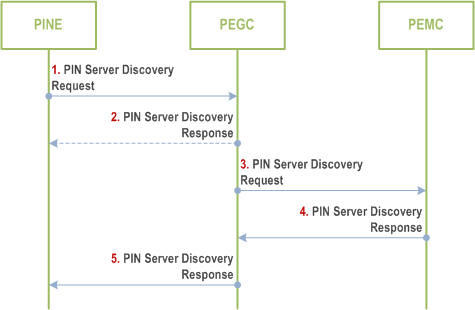
Step 1.
The PINE sends PIN server discovery request to PEGC. The requests include the GPSI, MAC address, if has, UE location.
Step 2.
(Optional) The PEGC can directly deliver the PIN server discovery response to PINE, including PIN server end point information to PIN elements. The end point information of PIN server includes URI(s), FQDN(s), IP address(es)) of PIN server.
Step 3.
If the PINE has open access to PEGC, that the PEGC should route the PIN server discovery request to PEMC that behind the PEGC.
Step 4-5.
The PEMC delivers the PIN server discovery response to PEGC and the PEGC routes the response to PINE, including PIN server end point information to PIN elements. The end point information of PIN server includes URI(s), FQDN(s), IP address(es)) of PIN server.
8.3.3 Information flows p. 30
8.3.3.1 General p. 30
The following information flows are specified for PIN creation:
- PIN server discovery request and response;
8.3.3.2 PIN server discovery request p. 30
Table 8.3.3.2-1 describes information elements in the PIN server discovery request from the PINE to the PEGC/PEMC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE Identifier | M | The identifier of the hosting UE (i.e. GPSI or identity token) or PINE. |
| MAC address | O | MAC address of the device. |
| UE location | O | The location information of the UE. The UE location is described in clause 7.2.7. |
8.3.3.3 PIN server discovery response p. 30
Table 8.3.3.3-1 describes information elements in the PIN server discovery response from the PEGC/PEMC to the PINE.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PIN server discovery request was successful. |
| > PIN server endpoint information | M | Includes URI(s), FQDN(s), IP address(es)) of PIN server. |
| Failure response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PIN server discovery request failed. |
| > Cause | M | Provides the cause for PIN server discovery request failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the IE shall be present.
|
||