Content for TS 23.437 Word version: 19.0.0
9.5 SM data source
9.5.1 General
9.5.2 SM data source registration
9.5.3 SM data source registration update
9.5.4 SM data source deregistration
9.5.5 SM data source discovery
...
...
9.5 SM data source p. 54
9.5.1 General p. 54
This clause provides registration related procedures for SM data source.
9.5.2 SM data source registration p. 54
9.5.2.1 General p. 54
The SM data source registration procedure registers the authorized SM information data source with SEAL SM server.
9.5.2.2 Procedure p. 54
Figure 9.5.2.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized VAL client, via a SEAL SM client, to register as a SM data source with the SEAL SM server.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEAL SM client has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SEAL SM server;
- The SEAL SM client has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SEAL SM server.
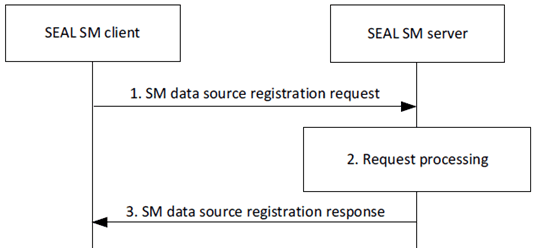
Step 1.
The SEAL SM client sends a SM data source registration request to the SEAL SM server. The request includes a requestor ID, security credentials, UE identifier, VAL client identifier, SEAL SM client notification endpoint and a SM data source profile including SM information details (e.g., provider identifier, type, position, state).
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SEAL SM server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SEAL SM server assigns a unique identifier for the registration and stores the SM data source profile provided in the request.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends a SM data source registration response to the SEAL SM client. If the SEAL SM server successfully stored the SM data source profile, the response includes an indication of success, the registration identifier and may include a proposed expiration time for the registration. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
9.5.2.3 Information flows p. 55
9.5.2.3.1 SM data source registration request p. 55
Table 9.5.2.3.1-1 describes information elements in the SM data source registration request from the SEAL SM client to the SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., SEAL SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Proposed expiration time | O | Proposed expiration time for the registration. |
| UE ID | O | The identifier of the hosting UE (i.e., GPSI). |
| VAL client ID | O | The identifier of the VAL client. |
| Notification endpoint | M | The endpoint for notifying the SM data source about a SM information request. |
| SM data source profile | M | The SM data source profile of the registering SM data source as described in Table 7.3.3.2-1. |
9.5.2.3.2 SM data source registration response p. 55
Table 9.5.2.3.2-1 describes information elements in the SM data source registration response from the SEAL SM server to the SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the registration request was successful. |
| > Registration ID | M | Identifier of the registration. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the registration. To maintain an active registration status, a registration update is required before the expiration time. If the Expiration time IE is not included, it indicates that the registration never expires. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the registration request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of registration request failure. |
9.5.3 SM data source registration update p. 56
9.5.3.1 General p. 56
The SM data source registration update procedure updates registration status of the authorized SM information data source to the SEAL SM server.
9.5.3.2 Procedure p. 56
Figure 9.5.3.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized VAL client, via a SEAL SM client, to update a registered SM data source information.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEAL SM client has successfully registered the SM data source with the SEAL SM server.
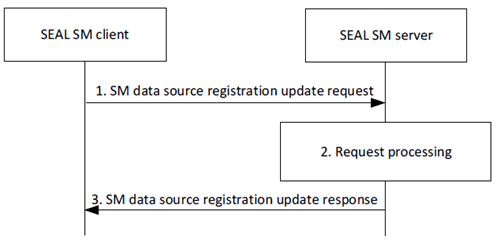
Step 1.
