Content for TS 23.437 Word version: 19.0.0
9.3 Spatial map management procedures
9.3.1 Create spatial map
9.3.2 Discover spatial map
9.3.3 Get spatial map information
9.3.4 Update spatial map
9.3.5 Delete spatial map
9.3.6 Spatial map subscription
...
...
9.3 Spatial map management procedures p. 40
9.3.1 Create spatial map p. 40
9.3.1.1 General p. 40
The create spatial map procedure enables the consumers to request the SEAL SM Server to create spatial map of the area of interest.
9.3.1.2 Procedure p. 41
Figure 9.3.1.2-1 depicts the procedure for creating a spatial map. For the request from VAL server or SEAL SM client, as a spatial map consumer, SEAL SM server creates a spatial map. A spatial map can be structured in layers where each layer signifies a specific aspect of the spatial information (e.g. three dimensional space of area of interest, objects).
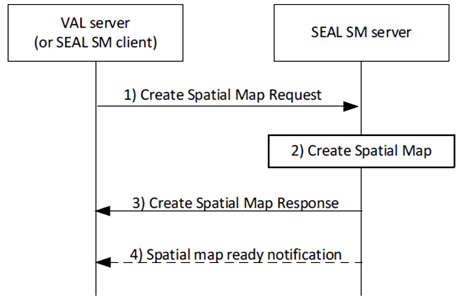
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., VAL server or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to create a spatial map. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, three-dimensional area of interest, information to be included in the spatial map such as access control rules defining which entities are permitted to discover and access the spatial map. The request may include spatial map layering information parameters and may also include augmented layer information that can be requested with the spatial map.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor, and validates the request. The SEAL SM server produces a requested spatial map using layering information and processed sensor data.
Step 3.
- If the augmented layer information indicates to include VAL UE information, the SEAL SM server fetches the list of VAL UEs in the area of interest from LM server using clause 9.3.10 of TS 23.434 and/or from NEF as specified in TS 23.502.
- If the augmented layer information indicates to include spatial anchors information within area of interest, the SEAL SM server fetches the list of spatial anchors in the area of interest as specified in clause 8.3.4.
The SEAL SM server sends response message to the requestor with a indication of success, in-progress or fail. If the requested spatial map has been created sussesfully, the response message includes assigned spatial map ID and information which includes three-dimensional space defined by the spatial map and can include a list of spatial map layers with their corresponding layer ID, objects belong to the layer, etc.. If the response indicates "in-progress", an assigned spatial map ID is included in the message. Further, if the response indicates "in-progress" and the requestor has not provided a notification target address, then the requestor subscribes for spatial map event to receive notification when the spatial map is created. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for the failure.
Step 4.
If the response indicates "in-progress", the SM server detects when the SEAL SM server has sufficient information to map all the objects related to area of interest and the spatial map is ready to provide service (e.g. employed for localization). If the requestor has provided a notification target address in the request or has subscribed for spatial map events, the SEAL SM server notifies the requestor with the spatial map ready notification message. The notification includes parameters as specifed in Table 9.3.6.3.3-1.
9.3.1.3 Information flows p. 42
9.3.1.3.1 Create spatial map request p. 42
Table 9.3.1.3.1-1 descibes the information elements from VAL server (or SEAL SM client) to SM server for create spatial map request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Application service ID | M | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Area of interest | M | Three-dimensional area information to produce the spatial map. |
| Notification Target Address | O | Notification target address (e.g. URL, URI, IP) where the notifications should be sent. |
| Information to include | O | Information to be included in the spatial map. |
| > Access control rules | O | Access control rules defining which entities are permitted to discover and access the spatial map. |
| > List of spatial map layers | O | List of spatial map layer information. Each element includes the information described below. |
| >> Spatial map layer information | O | Information to specify the corresponding spatial map layer specific information. |
| > Augmented layer information | O |
List of required augmented layer information. This IE can contain multiple values. Possible values are:
|
9.3.1.3.2 Create spatial map response p. 42
Table 9.3.1.3.2-1 descibes the information elements for create spatial map response from SM server to VAL server or SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application service ID | O | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Success response | O
(NOTE) | Information on the created spatial map. It contains information as specified in Table 7.3.3.1-1. |
| > Spatial map information | M | The information about the created spatial map as described in Table 7.3.3.1-1. |
| > Augmented layer information | O | Augmented layer information provided by SM server. |
| Failure response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates failed create spatial map. |
| > Cause | O | Cause of the failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.2 Discover spatial map p. 42
9.3.2.1 General p. 42
The discover spatial map procedure enables the consumers to request the SEAL SM Server to discover all spatial maps of the area of interest.
