Content for TS 23.542 Word version: 18.4.0
0…
5…
8…
8.3…
8.4…
8.5…
8.5.3…
8.5.4…
8.5.7…
8.5.8…
8.5.9…
8.5.10…
8.5.11…
8.5.12…
8.5.13…
8.5.14…
8.6…
8.7…
8.8…
8.9…
8.10…
A…
8.5.4 Multiple PEMCs/PEGCs
8.5.4.1 General
8.5.4.2 Procedure
8.5.4.2.1 PIN configuration with default and backup PEGCs
8.5.4.2.2 PIN management with multiple PEMCs
8.5.4.2.3 Notifying the PIN elements of PEGC details
8.5.5 PIN Profile Recovery
8.5.5.1 General
8.5.5.2 Procedure
8.5.5.3 Information flows
8.5.5.3.1 General
8.5.5.3.2 PIN Profile Query request
8.5.5.3.3 PIN Profile Query Response
8.5.6 Credential Provision
...
...
8.5.4 Multiple PEMCs/PEGCs p. 47
8.5.4.1 General p. 47
This clause describes the procedures for the configuration and use of multiple PEMCs and PEGCs in a PIN.
For a PIN having a large number of PIN elements, covering a large area, and/or requiring extra reliability, multiple PIN Elements may be assigned the role of PEMC and/or PEGC.
8.5.4.2 Procedure p. 48
8.5.4.2.1 PIN configuration with default and backup PEGCs p. 48
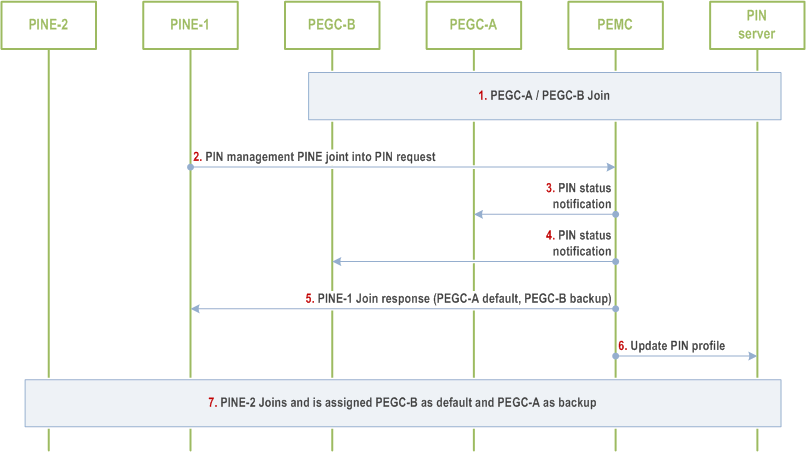
Figure 8.5.4.2.1-1 illustrates a procedure for configuring a new PIN Element, when requesting to join, with a default PEGC and one or more backup PEGCs.
Pre-conditions:
- The PEMC is pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server.
- The PEMC is authorized to access the PIN server.
- The PEMC has registered to the PIN server.
- The PEMC has requested and has been authorized by the PIN server to create a PIN.
- The required KPIs of the PIN have been configured.
- PINE-1, PINE-2, PEGC-A and PEGC-B have registered to the PEMC and PIN server.
- PINE-1, PINE-2, PEGC-A and PEGC-B have subscribed with the PEMC for the PIN status as specified in clause 8.5.X.2.1.
Step 1.
PEGCs (e.g., PEGC-A and PEGC-B) shall join the PIN by sending PIN management PINE join into PIN requests to the PEMC. The PIN Client Profile information (supported PIN roles, supported PEGC KPIs, Supported PEGC schedule, UE location) shall be included in the requests. The PEMC shall use this information to determine whether multiple PEGCs are needed to meet the required KPIs of the PIN and which PIN elements (e.g., PEGC-A and PEGC-B) are able to serve as PEGCs. The PEMC shall configure multiple PEGCs (e.g., PEGC-A and PEGC-B) with a role of PEGC if needed. The PEMC shall then send a PIN profile update to the PIN server informing the PIN server that of the multiple PEGCs.
Step 2.
