Content for TS 23.437 Word version: 19.0.0
8.3 Spatial anchors management procedures
8.3.1 Spatial anchor creation
8.3.2 Spatial anchor update
8.3.3 Spatial anchor deletion
8.3.4 Spatial anchor discovery
8.3.5 Spatial anchor subscription
...
...
8.3 Spatial anchors management procedures p. 17
8.3.1 Spatial anchor creation p. 17
8.3.1.1 General p. 17
Spatial anchor creation enables a SAn client or VAL server to create spatial anchor(s) with the SAn server.
8.3.1.2 Procedure p. 17
Figure 8.3.1.2-1 illustrates the spatial anchor creation procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SAn server;
- The SAn client or VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SAn server.
- For SAn client to trigger this procedure, the SAn client has received the required information from the VAL client over SAn-C interface.
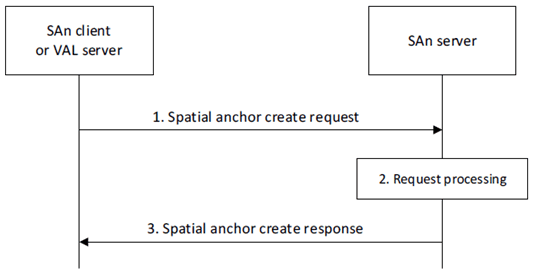
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor create request to the SAn server. The request includes a requestor identifier, security credentials, and list of spatial anchors to be created as described in clause 8.3.1.3.1. The request includes a position, access control rules defining which entities are permitted to discover and access the spatial anchor, and discoverability information (e.g., indicating whether the spatial anchor is discoverable by any user). If the request includes spatial anchor specific information, that information remains transparent to the SAn server and can be stored with the spatial anchor. The request can indicate to create multiple spatial anchors.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SAn server creates the spatial anchor(s), assigns spatial anchor identifier to the newly created spatial anchor(s) and stores the spatial anchor information.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor create response to the requestor. If the SAn server created spatial anchors, the response includes an indication of success and spatial anchor identifier(s) of newly created spatial anchor(s). Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and can include a reason for failure.
8.3.1.3 Information flows p. 18
8.3.1.3.1 Spatial anchor create request p. 18
Table 8.3.1.3.1-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor create request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| VAL service information | M | Information about the application service associated with the spatial anchor. |
| > Service ID | M | The identifier of the application service. |
| > Service endpoint | M | Endpoint information (e.g., URI, FQDN, IP address) used to communicate with the application service. |
| > Service connection information | O | The connection information (e.g., DNN, DNAI(s)) for establishing connectivity to the application service. |
| List of spatial anchors | M | List of spatial anchors to be created. |
| > Position information | M | Position information of the spatial anchor. |
| >> Position (NOTE) | O | The 3D geographic position of the spatial anchor in space (x, y and z coordinates). |
| >> Spatial map position (NOTE) | O | Position information of the spatial anchor within the spatial map. It includes the identifier of the Spatial map, identifier of spatial map layer(s) and the corresponding localization information (The localization information is specific to spatial map format). |
| > Spatial anchor specific information | O | A container to contain application specific information. |
| > Service area | O | The service area where the spatial anchor is accessible. |
| > Access control rules | O | Access control rules defining which entities are permitted to discover the spatial anchor. |
|
NOTE:
One of the IEs shall be present.
|
||
8.3.1.3.2 Spatial anchor create response p. 19
Table 8.3.1.3.2-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor create response from the SAn service.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the spatial anchor create request was successful. |
| > List of spatial anchor ID | O | The list of created spatial anchor identifiers. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the create spatial anchor request has failed. |
| > Cause | O | The cause for the request failure. |
8.3.2 Spatial anchor update p. 19
8.3.2.1 General p. 19
Spatial anchor update enables a SAn client or VAL server to update spatial anchor(s) with the SAn server.
8.3.2.2 Procedure p. 19
Figure 8.3.2.2-1 illustrates the spatial anchor update procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SAn server; and
- The SAn client or VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SAn server.
- For SAn client to trigger this procedure, the SAn client has received the required information from the VAL client over SAn-C interface.
