Content for TS 23.682 Word version: 19.1.0
1…
4.2
4.3…
4.4…
4.5…
4.5.7…
4.5.14…
4.6…
5…
5.3…
5.5…
5.6…
5.6.2…
5.6.6…
5.7…
5.8…
5.9…
5.13…
5.14…
5.15
5.16
5.17…
5.18
5.19…
A…
C…
5.9 Procedure for resource management of background data transfer
5.10 Communication Pattern parameters provisioning procedure
5.10.1 Communication Pattern parameters
5.10.2 Communication Pattern parameters provisioning to the MME
5.11 Setting up an AS session with required QoS procedure
5.12 Change the chargeable party at session set-up or during the session procedure
5.12.1 Set the chargeable party at session set-up
5.12.2 Change the chargeable party during the session
...
...
5.9 Procedure for resource management of background data transfer |R13| p. 95
This clause describes the procedure for resource management of background data transfer to a set of UEs, i.e. an SCS/AS requesting a time window and related conditions from the SCEF via the Nt interface.
The UEs targeted for background data transfer may be served by a single PCRF or may be spread across multiple PCRFs serving the same or different geographic areas. The operator shall ensure that any of the PCRFs in the network is able to make the decision about transfer policy for background data transfer for non-roaming UEs.
The transfer policy will be stored in the SPR together with a Reference ID. This ensures that the transfer policy is available to every PCRF responsible for a UE which is subject to this background data transfer in the future. In addition, other (or the same) PCRF can take this transfer policy into account during subsequent decisions about transfer policies for background data related to other SCS/AS.
At a later point in time, when the SCS/AS (acting as an AF), contacts the PCRF for individual UEs, e.g. to request sponsored connectivity for background data transfer, the SCS/AS needs to also provide the Reference ID together with the SCS/AS session information via the Rx interface. Alternatively, the SCS/AS activates the selected transfer policy via the SCEF, for each UE in the group, by using the "Set the chargeable party at session set-up" or "Change the chargeable party during the session" procedure from clauses 5.12.1 and 5.12.2 to provide the Reference ID to the same or different PCRF. The Reference ID enables the PCRF to correlate the SCS/AS request (that is related to the UE) with the transfer policy retrieved from the SPR (that is related to the SCS/AS). The PCRF finally triggers PCC procedures according to TS 23.203 to provide the respective policing and charging information to the PCEF.
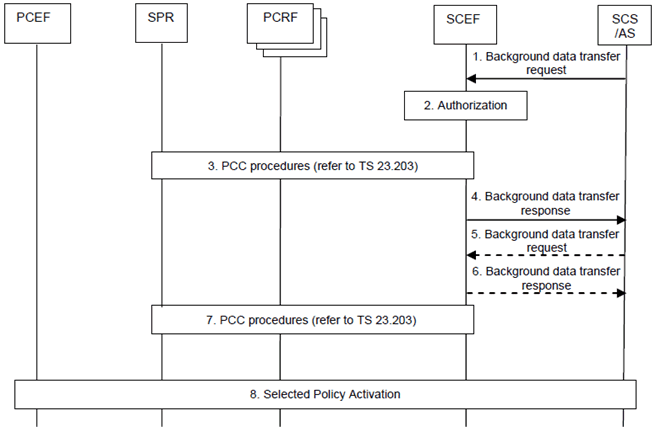
Step 1.
A 3rd party SCS/AS sends a Background data transfer request (SCS/AS Identifier, Volume per UE, Number of UEs, Desired time window) message to the SCEF. The Volume per UE describes the volume of data the SCS/AS expects to be transferred per UE. Number of UEs describes the expected amount of UEs participating in the data transfer. Desired time window describes the time interval during which the SCS/AS wants to realize the data transfer. Optionally, the SCS/AS can provide a geographic area information.
Step 2.
The SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request.
Step 3.
The SCEF selects any of the available PCRFs and triggers the Negotiation for future background data transfer procedure with the PCRF. The SCEF forwards the parameters provided by the SCS/AS. The PCRF responds to the SCEF with the possible transfer policies and a Reference ID. Refer to clause 7.11.1 of TS 23.203.
Step 4.
The SCEF forwards the Reference ID and the transfer policies to the 3rd party SCS/AS by sending a Background data transfer response (Reference ID, Possible transfer policies) message. The SCS/AS stores the Reference ID for the future interaction with the PCRF.
Step 5.
If more than one transfer policy was received, the 3rd party SCS/AS shall select one of them and send another Background data transfer request (SCS/AS Identifier, Selected transfer policy) message to inform the SCEF and PCRF about the selected transfer policy.