When PINEs (e.g., PINE-1) send a PIN management PINE join into PIN request to the PEMC, PIN Client Profile information (application client KPIs, application client schedule, UE location) shall be included in the request. The PEMC shall use this information and the PEGC information the PEMC received in step 1 to determine the optimal default and backup PEGCs for the PINE. For example, PEMC assigns PEGC-A as the default PEGC for PINE-1, and PEGC-B as the backup PEGC for PINE-1.
Step 3.
The PEMC shall send a default PEGC (e.g., PEGC-A) PIN status notification to update its local PIN Profile information to reflect that a PINE (e.g., PINE-1) is authorized to relay PIN communications via the PEGC.
Step 4.
The PEMC shall send any backup PEGCs (e.g., PEGC-B) PIN status notification to update their local PIN Profile information to reflect that a PINE (e.g., PINE-1) is authorized to relay PIN communications via the PEGC.
Step 5.
The PEMC shall return a PIN management PINE join into PIN response to PINE-1. The response shall include updated PIN client profile information informing the PINE that it shall use a specified PEGC (e.g., PEGC-A) as its default PEGC, and a specified PEGC (e.g., PEGC-B) as its backup PEGC.
Step 6.
The PEMC shall send a PIN profile update to the PIN server informing the PIN server of a PEGC (e.g., PEGC-A) serving as the default PEGC for a PINE (e.g., PINE-1) and any PEGCs (e.g., PEGC-B) serving as backup PEGCs for a PINE.
Step 7.
Steps 2 to 6 may be repeated for any additional PINEs joining the PIN. For example, based on PIN client profile information provided by PINE-2, the PEMC configures PEGC-B to serve as the default PEGC for PINE-2 and PEGC-A to serve as the backup PEGC for PINE-2.
8.5.4.2.2 PIN management with multiple PEMCs p. 49
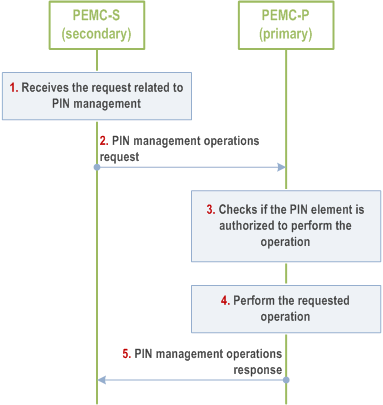
Figure 8.5.4.2.2-1 illustrates a procedure for managing the PIN with multiple PEMCs. PIN elements when registering with the PIN indicates that they have the capability to act as PEMC and are assigned with primary or secondary PEMC role as described in the subclause 8.4.2.2.1.
Pre-conditions:
- A PIN owner or admin creates a PIN and configured multiple PEMCs.
- PEMC-S is assigned with the role of secondary PEMC and PEMC-P is assigned with the role of primary PEMC.
- PEMC-S has direct connection or PIN direct connection with the PEMC-P.
Step 1.
PEMC-S receives a request from PIN owner or PIN admin to perform any of the PIN management operations. Some of the PIN management operations (PIN profile update, PIN element removal) shall be performed by secondary PEMC (PEMC-S) itself and some operations (PIN deletion, PIN activation and PIN deactivation) can be sent to primary PEMC (PEMC-P) which shall be validated and executed by the PEMC-P.
Step 2.
PEMC-S prepares the corresponding request including the required details for the requested operation and sends it to PEMC-P. These requests shall carry the PIN client ID of the PEMC-S mandatorily.
Step 3.
PEMC-P on receiving the request checks whether the PEMC-S is authorized as secondary PEMC in-order to perform the operation.
Step 4.
If the authorization succeeds, PEMC-P proceeds with the requested operation.
Step 5.
PEMC-P sends the response to PEMC-S containing the status or result of the requested operation.
