Content for TS 23.542 Word version: 18.4.0
0…
5…
8…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.5.3…
8.5.4…
8.5.7…
8.5.8…
8.5.9…
8.5.10…
8.5.11…
8.5.12…
8.5.13…
8.5.14…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
A…
8.5.10 PIN modification
8.5.10.1 General
8.5.10.2 Procedures
8.5.10.2.1 General
8.5.10.2.2 PIN modification after local PEMC failure
8.5.10.2.3 PIN modification with PEGC role change
8.5.10.2.4 PEMC replacement triggered internally within the PIN
8.5.10.2.5 PEGC replacement triggered by PEMC
8.5.10.3 Information flows
8.5.10.3.1 General
8.5.10.3.2 PIN configuration request
8.5.10.3.3 PIN configuration response
8.5.10.3.4 PIN management request
8.5.10.3.5 PIN management response
8.5.10.3.6 PIN PEMC role takeover request
8.5.10.3.7 PIN PEMC role takeover response
8.5.10.3.8 PIN PEGC role takeover request
8.5.10.3.9 PIN PEGC role takeover response
...
...
8.5.10 PIN modification p. 68
8.5.10.1 General p. 68
This clause describes PIN modification functionality.
8.5.10.2 Procedures p. 68
8.5.10.2.1 General p. 68
8.5.10.2.2 PIN modification after local PEMC failure p. 68
Figure 8.5.10.2.2-1 describes the PIN modification procedure to perform a PEMC role change due to the failure of the PEMC. An authorised administrator is the owner of the PIN and accesses PIN configuration using an application on a UE, which is one of the PEMC for the PIN. The authorised administrator can manage the PIN locally or through the 5G network. This procedure describes a PEMC (e.g., an authorized administrator on a UE) managing the PIN remotely via the 5G network.
The procedure may be used e.g. when a PEMC is available on a UE for PIN management by an authorised administrator. When there is a local PEMC failure, the authorized administrator can be enabled to manage the PIN remotely, via the 5G network, using the following steps.
Pre-conditions:
- The PIN server has authorized the creation of the PIN.
- The authorized administrator is the owner of the PIN and has created the PIN.
- The authorized administrator configures the active PEMC to provide PIN management for the PIN. UE/PEMC1 is the inactive PEMC.
- The active PEMC, PEGC, PINE-1, PINE-2, and the UE/PEMC1 are members of the PIN. PINE-1 has PEMC capability.
- The authorized administrator leaves the local area of the PIN (e.g., in a home) and is able to access the PIN remotely through the 5G network. As a result, the authorized administrator is able to manage the PIN through the 5G network.
- The UE/PEMC1 is subscribed to the PEGC for PIN connectivity notifications
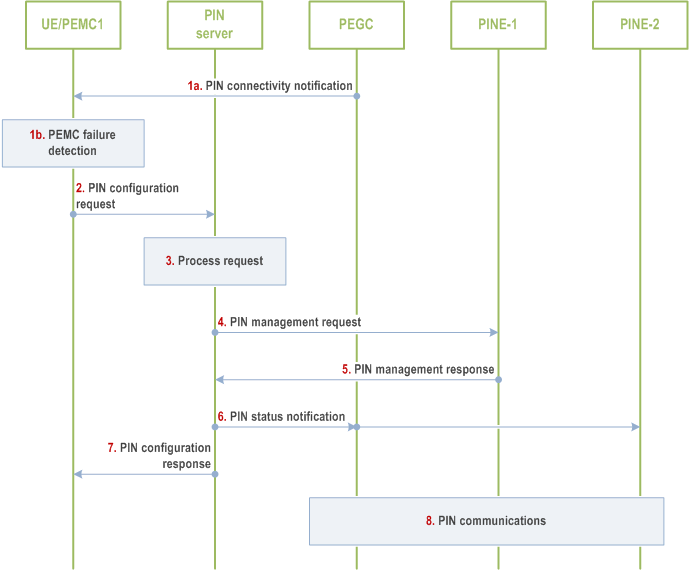
Step 1.
The UE/PEMC1 may detect that PEMC2 is unavailable or failed. In step 1a, the UE/PEMC1 may receive a PIN connectivity notification from PEGC indicating that there is a communication failure with PEMC2. Otherwise, in step 1b, the UE/PEMC1 may detect that PEMC2 is unavailable by using the PIN heartbeat mechanism or if a communication timeout happens with PEMC2.