The SEAL SM client sends a SM data source registration update request to the SEAL SM server. The request includes a requestor ID, security credentials, a registration ID, and may include an updated SM data source profile and a proposed expiration time for the updated registration.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SEAL SM server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SEAL SM server updates the SM data source profile based on the request information.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends the SM data source registration update response to the SEAL SM client. If the SEAL SM server successfully updated the SM data source profile, the response includes an indication of success. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
9.5.3.3 Information flows p. 57
9.5.3.3.1 SM data source registration update request p. 57
Table 9.5.3.3.1-1 describes information elements in the SM data source registration update request from the SEAL SM client to the SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., SEAL SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Registration ID | M | Identifier of the registration. |
| Proposed expiration time (NOTE) | O | Proposed expiration time for the registration. |
| Updated SM data source profile (NOTE) | O | The SM data source profile, as described in Table 7.3.3.2-1, with updated SM information details. Included only if there is an update in SM information details. |
|
NOTE:
At least one of the IEs is included.
|
||
9.5.3.3.2 SM data source registration update response p. 57
Table 9.5.3.3.2-1 describes information elements in the SM data source registration update response from the SEAL SM server to the SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the registration update request was successful. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the updated registration. To maintain an active registration status, a registration update is required before the expiration time. If the Expiration time IE is not included, it indicates that the updated registration never expires. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of the failure. |
9.5.4 SM data source deregistration p. 57
9.5.4.1 General p. 57
The SM data source deregistration procedure deregisters the authorized SM information data source from the SEAL SM server.
9.5.4.2 Procedure p. 57
Figure 9.5.4.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized SEAL SM client to deregister a SM data source.
Pre-conditions:
- The SEAL SM client has already registered the SM data source with the SEAL SM server.
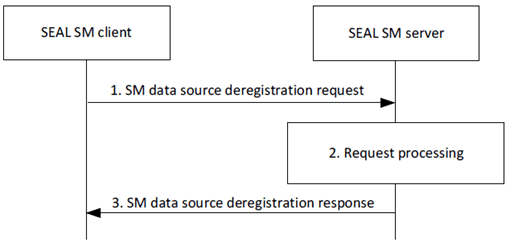
Step 1.
The SEAL SM client sends a SM data source deregistration request to the SEAL SM server. The request includes a requestor ID, security credentials, and a registration ID.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SEAL SM server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SEAL SM server ends the SM data source registration and removes the stored SM data source profile.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends the SM data source deregistration response to the SEAL SM client. If the SEAL SM server successfully deregistered the SEAL SM client, the response includes an indication of success. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
9.5.4.3 Information flows p. 58
9.5.4.3.1 SM data source deregistration request p. 58
Table 9.5.4.3.1-1 describes information elements in the SM data source deregistration request from the SEAL SM client to the SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., SEAL SM client). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Registration ID | M | Identifier of the registration. |
9.5.4.3.2 SM data source deregistration response p. 58
Table 9.5.4.3.2-1 describes information elements in the SM data source deregistration response from the SEAL SM server to the SEAL SM client.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the deregistration request was successful. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of the failure. |
9.5.5 SM data source discovery p. 59
9.5.5.1 General p. 59
The SM data source discovery procedure allows VAL server to discover the authorized SM information data sources from the SEAL SM server.
9.5.5.2 Procedure p. 59
Figure 9.5.5.2-1 depicts the procedure for an authorized VAL server to discover SM data source(s).
Pre-conditions:
- The VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SEAL SM server;
- The VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SEAL SM server.
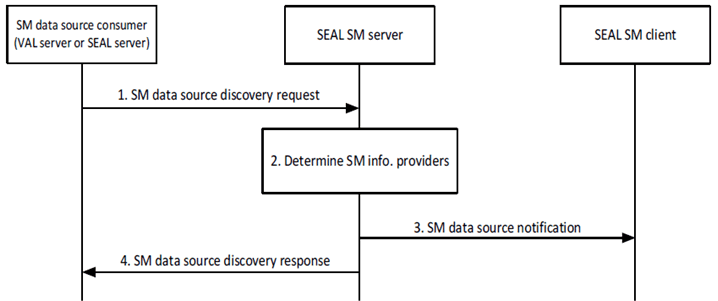
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g, VAL server or SEAL server) sends a SM data source discovery request to the SEAL SM server. The request includes a requestor ID, security credentials, discovery filters and endpoint information for receiving spatial mapping information from discovered SM data sources. Discovery filters inlcude the area of interest (e.g., three-dimensional area, localization information) and requirements on spatial mapping information as defined in clause 9.5.5.3.1.