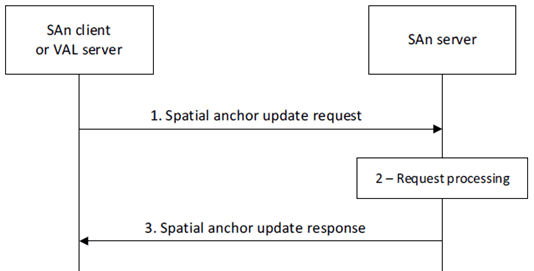
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor update request to the SAn server. The request includes a requestor identifier, security credentials, the identifier of spatial anchors, and spatial anchor information to update as described in clause 8.3.2.3.1. The request may include information to update multiple spatial anchors.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized and the spatial anchor identifier provided in the request is found, the SAn server updates the spatial anchor information based on information provided in the request.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor update response to the requestor. If the SAn server updated the spatial anchor, the response includes an indication of success and the identifier of updated spatial anchor(s). Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
8.3.2.3 Information flows p. 20
8.3.2.3.1 Spatial anchor update request p. 20
Table 8.3.2.3.1-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor update request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| > VAL service information | O | Information about the application service associated with the spatial anchor. |
| >> Service ID | O | The identifier of the application service. |
| >> Service endpoint | O | Endpoint information (e.g., URI, FQDN, IP address) used to communicate with the application service. |
| >> Service connection information | O | The connection information (e.g., DNN, DNAI(s)) for establishing connectivity to the application service. |
| List of spatial anchors | M | List of spatial anchors to be updated. |
| > Spatial anchor ID | M | Identifier of the spatial anchor to be updated. |
| > Position information | O | Position information of the spatial anchor. |
| >> Position (NOTE) | O | The 3D geographic position of the spatial anchor in space (x, y and z coordinates). |
| >> Spatial map position (NOTE) | O | Position information of the spatial anchor within the spatial map. It includes the identifier of the Spatial map, identifier of spatial map layer(s) and the corresponding localization information (The localization information is specific to spatial map format). |
| > Spatial anchor specific information | O | A container to contain application specific information. |
| > Service area | O | The service area where the spatial anchor is accessible. |
| > Access control rules | O | Access control rules defining which entities are permitted to discover the spatial anchor. |
|
NOTE:
If Position information is included, at least one of the IEs shall be present.
|
||
8.3.2.3.2 Spatial anchor update response p. 21
Table 8.3.2.3.2-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor update response from the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the update spatial anchor request was successful. |
| > List of spatial anchor ID | O | List of identifiers of the updated spatial anchors. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the update spatial anchor request has failed. |
| > Cause | O | The cause for the request failure. |
8.3.3 Spatial anchor deletion p. 21
8.3.3.1 General p. 21
Spatial anchor deletion enables a SAn client or VAL server to delete spatial anchor(s) with the SAn server.
8.3.3.2 Procedure p. 21
Figure 8.3.3.2-1 illustrates the spatial anchor deletion procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SAn server; and
- The SAn client or VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SAn server.
- For SAn client to trigger this procedure, the SAn client has received the required information from the VAL client over SAn-C interface.
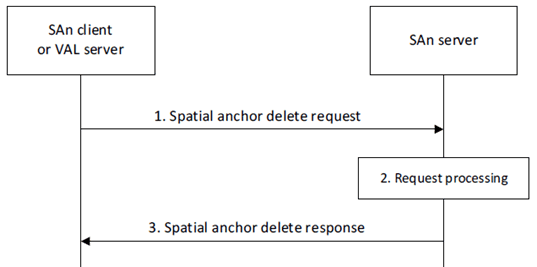
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor delete request to the SAn server. The request includes a requestor identifier, security credentials, the identifier of spatial anchors to delete as described in clause 8.3.3.3.1. The request may include information to delete multiple spatial anchors.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized and the spatial anchor identifier provided in the request is found, the SAn server deletes the spatial anchor information.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor delete response to the requestor. If the SAn server deleted the spatial anchor(s), the response includes an indication of success and the identifier of deleted spatial anchor(s). Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
8.3.3.3 Information flows p. 22
8.3.3.3.1 Spatial anchor delete request p. 22
Table 8.3.3.3.1-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor delete request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| List of spatial anchors ID | M | List of identifiers of the spatial anchors to be deleted. |
8.3.3.3.2 Spatial anchor delete response p. 22
Table 8.3.3.3.2-1 describes information elements for the delete spatial anchor response from the SAn server to the SAn client or VAL server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the delete spatial anchor request was successful. |
| > List of spatial anchor ID | O | List of identifiers of the deleted spatial anchors. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the delete spatial anchor request has failed. |
| > Cause | O | The cause for the request failure. |
8.3.4 Spatial anchor discovery p. 23
8.3.4.1 General p. 23
Spatial anchor discovery enables a SAn client or VAL server to discover spatial anchor(s) with the SAn server. The discovery of spatial anchor(s) is based on matching spatial anchor discovery filters provided in the request.