Step 2.
If UE/PEMC1 has detected that PEMC2 is unavailable or failed in step 1, an authorized administrator on UE/PEMC1 sends a PIN configuration request to the PIN server through the 5G network. The request includes the security credentials of the authorized administrator, the UE ID, the PIN ID, PIN member ID, authorization type indicating the role change (e.g., the request may indicate that PINE-1 be assigned the new PEMC).
Step 3.
If the PIN Server has received a PIN Configuration request in step 2, the PIN server processes the modification request and checks if the authorized administrator is allowed to modify the PIN. The PIN server verifies that PINE-1 has the capability to serve as a PEMC using information in the PIN profile.
Step 4.
If the authorized administrator is allowed to perform PIN modification or if the PIN Server has detected that PEMC2 is unavailable or failed and has determined that PINE-1 can be reassigned as the new PEMC, the PIN server sends a PIN management request to PINE-1 to assign PINE-1 as the new PEMC and provides PIN profile information to PINE-1.
Step 5.
PINE-1 processes the PIN management request indicating the PEMC assignment and a PIN management response to the PIN server indicating if the assignment was successful.
Step 6.
If the PIN management response in step 5 was successful, the PIN server notifies the other members of the PIN that PINE-1 will be the new PEMC for the PIN and updates PIN profile information.
Step 7.
If the PIN Server has received a PIN Configuration request in step 2, the PIN server sends a PIN configuration response to the UE/PEMC1, the response includes the updated PIN profile information if the PEGC assignment was successful; otherwise, the response indicates that the assignment failed.
Step 8.
If the PEGC assignment was successful, the PIN communications resume with PINE-1 serving as the new PEMC.
8.5.10.2.3 PIN modification with PEGC role change p. 70
Figure 8.5.10.2.3-1 describes a PIN modification procedure to perform a PEGC role change due to the unavailability of the PEGC. This procedure describes a PEMC detecting the unavailability of a PEGC (e.g. PEGC leaves the local service area of the PIN) and performing a PIN modification with the PIN Server to assign a new PEGC. As part of PIN management, a PEMC receives periodic PIN heartbeat messages from PEGCs to ensure PIN routing is available for members of the PIN at all times. If a PEMC does not receive the periodic PIN heartbeat messages from the PEGC, then the PEMC needs to assign a new PEGC or request the PIN server to assign the new PEGC.
Pre-conditions:
- The PIN server has authorized the PEMC to create PINs.
- The PEMC creates a local PIN with members: PEMC, UE serving as PEGC, PINE1, and PINE2.
- The PEMC maintains a PIN profile with information on the capabilities of each PIN member.
- PINE2 is a PIN member that also has gateway capability.
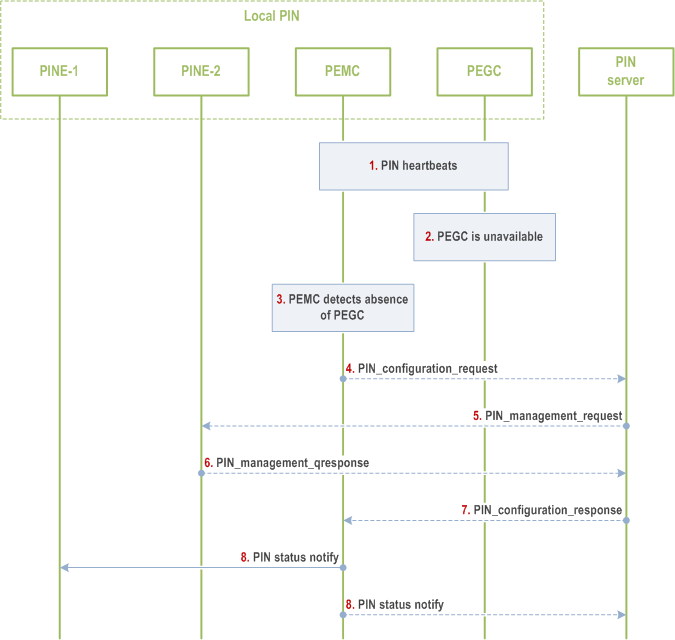
Step 1.
