Content for TS 23.542 Word version: 18.4.0
0…
5…
8…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.5.3…
8.5.4…
8.5.7…
8.5.8…
8.5.9…
8.5.10…
8.5.11…
8.5.12…
8.5.13…
8.5.14…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
A…
8.4 Registration
8.4.1 General
8.4.2 Registration Procedure
8.4.2.1 General
8.4.2.2 Procedure
8.4.2.2.1 PINE registration directly to PIN server
8.4.2.2.2 PINE registration indirectly to PIN server
8.4.2.2.3 PINE registration via PEGC before join
8.4.2.2.4 PINE registration during the PIN join via the PEGC
8.4.2.2.5 PINE de-registration directly to PIN server
8.4.2.2.6 PINE de-registration indirectly to PIN server
8.4.2.2.7 PINE update registration to PIN server
8.4.2.3 Information flow/elements
8.4.2.3.1 General
8.4.2.3.2 PINE Registration request
8.4.2.3.3 PINE Registration response
8.4.2.3.4 PINE de-registration request
8.4.2.3.5 PINE de-registration response
8.4.2.3.6 PINE update registration request
8.4.2.3.7 PINE update registration response
...
...
8.4 Registration p. 30
8.4.1 General p. 30
The PINE (including PEMC and PEGC) should have a registration procedure in PIN server, before consuming the certain PIN service.
The registration procedure includes the direct registration and indirect registration.
-
Direct registration:
- For the PEMC, the PEMC sends PINE Registration Request (MAC address, vendor name, device description, PEMC Address) to the PIN server. After successful registration in PIN server, the PIN server allocates the PIN client ID to this PEMC and the PEMC receives the role of PEMC.
- The PINE can also directly register to the PIN server via the PEGC, if the PEMC/PIN server has already provided the PIN server address to the PINE. And if the PINE is accessing the PEGC without any registration and authorization, the PEGC may reject the message from the PINE and request the PINE to perform the registration.
-
Indirect registration:
- For the PINE and PEGC, the PEMC substitutes the PINE/PEGC to register on PIN server with the device metadata from PINE/PEGC (MAC address, vendor name, device description, PINE/PEGC Address). After successful registration in PIN server, the PIN server allocates the PIN client ID to PINE/PEGC.
8.4.2 Registration Procedure p. 31
8.4.2.1 General p. 31
The PINE may register to the PIN server via either the PEMC or the PEGC depends on the communication range, supported RATs.
8.4.2.2 Procedure p. 31
8.4.2.2.1 PINE registration directly to PIN server p. 31
Figure 8.4.2.2.1-1 illustrates PIN registration procedure based on request/response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The UE Identifier is available;
- The PINE has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
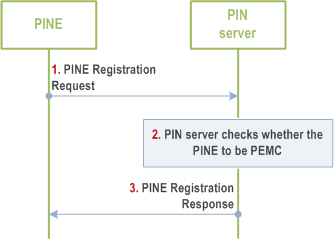
Step 1.
The PINE (including PINE/PEMC/PEGC) sends a PINE Registration Request to the PIN server. The request includes the security credentials of the PINE received during authorization procedure and also the request may include the GPSI, MAC address, vendor name, device description, PINE Address.
If the PEMC trigger the request, this registration request carries the PIN ID of the PIN for which it is intending to register as PEMC and the PIN element may indicate whether it is to be assigned with primary or secondary PEMC role.
Step 2.
The PIN server checks whether the UE identified by the GPSI has subscribed to be a PEMC. Also, the PIN server can check the whether the UE identified by the GPSI has subscribed to be a PEMC itself. If subscribed, it checks the subscription of PINE whether the requesting PIN element can be assigned with primary or secondary role and authorize the PIN element accordingly. In case if the PIN has already been created, the requesting PIN element is assigned with the secondary PEMC role irrespective of the role requested by the PIN element.
Step 3.
The PIN server responds to the PINE with PINE Registration Response with allocated PIN client ID in successful response.
If the registration procedure fails, the PIN server should give the failure response that indicates the cause of registration request failure.
8.4.2.2.2 PINE registration indirectly to PIN server p. 32
The following procedure defines the PEMC can substitute the PINE/PEGC to register into PIN server.
Pre-conditions:
- The PEMC has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The UE Identifier or PIN client Identifier is available;
- The PEMC has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
- The PINE/PEGC has already received the IP address of PEMC.