8.3.4.2 Procedure p. 23
Figure 8.3.4.2-1 illustrates the procedure for spatial anchor discovery following the request-response model.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SAn server; and
- The SAn client or VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SAn server.
- For SAn client to trigger this procedure, the SAn client has received the required information from the VAL client over SAn-C interface.
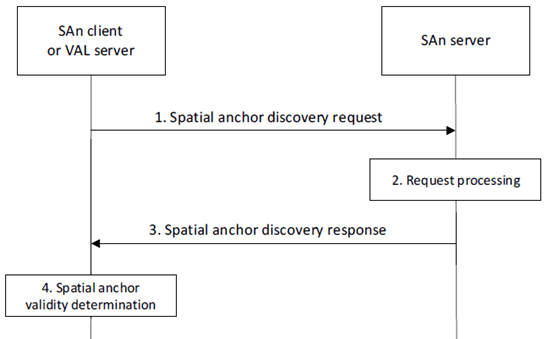
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor discovery request message to the SAn server to obtain information about spatial anchors of interest. The request includes a requestor identifier, security credentials, and can include spatial anchor discovery filters as described in clause 8.3.4.3.1. If the discovery request was triggered by a VAL client on a UE, the spatial anchor discovery request can additionally include a VAL client identifier.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SAn server identifies spatial anchor(s) that satisfies the spatial anchor discovery filters.
For each matching spatial anchor, the SAn server checks whether the requestor is authorized to obtain the spatial anchor based on the identity and location of the requestor, and based on the access control rules. To determine the location of interest of the requestor, the SAn server may use location information provided in the request. If location information is not provided in the request, the SAn server may obtain location information by invoking the 3GPP Core Network Location Services as described in TS 23.273 and TS 23.502 directly or via the NEF, or by invoking the SEAL Location Management APIs as described in TS 23.434.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor discovery response to the requestor. If the SAn server has identified spatial anchor(s), the response includes an indication of success and the identified spatial anchors and may includes the recommended list of spatial anchors. Otherwise, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
Step 4.
Upon receiving the spatial anchor discovery response, if the response indicates success, the requestor can store the spatial anchor information in a spatial anchor cache. The requestor evaluates the validity conditions associated with the discovered spatial anchors prior to using the spatial anchor. If the requestor is the SAn client, the SAn client can provide spatial anchor information to the VAL client(s). Upon receiving valid spatial anchor information, VAL client(s) can access the service(s) associated with each spatial anchor.
8.3.4.3 Information flows p. 24
8.3.4.3.1 Spatial anchor discovery request p. 24
Table 8.3.4.3.1-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor discovery request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| VAL client ID | O | The identifier of the VAL client when the requestor is a SAn client. |
| Discovery filters | O | The filters used for determining the spatial anchors. |
| > List of spatial anchor ID | O | The list of spatial anchor identifiers to discover. |
| > Area of interest | O | The area of interest (e.g., topological area and/or geographical area). |
| > Service ID | O | The identifier of a VAL service. |
| > Spatial anchor specific information | O | A container to contain application specific information. |
8.3.4.3.2 Spatial anchor discovery response p. 24
Table 8.3.4.3.2-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor discovery response from the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the spatial anchor discovery request was successful. |
| List of spatial anchors | O | List of discovered spatial anchors. |
| > Spatial anchor ID | M | Identifier of the discovered spatial anchor. |
| > Position | M | The 3D position of the spatial anchor in space (x, y and z coordinates). |
| > Spatial anchor specific information | O | A container to contain application specific information. |
| > VAL service information | M | Information about the application service associated with the spatial anchor. |
| >> Service ID | M | The identifier of the application service. |
| >> Service endpoint | M | Endpoint information (e.g., URI, FQDN, IP address) used to communicate with the application service. |
| >> Service connection information | O | The connection information (e.g., DNN, DNAI(s)) for establishing connectivity to the application service. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the spatial anchor discovery request has failed. |
| > Cause | O | The cause for the request failure. |
8.3.5 Spatial anchor subscription p. 25
8.3.5.1 General p. 25
Spatial anchor subscription enables a SAn client or VAL server to subscribe with the SAn server to receive notifications related to spatial anchors.
