Content for TS 23.437 Word version: 19.0.0
9 Spatial Map (SM) management
9.1 General
9.2 Functional model for spatial map management
9.2.1 General
9.2.2 On-network functional model description
9.2.3 Service based architecture
...
...
9 Spatial Map (SM) management p. 38
9.1 General p. 38
The Spatial Map (SM) management is a SEAL service that offers the spatial map related capabilities to vertical application(s).
9.2 Functional model for spatial map management p. 38
9.2.1 General p. 38
The functional model for the spatial map server is based on the generic functional model specified in clause 6 of TS 23.434. It is organized into functional entities to describe a functional architecture which addresses the support for spatial map aspects for vertical applications.This clause provides architecture for spatial map (SM) service. The on-network functional model is specified in clause 9.2.2, and service based architecture is specified in clause 9.2.3.
9.2.2 On-network functional model description p. 39
Figure 9.2.2-1 illustrates an on-network functional model for spatial map (SM) service.
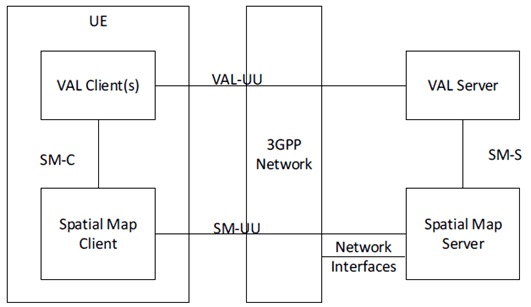
The Spatial map management functional entities are grouped into the vertical application layer and the Service Enabler Architecture Layer (SEAL) layer. The Spatial map management offers the capabilities to manage spatial map to the vertical application layer. The Spatial map management functional model is based on SEAL layer as specified in TS 23.434.
The Spatial map functional entities on the UE and in the network are respectively the spatial map (SM) client and spatial map (SM) server. The VAL client and VAL server are application client and server respectively to provide an application service to the user. The SM client and SM server provides client and server side functionalities respectively for managing spatial map for the application. The SM client is a SEAL client providing spatial map service to VAL client. The SM server is a SEAL server providing spatial map service to VAL server and UE. The interface between SM Client and SM Server is SM-UU. The SM client interacts with the VAL client using a SM-C interface. The SM server interacts with the VAL server using a SM-S. The SM server communicates with the underlying 3GPP network system (either directly or via NEF) using 3GPP interfaces specified by the 3GPP network system (e.g. T8, N33). When SM server is deployed by PLMN operator, the SM server communicates with 3GPP network system by directly invoking the APIs from exposed by 3GPP core network functions.
The SM server interacts with SAn server over SEAL-X (AnM) reference point as specified in clause 8.2.2.
9.2.2.1 Functional Elements p. 39
9.2.2.1.1 Spatial map (SM) server p. 39
The SM server acts as a SEAL server and it is used to provide services to create/update/delete/discover spatial map for the VAL application (i.e. metaverse application) and also provides spatial localization service. It can communicate with other SM server in the distributed SEAL deployments.
9.2.2.1.2 Spatial map (SM) client p. 39
The SM client acts as a SEAL client for spatial map function. It supports client side functionalities for creating/updating/deleting/discovering/retrieving spatial map for VAL application (i.e. metaverse application) and also provides spatial localization service. The SM client receives the request from VAL client to perform specific functionality.
9.2.2.1.3 VAL server p. 39
The VAL server is specified in clause 6.4.2.3 of TS 23.434. The VAL server provides the server side functionalities corresponding to the vertical applications (i.e. metaverse applications) to the client of a VAL user based on a service contract.
9.2.2.1.4 VAL client p. 40
The VAL client is specified in clause 6.4.2.2 of TS 23.434. The VAL client provides a metaverse services to the user. It uses the SM client to manage spatial maps for the application.
9.2.2.2 Reference Points p. 40
9.2.2.2.1 SM-UU p. 40
SM-UU reference point enables interactions between a SM client and SM server. It is used to create/update/delete/discover/retrieve spatial map for the VAL applications (i.e. metaverse applications).
9.2.2.2.2 SM-S p. 40
SM-S reference point enables interactions between a SM server and VAL servers (i.e. metaverse application servers). It can be used to create/update/delete/get/retrieve spatial map for the VAL applications (i.e. metaverse applications).
9.2.2.2.3 SM-C p. 40
SM-C reference point enables interactions between a SM client and VAL clients (i.e. metaverse application clients). It is used by the VAL client to share information regarding spatial maps related information to the SM client and also to get spatial maps related information from the SM client.
9.2.3 Service based architecture p. 40
Figure 9.2.3-1 illustrates the service-based SEAL architecture to support spatial map services.
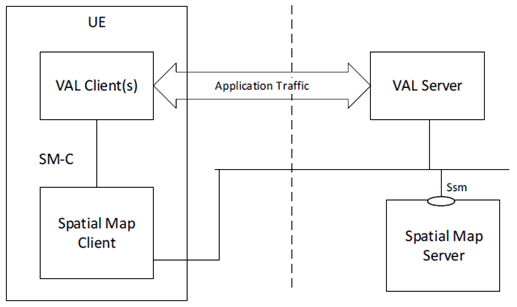
The SM server exposes the APIs over the Ssm interface to the VAL server and SM client. The VAL servers consume the services by interacting on the Ssm interface of the SM server. The CAPIF can be used by VAL functions to discover the services of the SM server.