Step 6.
The SCEF confirms the transfer policy selection to the 3rd party SCS/AS by sending a Background data transfer response (Cause) message.
Step 7.
The SCEF continues the Negotiation for future background data transfer procedure with the PCRF. The PCRF stores the Reference ID and the new transfer policy in the SPR. Refer to clause 7.11.1 of TS 23.203.
Step 8.
The SCS/AS (acting as an AF) contacts the same or a different PCRF for each individual UE (via the Rx interface), the SCS/AS shall provide the Reference ID. Alternatively, the SCS/AS activates the selected transfer policy via the SCEF, for each UE in the group, by using the "Set the chargeable party at session set-up" or "Change the chargeable party during the session" procedure from clauses 5.12.1 and 5.12.2 to provide the Reference ID to the same or different PCRF. The PCRF correlates the SCS/AS or SCEF request with the transfer policy retrieved from the SPR via the Reference ID. The PCRF finally triggers PCC procedures according to TS 23.203 to provide the respective policing and charging information to the PCEF for the background data transfer of this UE.
5.10 Communication Pattern parameters provisioning procedure |R13| p. 97
5.10.1 Communication Pattern parameters p. 97
A set of Communication Pattern (CP) parameters is defined in the Table below. All CP parameters are optional.
These CP parameters are specific for a UE or a group of UEs. Sets of these CP parameters are provided by the SCEF to the HSS which distributes them to the corresponding MME with relevant subscriber data. These CP parameter sets may be related to both PDN connection(s) and SMS transmission. The MME considers the sets of CP parameters (e.g. by merging per CP parameter if multiple sets are present), before using the parameters. Each CP parameter set shall have an associated validity time. The validity time indicates when the CP parameter set expires and shall be deleted by the HSS/MME. The validity time may be set to a value indicating that the particular CP parameter set has no expiration time. When the validity time expires, the involved nodes (SCEF, HSS, and MME) autonomously delete the associated CP parameter set with no additional signalling between the involved nodes.
| CP parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 1) Periodic communication indicator | Identifies whether the UE communicates periodically or not, e.g. only on demand. [optional] |
| 2) Communication duration time | Duration interval time of periodic communication [optional, may be used together with 1)]
Example: 5 minutes |
| 3) Periodic time | Interval Time of periodic communication [optional, may be used together with 1)]
Example: every hour |
| 4) Scheduled communication time | Time zone and Day of the week when the UE is available for communication [optional]
Example: Time: 13:00-20:00, Day: Monday |
| 5) Stationary indication | Identifies whether the UE is stationary or mobile [optional] |
| 6) Battery indication | Identifies power consumption criticality for the UE: if the UE is battery powered with not rechargeable/not replaceable battery, battery powered with rechargeable/replaceable battery, or not battery powered.
[optional] |
| X) Traffic Profile | Identifies the type of data transmission: single packet transmission (UL or DL), dual packet transmission (UL with subsequent DL or DL with subsequent UL), multiple packets transmission.
[optional] |
5.10.2 Communication Pattern parameters provisioning to the MME p. 98
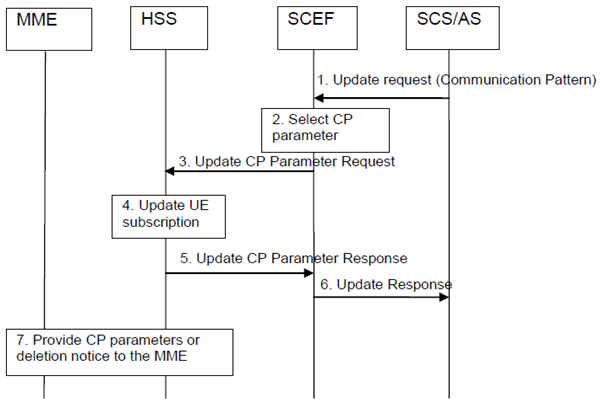
Figure 5.10.2-1: Signalling sequence for provisioning of CP Parameters
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
(⇒ copy of original 3GPP image)
Step 1.
The SCS/AS sends an Update Request (External Identifier or MSISDN or External Group Identifier, SCS/AS Identifier, CP parameter Set Id(s), CP parameter set(s), validity time(s), CP parameter Set Id(s) for Deletion, MTC Provider Information) message to the SCEF. The CP parameter set(s) include the parameters defined in Table 5.10.1-1. A CP parameter Set Id is assigned to each CP parameter set by the SCS/AS.