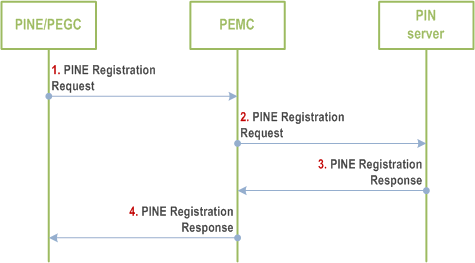
Step 1.
The PINE/PEGC sends PINE Registration Request to the PEMC. The request includes the security credentials of the PINE received during authorization procedure and also the request may include the GPSI, MAC address, vendor name, device description, PINE Address.
Step 2.
If the PEMC receives the PINE Registration Request from PINE, the PEMC may represent the PINE to register into PIN server by sending the PINE registration request to PIN server.
If the PEMC represents the PINEs to perform registration procedure, it should send a PINE Registration Request to PIN server including an Indication of representation registration and Lists of PINEs/PEGCs.
Step 3.
The PIN server responds to the PEMC with PINE Registration Response with allocated PIN client ID in successful response.
When the PINE Registration Request that containing Indication of representation registration, the PIN server shall verify whether PINE(s) and PEGC(s) included in the List of PINEs/PEGCs are allowed to fullfill the requested role or not. The PIN server responses to PEMC with a successful response and may include a list of accepted registration information and a list of rejected registration information (if any). If all the PINEs in the Lists of PINEs/PEGCs are rejected, the PIN server sends a failure response including the failure cause.
Step 4.
The PEMC sends the response received in step 3 to the PINE/PEGC.
When the PEMC receiving the PINE Registration response from PIN server, the PEMC should extract the accepted registration information and rejected registration information (if any) for all the PINEs, and send the result to each PINE in the Lists of PINEs/PEGCs.
8.4.2.2.3 PINE registration via PEGC before join p. 32
The PINE registration towards the PIN server via the PEGC based on request/response model is depicted in Figure 8.4.2.2.3-1.
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The PINE already establishes the connection with PEGC;
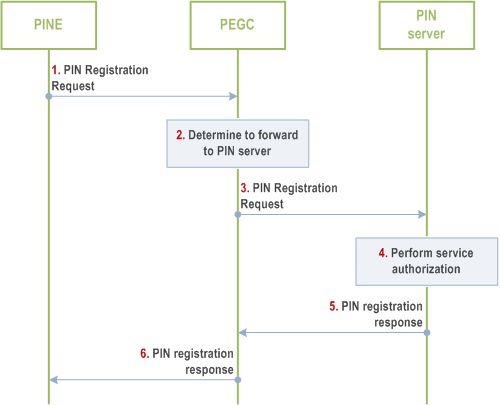
Step 1.
The PINE sends PIN registration request to the PIN server. The PIN registration request is routed to the PEGC. The PINE device identity, device credentials and other necessary formation which is also needed for PIN service authorization are included.
Step 2.
The PEGC identifies the received message is the PIN registration request which is allowed to be forwarded regardless the PINE is authorized or not.
Step 3.
The PEGC forwards the PIN registration request towards the PIN server.
Step 4.
The PIN server performs service authorization and verifies the PINE device with the information in the registration request. If authorized, the PIN server allocates the PIN client ID, authorization and security credentials for the PINE.
Step 5.
The PINE server returns the PIN registration response to the PEGC.
Step 6.
The PEGC forwards the PIN registration response to the PINE.
8.4.2.2.4 PINE registration during the PIN join via the PEGC p. 33
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The PINE already establishes the connection with PEGC;
- The PINE may get the PIN information from the PEMC, PEGC via PIN announcement after connecting to PEMC or PEGC.
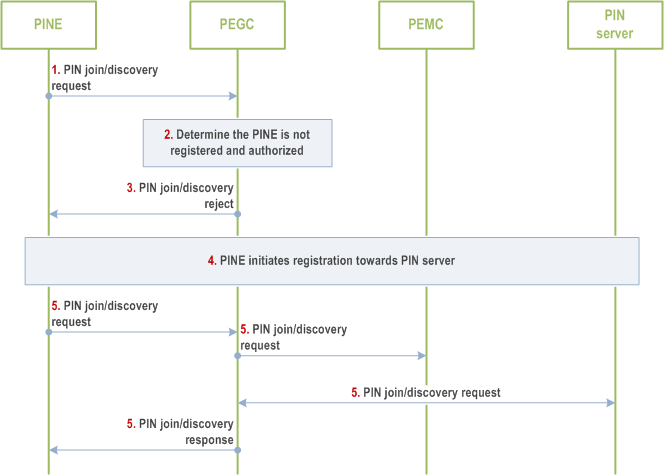
Step 1.