9.3.2.2 Procedure p. 43
Figure 9.3.2.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL SM client) to discover spatial map(s). The service is provided by SEAL SM server.
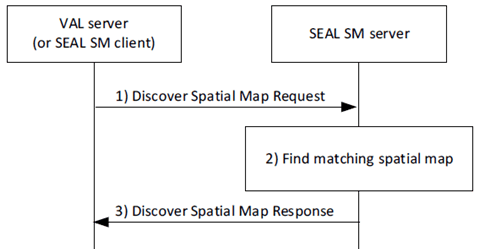
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g.,VAL server or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to discover spatial map(s). The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, three-dimensional area of interest or localization information to discover spatial maps in the area, optional discovery filters, i.e., a set of characteristics (e.g., a list of specific spatial map layers) to search the matching spatial maps when multiple spatial maps are allowed in the area of interest.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor, and validates the request. Then the server determines the spatial map(s) according to the requested filtering criteria.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends the discover spatial map response message to the requestor. If the request was succesful, the response includes the determined spatial map information, , otherwise the response includes an indication of failure and may include a failure reason.
9.3.2.3 Information flows p. 43
9.3.2.3.1 Discover spatial map request p. 43
Table 9.3.2.3.1-1 descibes the information elements from VAL server (or SEAL SM client) to SEAL SM server for discover spatial map request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Application service ID | M | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Filtering criteria | M | Criteria to get spatial map(s). |
| > Area of interest | O
(NOTE) | Three-dimensional area information to discover spatial maps. |
| > Location information | O
(NOTE) | Location, orientation and pose information that is used to identify relevant spatial maps. |
| > Optional discovery filters | O | A set of characteristics to search the matching spatial maps. |
| >> List of spatial map layers | O | The list of spatial map layers to discover spatial map(s) with matching layers. Each element includes the information described below. |
| >>> Spatial map layer information | O | Information to specify the corresponding spatial map layer specific information. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.2.3.2 Discover spatial map response p. 44
Table 9.3.2.3.2-1 descibes the information elements for Discover spatial map response from SEAL SM server to VAL server or SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application service ID | O | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Success response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates successful discovery. |
| > List of discovered spatial maps | M | List of ID(s) of the discovered spatial map(s). Each element includes the information described below. |
| >> Spatial map ID | M | ID of a spatial map discovered. |
| Failure response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates failed discovery. |
| > Cause | O | Cause of the failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.3 Get spatial map information p. 44
9.3.3.1 General p. 44
The get spatial map procedure enables the consumers to request the SEAL SM Server to get all details about the specific spatial map.
9.3.3.2 Procedure p. 44
Figure 9.3.3.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL SM client) to get the spatial map. The service is provided by SEAL SM server.
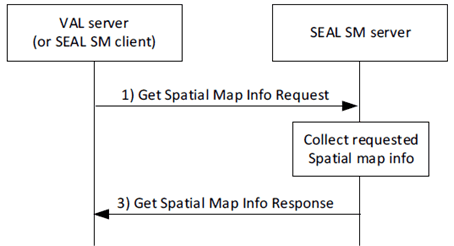
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., VAL server or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to get the spatial map information. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, spatial map ID.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor, and validates the request. If the request is authorized, the SEAL SM server determines information about the requested spatial map information.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends the get spatial map information response message to the requestor. If the request is successful, the response includes spatial map information, otherwise the response indicates a failure and may include a failurereason.