Step 2.
The SCEF checks if the SCS/AS is authorised to send CP requests to the UE or to each UE in the identified group. The SCEF filters and the selects the CP parameter set(s) for add/modify/delete based on operator policy or configuration. The SCEF does not check for potential overlapping of CP parameters if there are multiple CP parameter set(s) for the UE, but this is handled in the MME.
In this release, to avoid receiving CP parameter sets from multiple SCEFs that might be overlapping, the HSS shall accept CP parameter sets from only a single SCEF for a given UE.
Step 3.
The SCEF sends Update CP Parameter Request (External Identifier or MSISDN or External Group Identifier, SCEF Reference ID(s), SCEF Address, CP parameter set(s), validity time(s), SCEF Reference ID(s) for Deletion, MTC Provider Information) message to the HSS for delivering the selected CP parameter set(s) per UE. There may be multiple CP parameter sets included in this message where each CP parameter set for addition or modification has been determined to be non-overlapping with other CP parameter sets either included in the message or already provisioned for a given UE. The SCEF derives the SCEF Reference ID(s) for CP parameter sets to be sent to the HSS based on the CP parameter Set Id(s) from the SCS/AS.
Step 4.
The HSS examines the Update CP Parameter Request message, e.g. with regard to the existence of External Identifier or MSISSN or External Group Identifier. If the check fails, the HSS immediately sends a response message back to the SCEF following step 5. The HSS resolves the External Identifier or MSISDN to an IMSI or resolves the External Group Identifier to an IMSI-Group Identifier and stores the CP parameter set(s) and their validity time(s) as part of UE subscription data identified by the IMSI or IMSI-Group Identifier, so that the CP parameter set(s) can be forwarded to the serving MME(s) when the serving MME(s) are changed due to the mobility of the UE.
The HSS determines that a stored CP parameters set is to be modified by the fact that the SCEF Reference ID associated with the CP parameters set matches an SCEF Reference ID for a CP parameters set already stored for a given UE. If the HSS determines that an existing CP parameter set is to be modified, the HSS discards the already stored CP parameter set and stores the new CP parameter set and validity time under the same SCEF Reference ID.
The HSS stores a new CP parameter set along with the associated SCEF Reference ID and validity time.
If CP parameters sets are to be deleted, the HSS removes the CP parameters sets from the subscription.
If the validity time for a CP parameter set stored in the HSS expires, the HSS autonomously deletes the associated CP parameter set with no additional signalling.
Step 5.
The HSS sends Update CP Parameter Response (SCEF Reference ID, Cause) message to the SCEF. The cause value indicates successful subscription update or the reason of failed subscription update.
Step 6.
The SCEF sends the Update Response (CP parameter Set Id(s), Cause(s)) message to inform the SCS/AS whether the provision of the CP parameter set(s) was successful.
Step 7.
The HSS initiates an Insert Subscription Data procedure for each UE to send the CP parameter set(s) with the corresponding validity time(s), SCEF Reference ID(s), and SCEF Reference ID(s) for Deletion to the MME. Optionally, the HSS allocates a Provider-Group-ID (different from the IMSI-Group-Id) based on the MTC Provider Information and sends it to the MME to assist the serving node(s) when selecting and differentiating configurations for a given MTC Service Provider (e.g. to delete the CP Set Id(s) for a specific MTC Service Provider at the MME).
The MME determines that a stored CP parameters set is to be modified by the fact that the SCEF Reference ID associated with the CP parameters set matches an SCEF Reference ID for a CP parameters set already stored for the UE. If the MME determines that an existing CP parameter set is to be modified, the MME discards the already stored CP parameter set and stores the received CP parameter set with the associated validity time in the UE's (E)MM context under the same SCEF Reference ID.
The MME stores a new CP parameter set along with the associated SCEF Reference ID and validity time. The MME may use the CP parameter set(s) as described in TS 23.401.
If CP parameter sets are to be deleted, the MME removes the CP parameter sets from the subscription.
If the validity time for a CP parameter set stored in the MME expires, the MME autonomously deletes the associated CP parameter set with no additional signalling.
5.11 Setting up an AS session with required QoS procedure |R13| p. 99
This clause describes the signalling flow for setting up a 3rd party AS session with a specific QoS.