8.3.5.2 Procedures p. 25
8.3.5.2.1 Subscribe p. 25
Figure 8.3.5.2.1-1 illustrates the spatial anchor subscription procedure.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has received information (e.g. URI, IP address) related to the SAn server; and
- The SAn client or VAL server has received security credentials authorizing it to communicate with the SAn server.
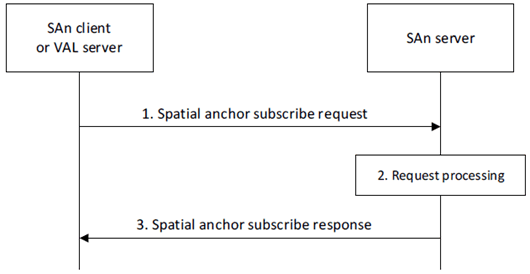
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor subscribe request to the SAn server. The request includes a requestor identifier, security credentials, a notification endpoint, and event information for which the requestor is subscribing. The request may include an expiration time.
Step 2.
- The requestor may include the "discovery" event type to indicate the SAn server to notify the requestor when the SAn server detects events related to the management of spatial anchors (e.g., creation, update, deletion) according to discovery event filters and spatial anchor filters provided in the request. If the requestor is a SAn client, the request includes a VAL client identifier.
- The VAL server may include the "UE with spatial anchor interest" event type to indicate the SAn server to notify the VAL server when the SAn server detects UE(s) with interest in specific spatial anchors according to the spatial anchor of interest event filters and spatial anchor filters provided in the request.
- The requestor may include the "spatial anchor in range" event type to indicate the SAn server to notify the requestor when the SAn server detects that spatial anchors become in range or out of range of the subscriber according to range event filters provided in the request. Range event filters can include a range for detecting spatial anchors, an indication to enable persistent search, the pose of the subscriber. If the requestor is a SAn client, the spatial anchor subscribe request includes a VAL client identifier.
Upon receiving the request from the requestor, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SAn server creates the subscription and stores the subscription information.
Step 3.
- If the subscribed event is for "discovery", the SAn server starts monitoring spatial anchors management events according to the discovery event filters and spatial anchor filters.
- If the subscribed event is for "UE with spatial anchor interest", the SAn server starts monitoring spatial anchors of interest according to the UE with spatial anchor interest event filters and spatial anchor filters. If the spatial anchors of interest have been discovered by a UE, the SAn server can obtain the UE location information from the 5GS or the SEAL Location Management service. Additionally, the SAn server can consider data analytics, such as UE mobility prediction. The SAn server may monitor the distance between UEs and the spatial anchor of interest to determine whether the UEs enters, exits or is within range of the spatial anchors of interest.
- If the subscribed event is for "spatial anchor in range" and the requestor is a SAn client, the SAn server starts monitoring the corresponding UE location and direction corresponding to the pose information according to the range event filters and spatial anchor filters. The UE location information can be obtained by using capabilities of the 5GS or the SEAL Location Management service. Additionally, the SAn server can consider data analytics, such as UE mobility prediction. The SAn server monitors the distance between UEs and the spatial anchor of interest to determine whether the spatial anchors becomes in-range or out-of-range of the UE. If persistent search is enabled, the SAn server monitors location of the user (or UE) and pose of the user, along with a direction of movement, and discovers a list of spatial anchors which becomes in-range or out of range of the user device based on the location of the user device, the pose of the user and in the user's field of view.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor subscribe response to the requestor. If the SAn server has created the subscription, the response includes an indication of success, the subscription identifier and may include an expiration time; to maintain the subscription, the requestor shall send a subscription update request before the expiration time, otherwise the spatial anchor subscription expires. If the SAn server has not created the subscription, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
8.3.5.2.2 Notify p. 26
Figure 8.3.5.2.2-1 illustrates the spatial anchor notify operation between the SAn server and a SAn client or VAL server.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has subscribed for spatial anchor notifications with the SAn server;
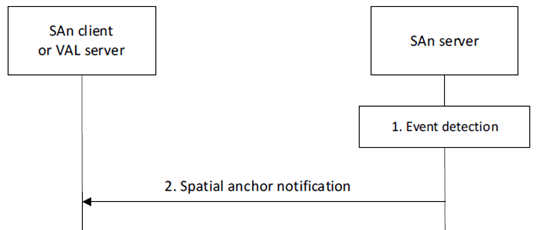
Step 1.