8.5.4.2.3 Notifying the PIN elements of PEGC details p. 50
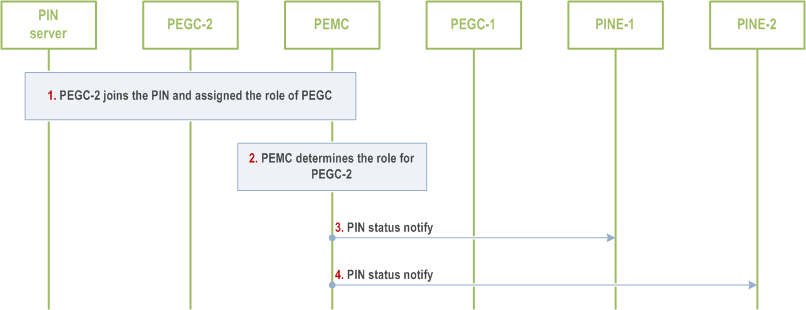
Figure 8.5.4.2.3-1 illustrates a procedure for notifying the PIN elements about the change in default or backup PEGC when multiple PIN elements have the PEGC capability.
Pre-conditions:
- The PIN is configured and PEGC-1 is the designed PEGC.
- PIN elements have subscribed for PIN status as specified in clause 8.5.9.2.1.
Step 1.
PEGC-2 is authorized to join the PIN as specified in the sub-clause 8.4 and is assigned with the role of PEGC.
Step 2.
Upon joining the PIN, the PEMC determines the list of PIN elements for which PEGC-2 can act as default PEGC or backup PEGC. (e.g. PEGC-2 is designated to be the backup PEGC for PINE-1 and default for PINE-2).
Step 3.
The PEMC sends the PIN status notify to PINE-1 indicating that PEGC-2 is the backup PEGC for PINE-1 as specified in as specified in clause 8.5.9.2.2.
Step 4.
The PEMC sends the PIN status notify to PINE-2 indicating that PEGC-2 is the default PEGC for PINE-2 as specified in as specified in clause 8.5.9.2.2.
8.5.4.3 Void
8.5.5 PIN Profile Recovery p. 51
8.5.5.1 General p. 51
The PIN profile recovery procedure describes how the PEMC retrieves a PIN profile from a PIN server.
8.5.5.2 Procedure p. 51
Pre-conditions:
- The PEMC in a PIN has been pre-configured or has discovered the address (e.g. IP address, FQDN, URI) of the PIN server;
- The PIN has already been created and a PIN ID is distributed by PIN server;
- The PEMC has been authorized to communicate with the PIN server;
- A PIN client has already received the role of PEMC from PIN server;
Step 1.
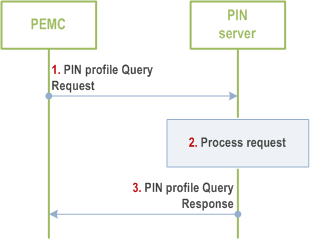
The PEMC sends PIN Profile Query requests (PEMC ID, PIN ID) to the PIN server.
Step 2.
The PIN server determines whether the PEMC is one of the managers of the PIN. The PIN Server validates if the PEMC is authorized to perform the operation; if the PEMC is authorized, the PIN Server verifies if the PEMC is authorized to manage the PIN. The PIN server processes the request.
Step 3.
The PIN server responds to the PEMC with the PIN Profile, which includes for example, the PIN name, PIN description, List of Device Info (PINE), PIN duration, PEGC information or others. The device information is the information of PINE that in the PIN.
8.5.5.3 Information flows p. 51
8.5.5.3.1 General p. 51
The following information flows are specified for PIN profile retrieval:
- PIN Profile Query request and response;
8.5.5.3.2 PIN Profile Query request p. 51
Table 8.5.5.3.2-1 describes information elements in the PIN Profile Query request from the PEMC to the PIN server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PIN ID | M | Identifier of the deleted PIN. |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials resulting from a successful authorization for the PIN service. |
| Identifier of PEMC | M | Indicates the PINE identifier authorized to be the PEMC of this PIN. |
8.5.5.3.3 PIN Profile Query Response p. 52
Table 8.5.5.3.3-1 describes information elements in the PIN Profile Query response from the PIN server to PEMC.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the PIN Profile Query request was successful. |
| > PIN profile | M | The PIN profile information retrieved from PIN server. The details of PIN profile information is described in clause 8.2.2.1. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the PIN Profile Query request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of PIN Profile Query request failure. |