The PINE sends PIN join/discovery request to the PEGC. The PINE device identity is included.
Step 2.
- For the PIN join request, the PIN ID is included.
- For the PIN discovery request, the discovery criteria are included.
The PEGC identifies the received message is the PIN join/discovery request, and the PINE is not registered and authorized due to no PIN client ID and credentials in the message.
Step 3.
The PEGC returns the PIN join/discovery reject message to the PINE. The registration and authorization indication are also included to instruct the PINE to perform registration.
Step 4.
The PINE if not registered, initiates the PIN registration towards the PIN server via the PEGC as described in clause 8.4.2.2.1.
Step 5-6.
After the registration, the PINE will use the PIN client ID and credentials to initiate the PIN join/discovery again.
8.4.2.2.5 PINE de-registration directly to PIN server p. 34
Figure 8.4.2.2.5-1 illustrates PIN de-registration procedure based on request/response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server and is already registered with the PIN server;
- The UE Identifier is available;
- The PINE has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
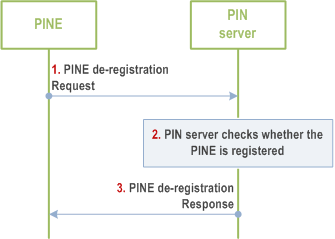
Step 1.
The PINE (including PINE/PEMC/PEGC) sends a PINE de-registration Request to the PIN server. The request includes the security credentials of the PINE received during authorization procedure and also the request may include the GPSI, MAC address, vendor name, device description, PIN element ID/PIN client ID, PINE Address.
Step 2.
The PIN server checks whether the UE identified by the GPSI has active registration with the PIN server.
Step 3.
The PIN server responds to the PINE with PINE de-registration response which contains the status of the PINE de-registration request. If the PINE is successfully de-registered, the PIN server deletes all the configuration information it has related to the PIN element that is being de-registered. If the de-registration procedure fails, the PIN server should give the failure response to indicates that indicates the cause of de-registration request failure.
8.4.2.2.6 PINE de-registration indirectly to PIN server p. 35
Figure 8.4.2.2.6-1 illustrates PINE De-registration request to PIN Server indirectly via PEMC based on request/response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The PEMC has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The UE Identifier or PIN client Identifier is available;
- The PEMC has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
- The PINE/PEGC has already received the IP address of PEMC.
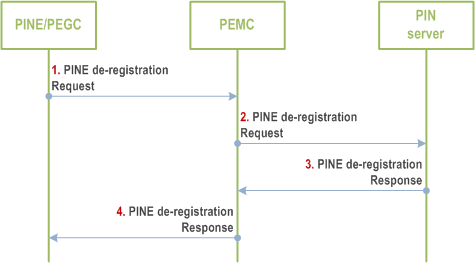
Step 1.
The PINE (including PINE/PEMC/PEGC) sends a PINE de-registration Request to the PEMC. The request includes the security credentials of the PINE received during authorization procedure and also the request may include the GPSI, MAC address, vendor name, device description, PIN element ID/PIN client ID, PIN ID, PINE Address.
Step 2.
The PEMC sends the PINE de-registration request to PIN server.
Step 3.
The PIN server checks whether the UE identified by the GPSI has active registration with the PIN server. The PIN server responds to the PINE with PINE de-registration response which contains the status of the PINE de-registration request. If the PINE is successfully de-registered, the PIN server deletes all the configuration information it has related to the PIN element that is being de-registered. If the de-registration procedure fails, the PIN server should give the failure response that indicates the cause of de-registration request failure.
Step 4.
The PEMC sends the response received in step 3 to the PINE/PEGC.
8.4.2.2.7 PINE update registration to PIN server p. 36
Figure 8.4.2.2.7-1 illustrates PIN update registration procedure based on request/response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The PINE has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server and is already registered with the PIN server;
- The UE Identifier is available;
- The PINE has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
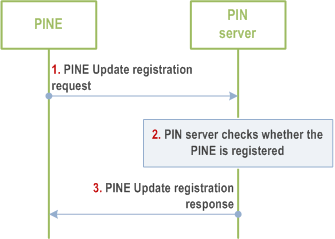
Step 1.
The PINE (including PINE/PEMC/PEGC) sends a PINE update registration request to the PIN server directly or via PEGC. The request includes the security credentials of the PINE received during authorization procedure and also the request may include the GPSI, MAC address, vendor name, device description, PIN element ID/PIN client ID, PINE Address.
If the registration request is sent from PINE to PEGC, the PEGC delivers the PINE update registration request to the PIN server.
Step 2.