PEMC receives periodic PIN heartbeats from PEGC to monitor the availability of the PEGC.
Step 2.
PEGC leaves the local coverage area of the PIN, e.g., leaves the home, and is not available to route PIN communications.
Step 3.
PEMC does not receive a periodic PIN heartbeat from PEGC at the configured interval and determines that PEGC is no longer providing PIN routing capability.
If secondary PEGC is available in PEMC, that the PEMC decides to configure this PEGC as the gateway of PIN, and skip the procedure from step 4 to step 7. And PEMC only notifies PIN server of newly selected PEGC in step 8.
If secondary PEGC is unavailable in PEMC, that the PEMC decides to trigger the PIN server to discover the PEGC as the gateway of PIN from step 4 to step 7. And PEMC only notifies PINE in this PIN of newly selected PEGC in step 8.
Step 4.
PEMC sends a PIN configuration request to the PIN server to select a new PEGC. The request includes the PIN ID, the PEMC ID, the PEGC ID, authorization type indicating the role change, the ID of a PIN member that can serve as the new PEGC (e.g., PINE2), and a timestamp.
Step 5.
The PIN server considers which member of the PIN can serve as the new PEGC, including the PIN member the PEMC provided, and selects a PIN member to serve as the new PEGC. The PIN server sends a PIN management request to PINE-2 with PIN profile and dynamic profile information. The dynamic profile information includes PIN traffic routing rules that PINE2 would need to make routing decisions.
Step 6.
PINE-2 sends a PIN management response accepting to serve as the new PEGC.
Step 7.
The PIN server sends a PIN configuration response with PIN profile and dynamic profile information to the PEMC with the status of the request, the ID of the new PEGC, and PIN traffic routing rules. The PIN server response triggers the PEMC to notify other PIN members of the PEGC role change.
Step 8.
PEMC notifies the PIN server or other members of the PIN that PINE2 will serve as the new PEGC. The PEMC includes PIN profile and dynamic profile information that includes traffic routing rules applicable to each member.
8.5.10.2.4 PEMC replacement triggered internally within the PIN p. 71
A PIN element could have been authorized to act as PEMC for a certain duration after which it is either removed from the PIN or de-authorized to act as PEMC. Another PIN element in the PIN takes over the role of PEMC.
When the duration of its role as PEMC is expiring or for some other reasons (implementation specific) the current PEMC requests another PINE to take the role of PEMC. Once the role assignment succeeds, the PIN server and other PIN elements including PEGC are notified of this role change.
Figure 8.5.10.2.4-1 illustrates PEMC replacement procedure triggered internally within the PIN by current PEMC.
Pre-conditions:
- PEMC-2 PIN element has already indicated that it can act as PEMC during the registration process.
- Dynamic profile information about the PIN is available at the current PEMC and PIN server
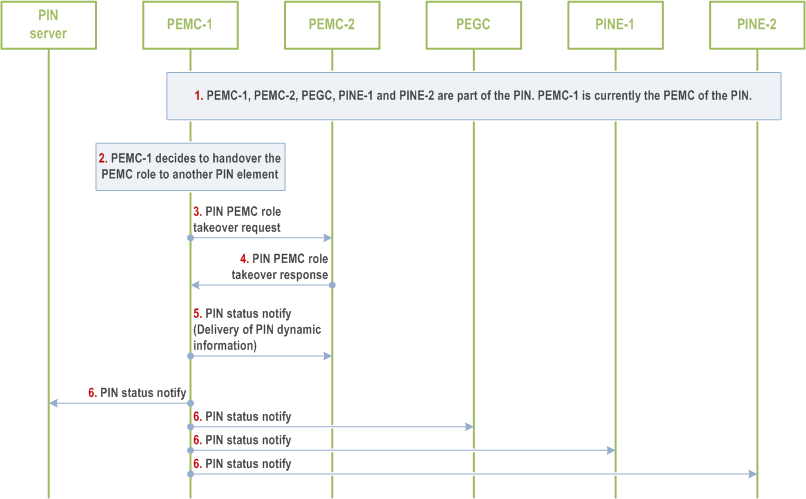
Step 1.