An event occurs at the SAn server that satisfies trigger conditions for notifying a subscriber (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) according to subscribed events and discovery filters provided for the events.
Step 2.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor notification to the requestor indicating the event. The notification includes a subscription identity and includes event-specific information.
- If the subscribed event is for "discovery", the notification includes the list of determined spatial anchors
- If the subscribed event is for "UE with spatial anchor interest", the notification includes information about UE with spatial anchor interest (e.g., UE identifier, spatial anchor identifier(s), range from the spatial anchor(s), entering or exiting the range, etc.).
- If the subscribed event is for "spatial anchor in range", the notification includes the list of determined spatial anchors that become in range, out of range of the subscriber.
8.3.5.2.3 Subscription update p. 27
Figure 8.3.5.2.3-1 illustrates the procedure for a SAn client or VAL server to update a subscription with the SAn server.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has subscribed for spatial anchor notifications with the SAn server;
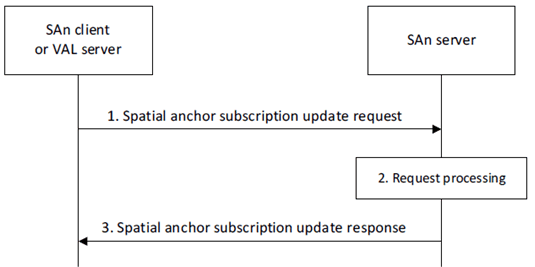
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor subscription update request to the SAn server. The request includes the requestor identifier, security credentials and the subscription identifier and may include subscribed event information and expiration time.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the requestor, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SAn server updates the subscription information.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor subscription update response to the requestor. If the SAn server has updated the subscription, the response includes an indication of success and may include an expiration time. To maintain the subscription, the requestor shall send a subscription update request before the expiration time, otherwise the spatial anchor subscription expires. If the SAn server has not updated the subscription, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
8.3.5.2.4 Unsubscribe p. 28
Figure 8.3.5.2.4-1 illustrates the procedure for a SAn client or VAL server to unsubscribe with the SAn server.
Pre-conditions:
- The SAn client or VAL server has subscribed for spatial anchor notifications with the SAn server;
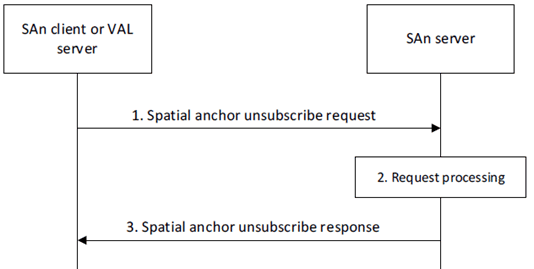
Step 1.
The requestor (e.g., SAn client or VAL server) sends a spatial anchor unsubscribe request to the SAn server. The request includes the requestor identifier, security credentials and the subscription identifier.
Step 2.
Upon receiving the request from the requestor, the SAn server validates if the requestor is authorized for the request. If the requestor is authorized, the SAn server cancels the subscription associated with the subscription identifier.
Step 3.
The SAn server sends a spatial anchor unsubscribe response to the requestor. If the SAn server has canceled the subscription, the response includes an indication of success. If the SAn server has not canceled the subscription, the response includes an indication of failure and may include a reason for failure.