9.3.3.3 Information flows p. 45
9.3.3.3.1 Get spatial map information request p. 45
Table 9.3.3.3.1-1 descibes the information elements for get spatial map request from the VAL server or SEAL SM client to the SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Application service ID | M | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Spatial map ID | M | ID of the spatial map to get information on it. |
| > List of spatial map layers | O | A list of spatial map layers for which information is requested. |
9.3.3.3.2 Get spatial map information response p. 45
Table 9.3.3.3.2-1 descibes the information elements for get spatial map response from the SEAL SM server to the VAL server or SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial map ID | M | ID of the requested spatial map to get information. |
| Application service ID | O | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Success response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates successful get information. |
| > Spatial map information | M | Information about the requested spatial map as specified in Table 7.3.3.1-1. |
| Failure response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates failed get information. |
| > Cause | O | Cause of the failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.4 Update spatial map p. 46
9.3.4.1 General p. 46
The update spatial map procedure enables the consumers to request the SEAL SM Server to update a spatial map.
9.3.4.2 Procedure p. 46
Figure 9.3.4.2-1 depicts the procedure to update the spatial map. For the request from the spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL SM client), SEAL SM server updates the spatial map as requested.
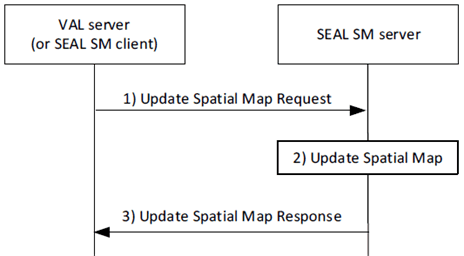
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., VAL server or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to update a spatial map. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, spatial map ID, information on what to update such as updated spatial map layering information and updated spatial map coverage area. As a part of update, the request may include augmented layer information (e.g., VAL users, spatial anchors).
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor and validates the request. The SEAL SM server updates the spatial map as requested.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends response message to the requestor with result of the request and updated spatial map information with the spatial map ID. SEAL SM server may include the requested augmented layer information in the response message.
9.3.4.3 Information flows p. 47
9.3.4.3.1 Update spatial map request p. 47
Table 9.3.4.3.1-1 descibes the information elements for update spatial map request from VAL server or SEAL SM client to SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Application service ID | M | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Spatial map ID | M | ID of the spatial map to update. |
| Spatial map update information | M | The spatial map Information to update as described in described in Table 7.3.3.1-1. Only IEs which need to be updated are included. |
| > Augmented layer information | O |
List of required augmented layer information. This IE can contain multiple values. Possible values are:
|
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.4.3.2 Update spatial map response p. 47
Table 9.3.4.3.2-1 descibes the information elements for update spatial map response from the SEAL SM server to the VAL server or SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial map ID | M | ID of the requested spatial map to get information. |
| Application service ID | O | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Success response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates successful update. |
| > Spatial map information | M | Updated spatial map information. It contains information as specified in Table 7.3.3.1-1. |
| > Augmented layer information | O | Augmented layer information. |
| Failure response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates failed update. |
| > Cause | O | Cause of failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.5 Delete spatial map p. 47
9.3.5.1 General p. 47
The delete spatial map procedure enables the consumers to request the SEAL SM Server to delete a spatial map.
9.3.5.2 Procedure p. 47
Figure 9.3.5.2-1 depicts the procedure to delete the spatial map. For the request from the spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL SM client), SEAL SM server deletes the spatial map as requested.
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., VAL server or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to delete the spatial map. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, a spatial map ID.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor and validates the request. The SEAL SM server deletes the spatial map as requested.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends response message to the requestor with the result of success or failure.