PEMC-1, PEMC-2, PEGC, PINE-1 and PINE-2 are part of same PIN. PEMC-1 is currently the PEMC of the PIN.
Step 2.
PEMC-1 decides to relinquish its PEMC role and handover to another PIN element. It may decide if it detects that its UE power is draining or its role as PEMC is nearing expiry.
Step 3.
The PEMC-1 looks into the PIN dynamic profile information to identify the new PINE which can take up the role of PEMC (here PEMC-2 PIN element) and requests PEMC-2 to take the role of PEMC by sending PIN PEMC role takeover request which includes the PIN identifier, PIN element identifier of PEMC-2.
Step 4.
If the PEMC-2 PINE decides to take up the role of PEMC it sends the PIN PEMC role takeover success response to the PEMC-1.
Step 5.
The PEMC-1 updates the PIN dynamic profile information with this role change details and delivers the PIN dynamic profile information to the PEMC-2 by consuming PIN status notify message.
Step 6.
The PEMC-1 signals all the PINEs in the PIN including the PEGC and PIN server about the change in the PIN element acting as PEMC and its reachability information by sending PIN status notify message. On receiving this notification PIN server and PEGC updates the PIN dynamic profile information with the details of PEMC-2.
8.5.10.2.5 PEGC replacement triggered by PEMC p. 72
In some scenarios, like hardware failure, crash or power drain, the current PEGC may not be in a position to indicate to the PIN server or request the PIN server to assign the role of PEGC to another PIN element. In these cases, the PEMC on detecting the unavailability of the PIN element acting as PEGC, need to assign the PEGC role to another PINE and deliver the PIN dynamic information to the new PEGC.
Figure 8.5.10.2.5-1 illustrates PEGC replacement procedure triggered by PEMC on detecting current PEGC is unavailable or PEGC role change is required.
Pre-conditions:
- PEGC-2 PIN element has already indicated that it can act as PEGC during the registration process.
- Dynamic information about the PIN is available at the PEMC.
- PIN has only one PIN element configured with the role of PEGC.
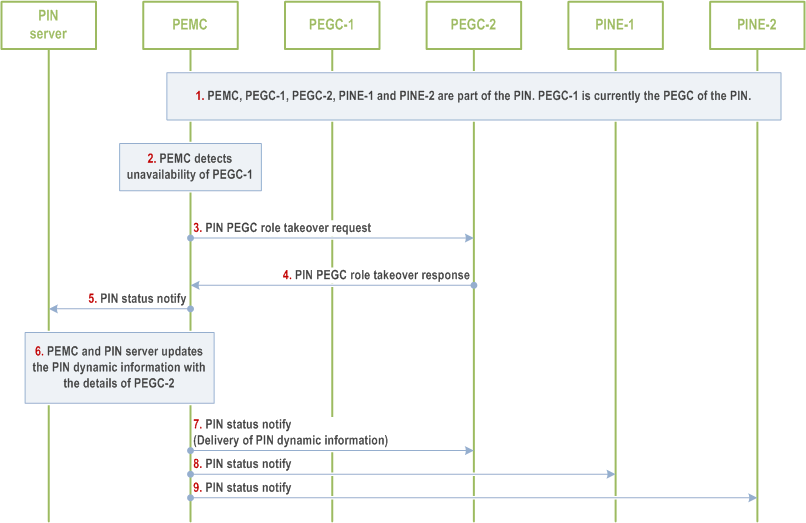
Step 1.
PEMC, PEGC-1, PEGC-2, PINE-1 and PINE-2 are part of same PIN. PEGC-1 is currently the PEGC of the PIN.
Step 2.
The PEMC identifies that it is no longer receiving periodic PIN heartbeats from PEGC-1 or its duration to act as PEGC is ending.
Step 3.
The PEMC looks into the PIN profile and PIN dynamic information to identify the new PINE which can take up the role of PEGC (here PEGC-2 PIN element) and requests PEGC-2 to take the role of PEGC by sending PIN PEGC role takeover request and this request includes the PIN Element ID of PEGC-2, PIN identifier and time duration to act as PEGC etc.
Step 4.
If the PEGC-2 PINE decides to take up the role of PEGC it sends the success PIN PEGC role takeover response to the PEMC.
Step 5.