Step 2.
The SEAL SM server authorizes the requestor and validates the request. If the request is authorized, the SEAL SM server determines one or more registered SM data source(s) according to the discovery filters.
The SEAL SM server evaluates if the SM data source location is in accordance with the area of interest included in the discovery request to determine the SM data source(s). The SEAL SM server can obtain UE location information from the 3GPP core network by invoking the 3GPP Core Network Location Services exposed by the NEF as described in TS 23.273 and TS 23.502, or by invoking the SEAL Location Management APIs as described in TS 23.434.
Step 3.
The SEAL SM server sends a SM data source notification to trigger the determined SEAL SM client(s) to send spatial mapping information. The notification includes details about the requested spatial mapping information and endpoint information for sending the spatial mapping information to the requestor. The SEAL SM client provides the information included in the notification to the VAL client that will send the spatial mapping information.
Step 4.
The SEAL SM server sends a SM data source discovery response to the requestor. The response includes information about SM data source(s) when at least one SM data source has been determined. If no SM information provided was determined, the SEAL SM server sends a failure indication with a reason for failure.
9.5.5.3 Information flows p. 60
9.5.5.3.1 SM data source discovery request p. 60
Table 9.5.5.3.1-1 describes information elements in the SM data source discovery request from the VAL server to the SEAL SM server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| Area of interest | M | Three-dimensional area of interest or localization information to discover SM data source(s) in the area. |
| SM data reporting endpoint | O | The endpoint information where the triggered spatial mapping data source sends the SM data. |
| Discovery filters | O | Set of characteristics to determine SM data source(s) in the area of interest. |
| > SM information details | O | The SM information details to match. |
| >> SM data identifier | O | The identifier of SM information. |
| >> SM data type (NOTE) | O | The type of SM information (e.g., LiDAR camera, RGB-D camera, high-resolution cameras, etc.) that is provided by the application layer. |
| >> SM data format | O | The format of a SM information (e.g., raw, processed, etc.). |
|
NOTE:
The definition of SM data types is application specific (e.g., VAL client) for the current release.
|
||
9.5.5.3.2 SM data source discovery response p. 60
Table 9.5.5.3.2-1 describes information elements in the SM data source discovery response from the SEAL SM server to the SM data source consumer (e.g., VAL server or SEAL server).
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the discovery request was successful. |
| > SM data source profiles | O | The list of SM data source profiles as described in Table 7.3.3.2-1. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of the failure. |
9.5.5.3.3 SM data source notification p. 60
Table 9.5.5.3.3-1 shows the notification sent by a SEAL SM server to a SEAL SM client for triggering a spatial mapping information session from a SM data source.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor ID | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., SEAL SM server, VAL server). |
| Requestor security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| SM data source ID | M | The identifier of the SM data source. |
| SM information reporting session | M | The characteristics of SM information reporting session. |
| > SM data identifier | M | The identifier of spatial SM data to report. |
| > SM data type (NOTE) | O | The type of SM information data to report. (e.g., LiDAR camera, RGB-D camera, high-resolution cameras, etc.) that is provided by the application layer. |
| > SM data format | O | The format of a SM information data to report. (e.g., raw, processed, etc.). |
| > SM duration | O | The duration for which the SM data is reported. |
| > SM frequency | O | The frequency at which the SM data is reported. |
| > SM endpoint | M | The endpoint where to report the SM data. |
|
NOTE:
The definition of SM data types is application specific (e.g., VAL client) for the current release.
|
||