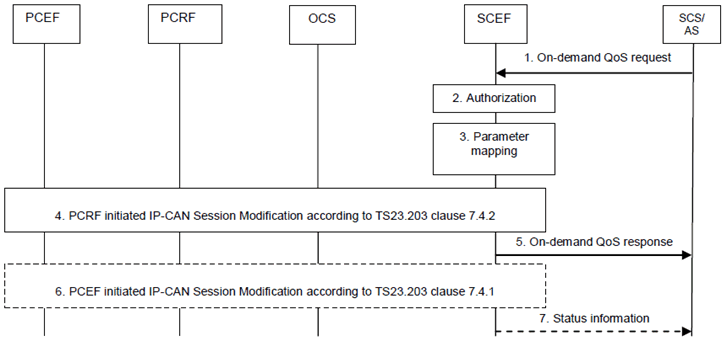
Step 1.
When setting up the connection between SCS/AS and the UE with required QoS for the service, the SCS/AS sends an On-demand QoS request message (UE IP address, SCS/AS Identifier, Description of the application flows or External Application Identifier, QoS reference) to the SCEF. Optionally, a period of time or a traffic volume for the requested QoS can be included in the SCS/AS request. The SCEF assigns a TLTRI to the On-demand QoS request.
Step 2.
The SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request and may apply policies to control the overall amount of pre-defined QoS authorized for the SCS/AS. If the authorisation is not granted, steps 3 and 4 are skipped and the SCEF replies to the SCS/AS with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
The SCEF maps the UE IP address, the SCS/AS Identifier, the Description of the application flows and the QoS reference to existing Rx parameters (including the optionally received period of time or traffic volume which is mapped to sponsored data connectivity information). The SCEF acts as an AF defined in TS 23.203.
Step 4.
The SCEF interacts with the PCRF via the Rx interface and triggers a PCRF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification as described in clause 7.4.2 of TS 23.203. The SCEF shall request to be notified about the transmission resource status.
The PCRF derives the required QoS based on the information provided by the SCEF and determines whether this QoS is allowed (according to the PCRF configuration for this 3rd party SCS/AS), and notifies the result to the SCEF.
The PCRF notifies the SCEF whether the transmission resources corresponding to the QoS request are established or not.
Step 5.
The SCEF sends an On-demand QoS response message (TLTRI, Result) to the SCS/AS. Result indicates whether the QoS request is granted or not.
Step 6.
The PCRF may notify the SCEF about bearer level events for the Rx session (e.g. transmission resources are released/lost) with a PCEF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification as described in clause 7.4.1 of TS 23.203.
Step 7.
If the SCEF gets informed by the PCRF about bearer level events for the Rx session (e.g. transmission resources are released/lost) the SCEF sends a Status information message (SCS/AS Identifier, TLTRI, Status) to the SCS/AS. The status indicates the bearer level event received from the PCRF.
5.12 Change the chargeable party at session set-up or during the session procedure |R13| p. 101
5.12.1 Set the chargeable party at session set-up p. 101
This clause describes the signalling flow for setting the chargeable party at AS session set-up. The SCS/AS may either request to sponsor the traffic from the beginning or may request to become the chargeable party at a later point in time.
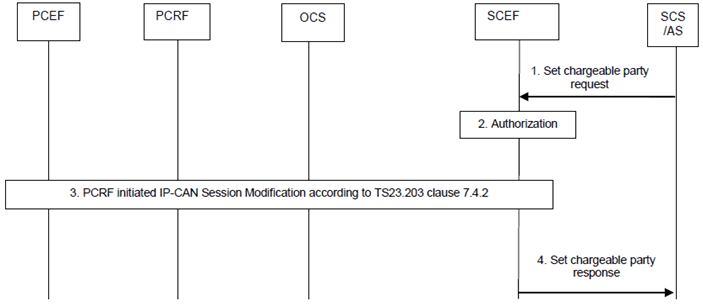
Step 1.
When setting up the connection between the AS and UE, the SCS/AS may request to become the chargeable party for the session to be set up by sending a Set chargeable party request message (SCS/AS Identifier, Description of the application flows or External Application Identifier, sponsor information, Sponsoring Status, Reference ID) to the SCEF, including optionally a usage threshold. The Sponsoring Status indicates whether sponsoring is started or stopped, i.e. whether the 3rd party service provider is the chargeable party or not. The Reference ID parameter identifies a previously negotiated transfer policy for background data transfer as defined in clause 4.5.9. The SCEF assigns a TLTRI to the Set chargeable party request.
Step 2.
The SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request to sponsor the application traffic and stores the sponsor information together with the SCS/AS Identifier and the TLTRI. If the authorisation is not granted, step 3 is skipped and the SCEF replies to the SCS/AS with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
The SCEF interacts with the PCRF by triggering a PCRF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification as described in clause 7.4.2 of TS 23.203 and provides IP filter information, sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.203), Reference ID (if received from the SCS/AS) and Sponsoring Status (if received from the SCS/AS) to the PCRF.
The PCRF determines whether the request is allowed and notifies the SCEF if the request is not authorized. If the request is not authorized, SCEF responds to the SCS/AS in step 4 with a Result value indicating that the authorization failed.
As specified in TS 23.203, the PCRF determines the PCC rule(s) for the specified session including charging control information. Charging control information shall be set according to the Sponsoring Status (if received over Rx), i.e. either indicating that the 3rd party service provider is the chargeable party or not. The PCC rule(s) for the specified session shall then be provided to the PCEF. In the case of online charging and depending on operator configuration, the PCEF may request credit when the first packet corresponding to the service is detected or at the time the PCC Rule was activated.
The PCRF notifies the SCEF that the request is accepted.
Step 4.
The SCEF sends a Set chargeable party response message (TLTRI, Result) to the SCS/AS. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.
5.12.2 Change the chargeable party during the session p. 102
This clause describes the signalling flow for changing the chargeable party during an ongoing AS session, i.e. the SCS/AS starting or stopping to sponsor the application traffic.
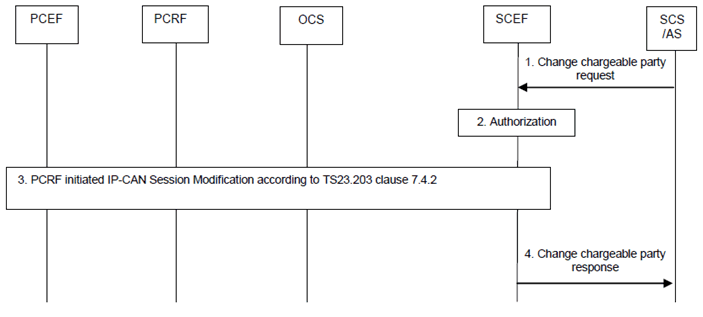
Step 1.
For the ongoing AS session, the SCS/AS may send a Change chargeable party request message (SCS/AS Identifier, TLTRI, Sponsoring Status, Reference ID) to the SCEF, including optionally a usage threshold. The Sponsoring Status indicates whether sponsoring is enabled or disabled, i.e. whether the 3rd party service provider is the chargeable party or not. The Reference ID parameter identifies a previously negotiated transfer policy for background data transfer as defined in clause 4.5.9. The TLTRI provided in the Change chargeable party request message is set to the TLTRI that was assigned, by the SCEF, to the Set chargeable party request.
Step 2.
The SCEF authorizes the SCS/AS request of changing the chargeable party. If the authorisation is not granted, step 3 is skipped and the SCEF replies to the SCS/AS with a Result value indicating that the authorisation failed.
Step 3.
Based on the SCS/AS Identifier and the TLTRI the SCEF determines the relevant Rx session and interact with the PCRF by triggering a PCRF initiated IP-CAN Session Modification as described in clause 7.4.2 of TS 23.203. The SCEF provides sponsored data connectivity information (as defined in TS 23.203), Reference ID (if received from the SCS/AS), and the Sponsoring Status to the PCRF.
The PCRF determines whether the request is allowed and notifies the SCEF if the request is not authorized. If the request is not authorized, SCEF responds to the SCS/AS in step 4 with a Result value indicating that the authorization failed.
The PCRF identifies the affected PCC rule(s) and reacts based on their current status. If the traffic is subject to subscriber charging in the PCEF and the PCRF receives a Sponsoring Status indicating that sponsoring is started, the PCC rule(s) for the specified session shall be modified so that the charging control information indicates that the 3rd party service provider is charged for the traffic. If the traffic is subject to 3rd party charging in the PCEF and the PCRF receives a Sponsoring Status indicating that sponsoring is stopped, the PCC rule(s) for the specified session shall be modified so that the charging control information indicates that the 3rd party service provider is no longer charged for the traffic. As specified in TS 23.203, PCRF modifies the PCC rule(s) of the service data flow accordingly and provides them to the PCEF. In the case of online charging and depending on operator configuration, the PCEF may request credit when the first packet corresponding to the service is detected or at the time the PCC Rule was activated.
The PCRF notifies the SCEF that the request is accepted.
Step 4.
The SCEF sends a Change chargeable party response message (Result) to the SCS/AS. Result indicates whether the request is granted or not.