9.3.5.3 Information flows p. 48
9.3.5.3.1 Delete spatial map request p. 48
Table 9.3.5.3.1-1 descibes the information elements for delete spatial map request from VAL server or SEAL SM client to SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Spatial map ID | M | Spatial map ID to delete. |
9.3.5.3.2 Delete spatial map response p. 48
Table 9.3.5.3.2-1 descibes the information elements for delete spatial map response from SEAL SM server to VAL server or SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Success response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates successful delete. |
| Failure response | O
(NOTE) | Indicates failed delete. |
| > Cause | O | Cause of failure. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the information elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.6 Spatial map subscription p. 48
9.3.6.1 General p. 48
This clause provides subscription related procedures to spatial map specific events.
9.3.6.2 Procedures p. 49
9.3.6.2.1 Subscribe spatial map event p. 49
Figure 9.3.6.2.1-1 depicts the procedure for the authorized spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL SM client) to subscribe the spatial map event. The service is provided by SEAL SM server. Spatial map consumer can get notification information when the the SM server detects subscribed event.
Step 1.
The VAL server (or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to subscribe spatial map event. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials, a notification endpoint, a spatial map ID, event to subscribe which triggers the notification. The request message may also include a list of spatial map layers with its corresponding layer IDs to subscribe spatial map layering information related events. The requestor (VAL server or SEAL SM client) may subscribe to one or more of the following events:
Step 2.
- "changes of objects" events to indicate the SM server to notify the requestor when changes of the objects are detected. The notification triggering criteria for "changes of objects" event may include added or removed objects, position or direction changes of the spatial map objects.
- "layers modification" events to indicate the SM server to notify the requestor when any layer in the spatial map is added or updated or removed.
- "spatial map ready" events to indicate the SM server to notify the requestor when the SEAL SM server has sufficient information to map all the objects related to area of interest the spatial map and the spatial map is ready to provide service (e.g. employed for localization). This event is used when the result IE in the Create spatial map response indicates "in-progress".
The SEAL SM server authorizes VAL server (or SEAL SM client), and validates the request. Then server add the requestor into the subscriber list of the event. SM server starts monitoring the events.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends response message with the result. For the successful subscribe request, a subscription ID is included in the message. Otherwise, the response message includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
9.3.6.2.2 Notify spatial map event p. 49
Figure 9.3.6.2.2-1 depicts the notify spatial map event operation between the authorized spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL LM client) and SEAL SM server.

Step 1.
The SEAL SM server detects an event that triggers the notification to the subscribers for the corresponding event.
Step 2.
- If the subscribed event is "changes of objects", the SM server detects any changes of the spatial map objects.
- If the subscribed event is "Layers modification", the SM server detects any changes of the spatial map layers information.
- If the subscribed event is "spatial map ready", the SM server detects when the SEAL SM server has sufficient information to map all the objects related to area of interest the spatial map and the spatial map is ready to provide service (e.g. employed for localization).
The SEAL SM server notifies the VAL servers (or SEAL SM clients) which subscribed the corresponding event. The notification includes a subscription ID and event-specific information. If the event is "changes of objects", spatial map notification message includes the information on the detected triggering event, e.g. added or removed objects, position or direction changes of the objects in the spatial map etc. If the event is "Layer modification", the notification message includes the list of all layers for the spatial map.
9.3.6.2.3 Unsubscribe spatial map p. 50
Figure 9.3.6.2.3-1 depicts the procedure for the authorized spatial map consumer (VAL server or SEAL CM client) to unsubscribe from the spatial map event. The service is provided by SEAL SM server.
Step 1.