8.3.5.3 Information flows p. 28
8.3.5.3.1 Spatial anchor subscribe request p. 28
Table 8.3.5.3.1-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor subscribe request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | The security credentials of the requestor. |
| VAL client ID | O | The identifier of the VAL client when the requestor is a SAn client. |
| Notification Target Address | M | Notification target address (e.g. URL) where the notifications should be sent. |
| Proposed expiration time | O | Proposed expiration time for the subscription. |
| Event type | M |
The type of event for which the requestor is subscribing. Supported event types include:
|
| Persistent Search (NOTE) | O | Indicates to enable persistent search. |
| Event detection filters | O | Event type specific detection filters. |
| > Discovery event filters | O | Event filters applicable to the "discovery" event type. The event filter is considered by the SAn server for triggering the notification and can include management events (e.g., creation, update, deletion). |
| > UE with spatial anchor interest event filters | O | Event filters applicable to "UE with spatial anchor interest" event type. The event filter is considered by the SAn server for triggering the notification and can include an indication for detecting UEs that have discovered spatial anchors, that are within range or become out of range of spatial anchors, or that enter or leave the range of a spatial anchor, and a value for the range. |
| > Range event filters | O | Event filters applicable to "spatial anchor in range" event type. The event filter is considered by the SAn server for triggering the notification and can include an indication for spatial anchors becoming in range of the UE, out of range of the UE, or both and a value for the range. |
| >> current location | O | Current location of the user and direction. |
| >> pose | O | Current pose of the user. |
| >> application specific range | M | Specifies range within which the spatial anchors are monitored to be in range or out of range of the subscriber's field of view. |
| >> Spatial anchor specific information | O | A container to contain application specific information. |
| Spatial anchor filters | O | The characteristics of spatial anchors that the SAn server considers for triggering a notification. |
| > Spatial anchor ID list | O | Identifiers of the spatial anchors of interest. |
| > Service ID list | O | Identifiers of the associated application services of interest. |
| > Area of interest | O | The area of interest (e.g., topological and/or geographical). |
|
NOTE:
This IE can be included with "spatial anchor in range" event.
|
||
8.3.5.3.2 Spatial anchor subscribe response p. 29
Table 8.3.5.3.2-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor subscribe response sent by the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the subscription request was successful. |
| > Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the subscription. To maintain an active subscription, a subscription update is required before the expiration time. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the subscription request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of subscription request failure. |
8.3.5.3.3 Spatial anchor notification p. 30
Table 8.3.5.3.3-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor notification sent by the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription. |
| Event type | M |
The type of event notification. Supported event types include:
|
| Detected event | O | Identifier of the event that was detected and that triggered the server to send a notification (e.g., spatial anchors becoming in range of the UE or out of range of the UE; or, UE entering the range of a spatial anchor or leaving the range of a spatial anchor). |
| Spatial anchor list | O | List of discovered spatial anchors (as detailed in spatial anchor discovery response). Applicable for "discovery" and "spatial anchor in range" events. |
| UE with spatial anchor interest list | O | List of UE with spatial anchor interest. Applicable for "UE with spatial anchor interest" and "spatial anchor in range" events. |
| > UE ID | O | Identifier of the UE with spatial anchor interest. |
| > Spatial anchor ID | O | Identifier of the spatial anchor of interest. |
| > Spatial anchor range | O | The spatial anchor range. |
8.3.5.3.4 Spatial anchor subscription update request p. 30
Table 8.3.5.3.4-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor subscription update request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials of the requestor. |
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription to be updated. |
| Notification Target Address | O | Notification target address (e.g. URL) where the notifications should be sent. |
| Proposed expiration time | O | Proposed expiration time for the subscription. |
| Event detection filters | O | Event type specific detection filters that the SAn server considers for triggering a notification, as detailed in Table 8.3.5.3.1-1. |
| Spatial anchor filters | O | The characteristics of spatial anchors that the SAn server considers for triggering a notification, as detailed in Table 8.3.5.3.1-1. |
8.3.5.3.5 Spatial anchor subscription update response p. 31
Table 8.3.5.3.5-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor subscription update response sent by the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the subscription update request was successful. |
| > Expiration time | O | Indicates the expiration time of the updated subscription. To maintain an active subscription, a subscription update is required before the expiration time. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the subscription update request failed. |
| O | Indicates the cause of subscription update request failure. |
8.3.5.3.6 Spatial anchor unsubscribe request p. 31
Table 8.3.5.3.6-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor unsubscribe request from the SAn client or VAL server to the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Requestor identifier | M | The identifier of the requestor (e.g., VAL server or VAL UE and VAL user). |
| Security credentials | M | Security credentials of the EEC. |
| Subscription ID | M | Subscription identifier corresponding to the subscription to be unsubscribed. |
8.3.5.3.7 Spatial anchor unsubscribe response p. 31
Table 8.3.5.3.7-1 describes information elements for the spatial anchor unsubscribe response sent by the SAn server.
| Information element | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Successful response | O | Indicates that the unsubscribe request was successful. |
| Failure response | O | Indicates that the unsubscribe request failed. |
| > Cause | O | Indicates the cause of unsubscribe request failure. |