The PIN server checks whether the UE identified by the GPSI has active registration with the PIN server.
Step 3.
The PIN server responds to the PINE with PINE update registration response directly or via PEGC which contains the status of the PINE update registration request. If the update registration procedure fails, the PIN server should give the failure response to indicates that indicates the cause of update registration request failure.
8.4.2.3 Information flow/elements p. 37
8.4.2.3.1 General p. 37
The following information flows are specified for PIN registration:
- PINE Registration request and response;
8.4.2.3.2 PINE Registration request p. 37
Table 8.4.2.3.2-1 describes information elements in the PINE Registration request from the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs) to the PIN server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE Identifier | M | The identifier of the hosting UE (i.e. GPSI or identity token) of PINE/ PEMC/PEGC. |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the PIN service. |
| Indication of representation registration | O | If PEMC represents PINE/PEGC to perform registration to PIN server, this indication is included. |
| Lists of PINEs/PEGCs | ||
| > MAC address | O | MAC address of the requested PINEs. |
| > Vendor name | O | The vendor name of the PINE. |
| > Device description | O | Description of the device. |
| > PINE Address | M | The IP address of PINE, if available. |
| > Port number | M | Port number of PIN client on PINE/PEMC/PEGC to support PIN enabler layer communication. The port number is the port used by a PINE to expose a service within the PIN. |
| > PINE Capabilities | O | Identify whether the PINE is capable of becoming a PEMC, a PEGC or both. |
| > > Maximum number of PINEs (see NOTE) | O | Indicates the maximum number of PINE that can be managed by the PEMC or PEGC. |
| Services that PINE provide | O | Indicate the service that PINE can provide. |
|
NOTE:
Only present if PINE Capabilities is present.
|
||
8.4.2.3.3 PINE Registration response p. 37
Table 8.4.2.3.3-1 describes information elements in the PINE Registration response from the PIN server to the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PINE Registration request was successful. |
| > PIN client ID | M | Identifier of the newly assigned PIN client ID to PINEs. |
| > Role of PEMC | O | The UE identified by the GPSI has subscribed to be a PEMC. |
| > Role of PEGC | O | The UE identified by the GPSI has subscribed to be a PEGC. |
| Failure response | O
(see NOTE) | Indicates that the PIN registration request failed. |
| > Cause | M | Provides the cause for PIN registration request failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the IE shall be present.
|
||
8.4.2.3.4 PINE de-registration request p. 38
Table 8.4.2.3.4-1 describes information elements in the PINE de-registration request from the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs) to the PIN server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE Identifier | M | The identifier of the hosting UE (i.e. GPSI or identity token) of PINE/PEMC/PEGC. |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the PIN service. |
| MAC address | O | MAC address of the requested PINEs. |
| Vendor name | O | The vendor name of the PINE. |
| Device description | O | Give the description of the device. |
| PINE Address | O | The IP address of PINE, if available. |
8.4.2.3.5 PINE de-registration response p. 38
Table 8.4.2.3.5-1 describes information elements in the PINE de-registration response from the PIN server to the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| De-registration status | M | Indicates whether the PINE de-registration request was successful or not. Includes the cause of the failure if the de-registration fails. |
8.4.2.3.6 PINE update registration request p. 38
Table 8.4.2.3.6-1 describes information elements in the PINE update registration request from the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs) to the PIN server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UE Identifier | M | The identifier of the hosting UE (i.e. GPSI or identity token) of PINE/PEMC/PEGC. |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the PIN service. |
| MAC address | O | MAC address of the requested PINEs. |
| Vendor name | O | The vendor name of the PINE. |
| Device description | O | Give the description of the device. |
| PINE Address | O | The IP address of PINE, if available. |
| Port number | M | Port number of PIN client on PINE/PEMC/PEGC to support PIN enabler layer communication. The port number is the port used by a PINE to expose a service within the PIN. |
| PINE Capabilities | O | Identify whether the PINE is capable of becoming a PEMC, a PEGC or both. |
| > Maximum number of PINEs (see NOTE) | O | Indicates the maximum number of PINE that can be managed by the PEMC or PEGC. |
| Services that PINE provide | O | Indicate the service that PINE can provide. |
|
NOTE:
Only present if PINE Capabilities is present.
|
||
8.4.2.3.7 PINE update registration response p. 39
Table 8.4.2.3.7-1 describes information elements in the PINE de-registration response from the PIN server to the PINE (including PEMC, PEGC, PINEs).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Update registration status | M | Indicates whether the PINE update registration request was successful or not. Includes the cause of the failure if the update registration fails. |