The VAL server (or SEAL SM client) sends a request message to the SEAL SM server to unsubscribe from spatial map event. The request includes requestor ID, security credentials and the subscription ID for the event.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes VAL server (or SEAL SM client), and validates the request. Then SM server removes the requestor's subscription ID from the subscriber list for the spatial map event.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends unsubscribe spatial map event response message with the result. If successful, the response includes an indication of success. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
9.3.6.3 Information flows p. 51
9.3.6.3.1 Subscribe spatial map request p. 51
Table 9.3.6.3.1-1 shows the subscribe spatial map event request sent by VAL server (or SEAL SM client) to SEAL SM server to subscribe for spatial map event(s).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Application service ID | M | ID of the requesting VAL application service. |
| Expiry time | O | Proposed subscription expiry time. |
| Target spatial map(s) | M | Spatial map(s) to subscribe. |
| > List of spatial map IDs | O | ID(s) of the spatial map(s) to subscribe. |
| > Area of interest | O | Three-dimensional area information to discover spatial map(s) to subscribe. |
| List of events | M | Events to subscribe. Each element includes the information described below. |
| > Event type | O |
List of events to subscribed. Possible values are:
|
| > specified objects | O | List of specified objects for "change of objects" event. |
| > Triggering criteria | O | Specifies the condition to determine whether the event is occurred, e.g. Spatial map is employed and ready for localization service. |
| >> Changes in objects | O
(NOTE) | Triggers notification if any or specified (or specified type of) objects are added, removed, etc. |
| >> Layer IDs | O
(NOTE) | List of layers. Triggers notification if any or specified spatial map layer change is detected. |
| > Notification intervals | O |
Specifies when to notify the detected event,
Possible values are:
|
| > interval time | O | Time between consecutive notifications (applicable only if notification intervals is set to intervals). |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the sub-elements shall be provided.
|
||
9.3.6.3.2 Subscribe spatial map response p. 51
Table 9.3.6.3.2-1 shows the subscribe spatial map event response sent by SEAL SM server to VAL server (or SEAL SM client) as the response to the subscribe spatial map event request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Result | M | Result of the subscribe spatial map event request. |
| Subscription Id (NOTE) | O | Identity of the subscription. |
| Expire time | O | Subscription expire time. |
| Failure cause | O | Indicates reason for the failure. |
|
NOTE:
This IE is mandatory when Result IE indicates success.
|
||
9.3.6.3.3 Notify spatial map event p. 52
Table 9.3.6.3.3-1 shows the spatial map notification sent by SEAL SM server to VAL server (or SEAL SM client) to notify about spatial map event(s).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription ID for the event. |
| Notification information | M | Specifies what matches the triggering notification condition, including related information. |
| > Spatial map ID | M | ID of the spatial map for which the event is detected. |
| > Event type | M | Type of event detected. One of the event as specified in Table 9.3.6.3.1-1. |
| >> Changed object | O
(NOTE 1) | Information on the object which triggered the notification. |
| >>> Object ID | O | ID of the changed object. |
| >>> Type of change | O | Specifies the detected type of change for the object (e.g., added, removed, or changed position or direction). |
| >>> Changed object information | O | A container to carry the changed object specific information. |
| >> list of layers
(NOTE 2) | O | Information about layers for the spatial map. |
|
NOTE 1:
This IE is applicable for "Change of objects" event type.
NOTE 2:
This IE is applicable for "Layer modification" event type.
|
||
9.3.6.3.4 Unsubscribe spatial map request p. 52
Table 9.3.6.3.4-1 shows the unsubscribe spatial map event request sent by VAL server (or SEAL SM client) to SEAL SM server to subscribe for spatial map event(s).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identity | M | The identity of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription ID for the event. |
9.3.6.3.5 Unsubscribe spatial map response p. 52
Table 9.3.6.3.5-1 shows the unsubscribe spatial map event response sent by SEAL SM server to VAL server (or SEAL SM client) as the response to the unsubscribe spatial map event request.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Result | M | Result of the subscribe spatial map event request. |
| Failure cause | O | Indicates reason for the failure. |