The PEMC notifies the PIN server that PEGC-2 is the new PEGC of the PIN and it is releasing PEGC-1 from its role as PEGC by sending PIN status notification request containing the required details.
Step 6.
The PEMC and PIN server updates the PIN dynamic information with the relevant details of PEGC-2.
Step 7.
The PEMC delivers the PIN dynamic information to the PEGC-2 by consuming PIN status notify message.
Step 8.
The PEMC sends PIN status notify message to notify the relevant PINEs in the PIN about the change in the PIN element acting as PEGC and its reachability information.
8.5.10.3 Information flows p. 73
8.5.10.3.1 General p. 73
Void.
8.5.10.3.2 PIN configuration request p. 73
Table 8.5.10.3.2-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN configuration request sent by a PIN Element to the PIN server to obtain authorization for the modification of a PIN.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Requester PINE ID | M | The identifier of the PIN Element making the request. |
| Authorization type | M | Request for the authorization to modify the configuration of a PIN: PEMC role change, PEGC role change. |
| PINE ID of predecessor in the role | M | PINE ID of the element serving in the indicated role and needs to be changed e.g. due to being unavailable. |
| PINE ID of proposed successor in the role | O | PINE ID of the element proposed to assume the role. |
| Additional PEMCs | O | Indicate additional PEMCs (with identifier of PEMC) that are requested to manage the PIN. |
8.5.10.3.3 PIN configuration response p. 73
Table 8.5.10.3.3-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN configuration response provided by the PIN server to authorize the modification of a PIN.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Response | M | The response (authorize or not authorize) from the PIN Server. |
| PIN profile information | M | The IEs from the PIN profile information that the PIN Server has updated for modifying the PIN. |
| Dynamic PIN profile information | M | The IEs from the dynamic PIN profile information that the PIN Server has authorized for modifying the PIN. |
| Additional PEMCs | O | Indicate additional PEMCs (with identifier of PEMC) that are allowed to manage the PIN. |
8.5.10.3.4 PIN management request p. 74
Table 8.5.10.3.4-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN management request sent to PIN elements to make changes to the configuration of the PIN.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the PIN Server or PIN Element making the request. |
| Modification type | M | Request for the modification of the PIN: PEMC assignment, PEGC assignment. |
| Dynamic PIN profile information | M | IEs from the dynamic PIN profile information that the PINE needs to operate in the new role. |
8.5.10.3.5 PIN management response p. 74
Table 8.5.10.3.5-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN management response received from the PIN element to the PIN modification request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Response | M | The response (accept or deny) from the PIN Element to the PIN management request. |
8.5.10.3.6 PIN PEMC role takeover request p. 74
Table 8.5.10.3.6-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN PEMC role takeover request sent from current PEMC of the PIN to another PIN element with PEMC capability.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Current PEMC identifier | M | The identifier of the current PEMC making the request. |
| New PEMC identifier | M | The identifier of the new PIN element requested to take the role of PEMC. |
8.5.10.3.7 PIN PEMC role takeover response p. 74
Table 8.5.10.3.7-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN PEMC role takeover response sent from requested PIN element to the current PEMC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Success response (see NOTE) | O | Indicates that PEMC role takeover request is successful. |
| Failure response (see NOTE) | O | Indicates that PEMC role takeover request is failure. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the reason for the failure. |
|
NOTE:
Only one of the IE is included in the response
|
||
8.5.10.3.8 PIN PEGC role takeover request p. 75
Table 8.5.10.3.8-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN PEGC role takeover request sent from current PEMC of the PIN to another PIN element with PEGC capability.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Current PEMC identifier | M | The identifier of the current PEMC making the request. |
| New PEGC identifier | M | The identifier of the new PIN element requested to take the role of PEGC. |
8.5.10.3.9 PIN PEGC role takeover response p. 75
Table 8.5.10.3.9-1 shows the informational elements of the PIN PEGC role takeover response sent from requested PIN element to the current PEMC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | The identifier of the PIN. |
| Success response (see NOTE) | O | Indicates that PEGC role takeover request is successful. |
| Failure response (see NOTE) | O | Indicates that PEGC role takeover request is failure. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the reason for the failure. |
|
NOTE:
Only one of the IE is included in the response.
|
||